Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Saturated fats are mainly animal fats. They are perceived mainly as a source of energy supplied to the body, but they also have other functions. It is widely believed that saturated fats contribute to heart disease and raise cholesterol levels. The latest research results indicate that their role is overly demonized.
What are saturated fats?
Saturated fat are defined as compounds of fatty acids and glycerin. The basis of their internal structure is the carbon chain. If there are single bonds between the individual carbon atoms, then we are dealing with saturated fats. If, on the other hand, at least one of the bonds is double, the fat is referred to as unsaturated.
Saturated fat most often they appear as amorphous, whitish solids. Moreover, they are not soluble in water.
Nutrition organizations, based on research, suggest a significant limitation saturated fat in your daily diet. It is recommended that they cover a maximum of 6% of the demand energy. This is approximately 120 kcal (13 grams) saturated fat daily.
Sources of saturated fat
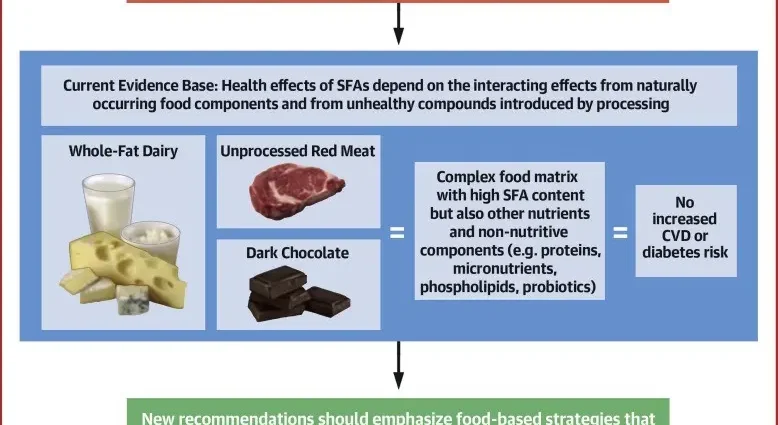
Saturated fats are overwhelmingly large of animal origin. The most recognized exception is coconut oil. Its unique properties have been emphasized for a long time. It was used for food and cosmetic purposes. It was a well-known theory that people who consume coconut oil in large amounts reduce the incidence of heart disease. Recent studies indicate, however, that the aforementioned vegetable fat, with prolonged use, may be harmful to health.
Usually in food unsaturated fats mix with saturated fats. For the products they represent source of fats saturated, includes: butter, lard, tallow, coconut oil, palm oil, milk, cheese, cream, eggs, meat (mainly red), offal, fish.
Functions of saturated fat in the body
Saturated fat primarily source of energy for human. Besides, they perform a number of others functions in the body:
- they dissolve vitamins A, D, E and K, and then participate in their transport around the body;
- build subcutaneous fat, which is the body’s thermal protection;
- protect internal organs from damage;
- may be important in preventing the growth of cancer cells due to the presence of lactic acid;
- regulate the body’s hormonal balance;
- are involved in the production of omega-3 fatty acids when they are not present in food.
The influence of saturated fat on human health
When the body’s need for energy increases, regular consumption is recommended saturated fat. They have the highest caloric value of all the nutrients. Research scientists saturated fat pay attention to the beneficial effects of the acids they contain: butyric, palmitic, myristic and lauric acids. They are responsible for the proper functioning of the processes taking place in the body.
Clinical studies prove that eating saturated fat excessively raises the level of “bad” cholesterol – LDL, which may accelerate the development of atherosclerosis, embolism, vascular syndromes, ischemic heart disease, and stroke.
However, opponents of the above theory emphasize that the changes in the LDL fraction concern its longer subtype, and this has no influence on the occurrence of pathological changes.
Limit saturated fat it is recommended for people who are overweight, obese, with advanced atherosclerotic lesions, after myocardial infarction, and stroke. Patients suffering from diseases of the digestive system, liver and pancreatic insufficiency, but also malabsorption should also be particularly careful.
An important assumption in the prevention of diseases that are affected by consumption saturated fatis to lead a proper lifestyle. The priority is to pay attention to the appropriate composition of everyday ingredients diet and its caloric value. Diet it should be adjusted to gender, age, job, level of physical activity. Ruch in any form, it improves the metabolic process. As a result, it also prevents obesity and significantly increases the body’s efficiency.
Nowadays, the sciences of nutrition are rapidly developing, and therefore dietary recommendations are changed regularly. Current research indicates that there is no reason to over-avoid consumption saturated fat. Specialists propose moderation, as well as eating saturated fat and insatiable.