Contents
Sarcocystosis is a zoonotic invasion of the gastrointestinal tract, smooth and striated muscles caused by Sarcocystis hominis. The symptoms of the disease are nausea, diarrhea, myositis, fever. Sarcocystosis is symptomatically treated with pharmacological agents.
Sarkocystoza — epidemiologia
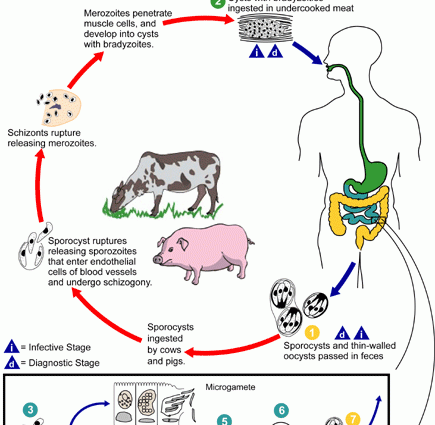
Sarcocystosis is a cosmopolitan parasitosis of humans and animals (dogs, cats, cattle, pigs, small rodents). The final host is usually carnivorous animals, and the intermediate host – herbivores. Human infection occurs after eating raw or semi-raw meat (pork, beef) containing protozoan tissue cysts. The source of infestation may also be water or food contaminated with sporocysts. It is estimated that two-thirds of animal infections occur after consuming water or food contaminated with human faeces.
Sarcocystosis – causes
The etiological factor in sarcocystosis is one of the two species of Sarcocystis hominis (S. suihominis, S. bovihominis) – a protozoan belonging to coccidia. Man can be the intermediate and final host of this parasite. Most cases of human sarcocystosis are reported from the hot Southeast Asian climate countries.
Sarcocystosis – symptoms
Invasion causes segmental eosinophilic enteritis or segmental necrotizing enterocolitis. The changes are located at the end of the small intestine. In parenteral locations, sarcocystosis occurs in transversely striated and smooth muscle tissue, causing eosinophilic inflammation.
Most infections with sarcocystosis are asymptomatic. In clinical cases, when humans are the definitive host, Sarcocystis hominis infestation is characterized by mild gastrointestinal disturbance. Experimental infections (human consumption of meat containing tissue cysts) caused nausea, abdominal discomfort and self-limiting diarrhea. Clinical manifestation depended on the infectious dose. Usually it is diarrhea that occurs suddenly, up to 48 hours of invasion. Eosinophilic myositis is usually associated with fever, lymphadenopathy, allergic cutaneous reactions, bronchospastic symptoms, arthritis, and infiltrates (nodules) in the subcutaneous tissue.
Sarcocystosis – diagnosis
The diagnosis that the patient suffers from sarcocystosis is made on the basis of the results of the stool parasitological examination. The use of flotation (thickening) techniques favors the discovery of Sarcocystis hominis sporocysts. The preparation of stool smears using the Kato and Miura method also facilitates the diagnosis of sarcocystosis. In one third of cases, eosinophilia is found in the peripheral blood. Sarcocystosis should be differentiated from intestinal catarrh of a different etiology and from Crohn’s disease (ileitis terminalis, enteritis segmentalis).
Treatment of sarcocystosis
There is no fully effective treatment for the causal sarcocystosis. Albendazole relieves discomfort and symptoms. Glucocorticosteroids are indicated in eosinophilic myositis.
Sarcocystosis and prevention
Avoiding eating raw, undercooked or undercooked meat. Hygienic food preparation and personal hygiene. Consuming boiled water or water from a proven source.
Source: J. Cianciara, J. Juszczyk, Infectious and parasitic diseases; Czelej Publishing House