Contents
Ryadovka Gulden is one of the many representatives of the mushrooms of the Ryadovkovy family. It was first described in 2009 and classified as conditionally edible. It is not distinguished by bright external signs and high taste properties. The fruit bodies of this row are found in northern Europe in forests where spruce grows.
What does the Gulden row look like?
In nature, there are more than 100 varieties of mushrooms related to rows. Of these, approximately 45 species grow in Our Country, including especially valuable subspecies, but Gulden does not belong to them. In the literature, the name of this fungus is also used – Tricholoma guldeniae.
In one of the first descriptions, the researchers noted that this mushroom is rare and grows only in the forests of Northern Europe.

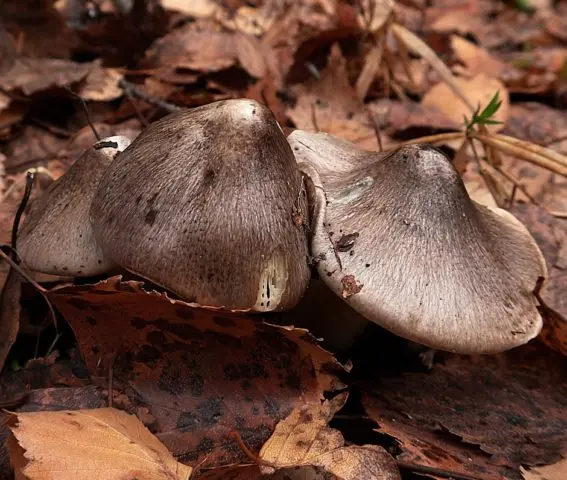
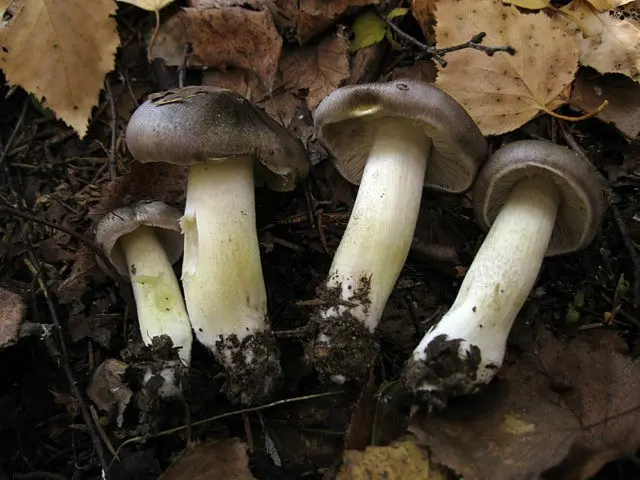
Outwardly rowing Gulden does not look attractive. Due to the gray-white flowers in the color of the fruiting body, inherent in many other Ryadovkovs, and the lack of bright characteristic features, this species is not easy to identify.
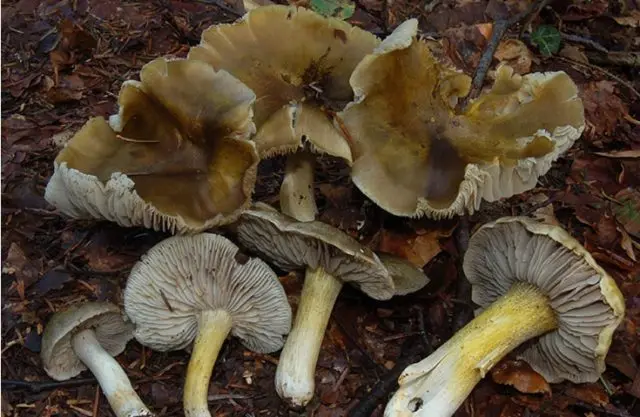
Morphologically, the fungus belongs to the group of different rows (Tricholoma sejunctum). This is a northern variety of dirty yellow rowing (Tricholoma luridum), which is found only on calcareous soils, in mountain mixed forests of central and southern Europe, where spruce, fir, and beech are present.
Dirty yellow row:

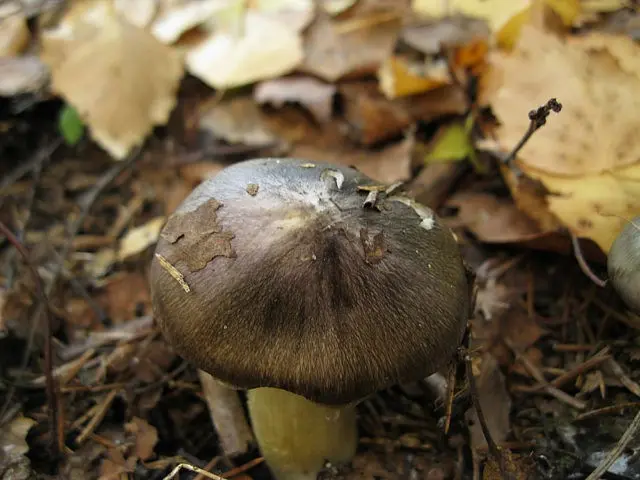
Features of the appearance of tricholoma Guilder:
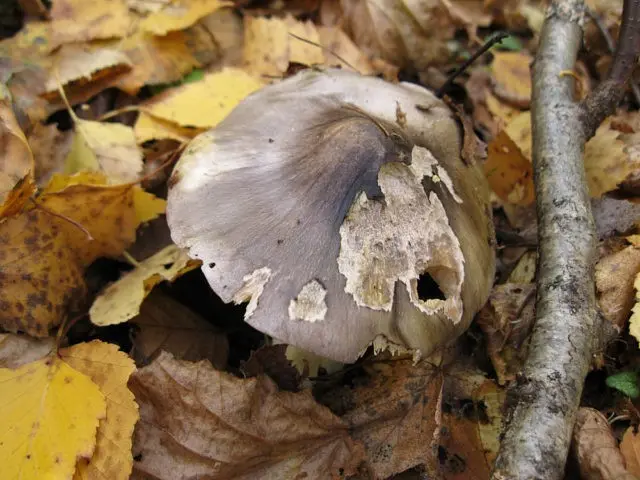
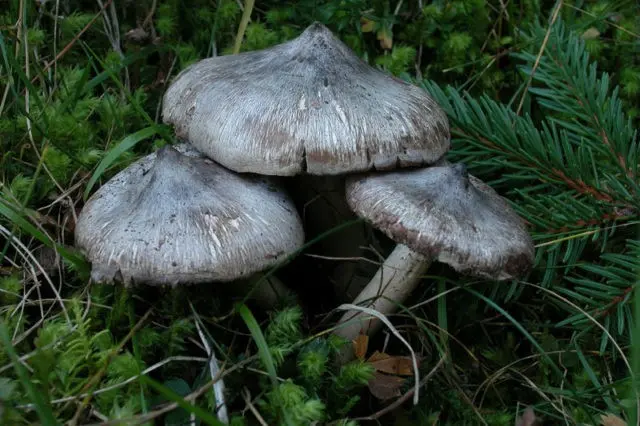
- Hat. The average cap diameter is 4 – 8 cm. Sometimes you can find larger specimens up to 10 cm in diameter. At high humidity, the surface is covered with a sticky film and can be painted in different shades of gray palette: from dark to olive gray. The coloring is not solid, but textured. A light background with an olive, yellowish or light green undertone appears through the dyed, oriented from the top to the edges, fibers. Young fruiting bodies have a conical bell-shaped cap with folded edges. With age, it becomes prostrate, with a tubercle in the upper part. Its edges at a mature fruiting body are even or slightly bent upwards.

- Pulp. This species is characterized by loose, loose flesh. It is light, with a shade of gray or yellowish green. In places of damage, it acquires a dark gray color. The smell and taste of her are not clearly expressed, they give off floury notes.

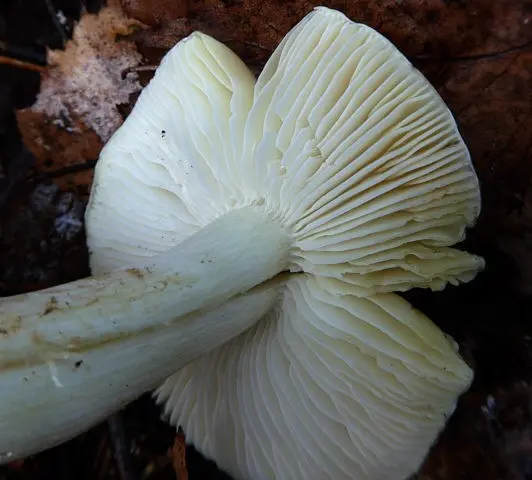
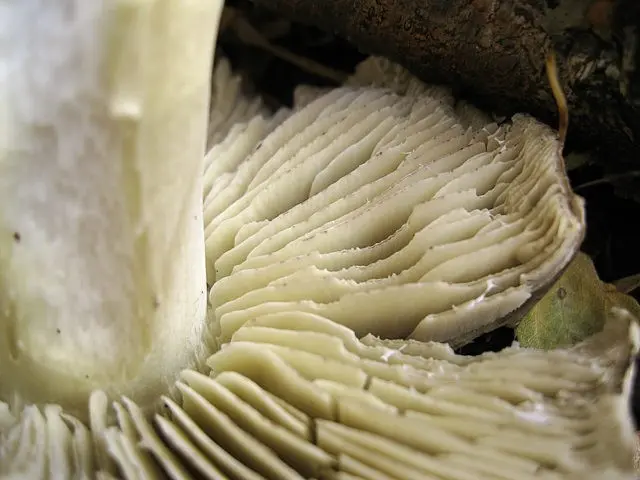
- Records. The color of the plates is uniform, dull yellow or whitish green. They are wide, grown, located infrequently. On the edge of each of them there may be a tooth or notch. With age, in dry weather, the plates along the edge of the cap dry up. The yellowness in their color intensifies, shades of gray appear. Places of damage to the plates may have gray edges. In cold weather, grayness appears to a lesser extent.
 Attention! Grayish shades in the color of the plates of mature specimens are an uninformative sign. They do not appear every year and not in all populations of Ryadovka Gulden.
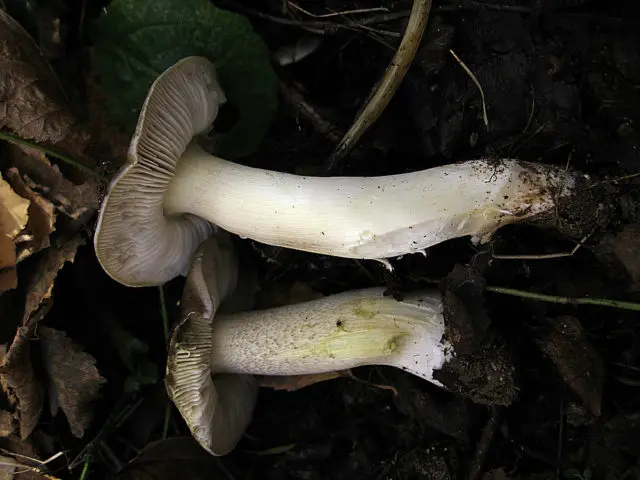
Attention! Grayish shades in the color of the plates of mature specimens are an uninformative sign. They do not appear every year and not in all populations of Ryadovka Gulden. - Leg. The shape of the leg is incorrect. It has a slight taper, tapering towards the base. There are young representatives in which the leg may have a thickening in the lower third. Its size range varies widely: length – 4 – 10 cm, diameter – 0,8 – 1,5 cm. In specimens growing in tall dense grass, the leg is longer. Representatives of the same population may have legs, both with a smooth and with a pronounced scaly surface. The color of the scales can be from light to dirty gray.


- Disputes. The spore powder of this species is white. Spores with a smooth surface have a heterogeneous shape: they are spherical and elliptical.

Row isolated:
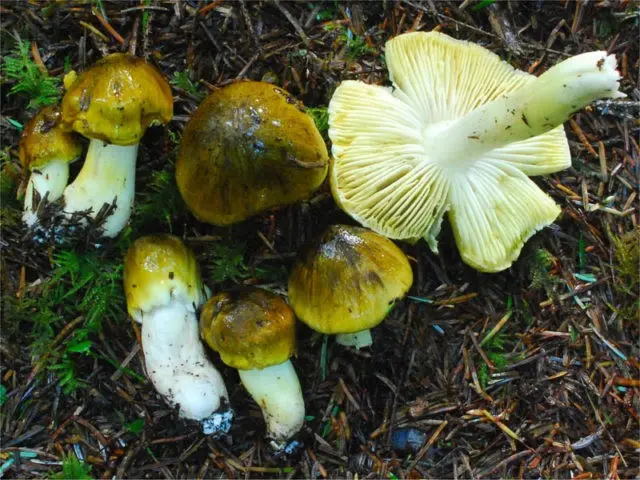

Where does the Gulden row mushroom grow?
The Gulden rowing season starts in mid-September and continues until early November. They prefer loamy as well as calcareous soils. The species is found in coniferous and mixed forests with a predominance of spruce. Occasionally it is found in forest plantations, where there are also birch, hazel, mountain ash, aspen.
Some mycologists believe that Gulden forms mycorrhiza with spruce. But there is no exact data to support this.
Is it possible to eat row Gulden
Row Gulden is described as a conditionally edible mushroom. It is eaten after preliminary heat treatment.
The taste of the mushroom
There is information about the pleasant taste of this mushroom, reminiscent of wheat flour. The smell of rowing Guilder flour, barely perceptible.
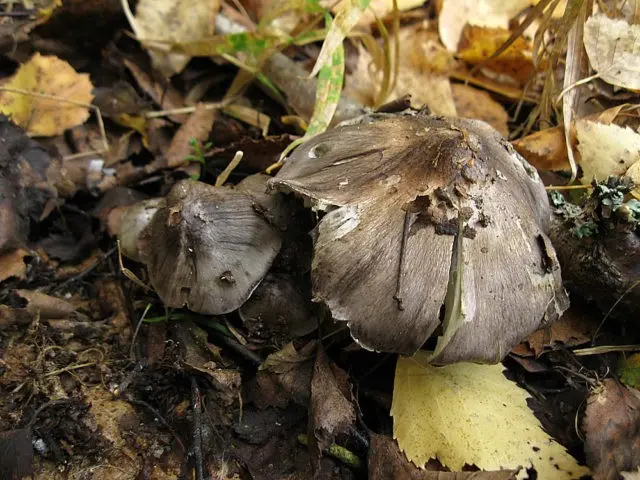

Benefits and harm to the body
This fungus has been little studied. In the studies of Danish scientists, it is emphasized that it is rare, only a few of its specimens have been found. There are no data on its beneficial and harmful properties for the human body.
False doubles
Experienced mycologists recognize this species by examining their spores under a microscope. They are heterogeneous in size and shape. In addition, spores from different Gulden specimens of the same population may have significantly different average sizes.
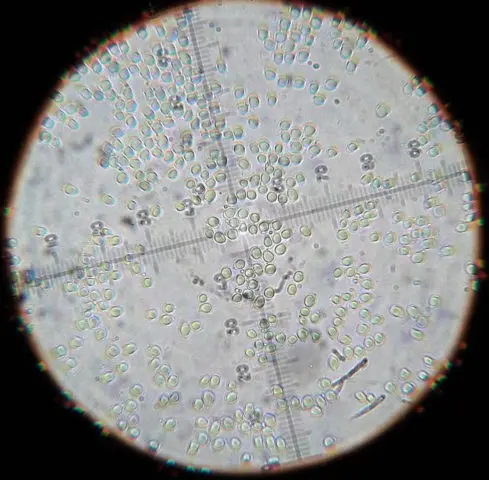
The Gulden row has the greatest external resemblance to the sulfur row, which grows only in pine forests on sandy soils. There are no gray tones in the color of her plates.
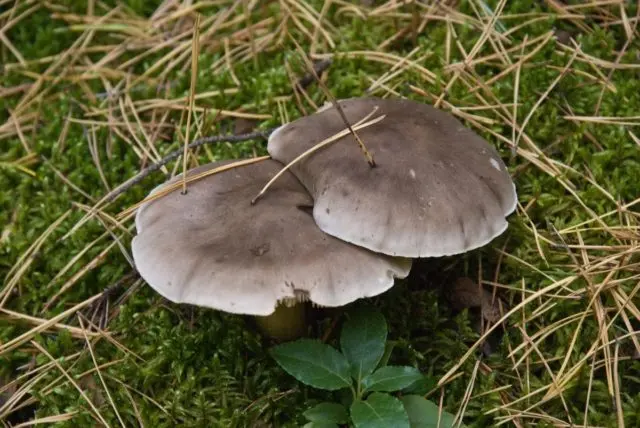

Very similar to Gulden, the mushroom row is pointed. Its fruiting body is poisonous. It has three important distinguishing features:
- thin leg;
- bulge on the hat;
- gray plates.

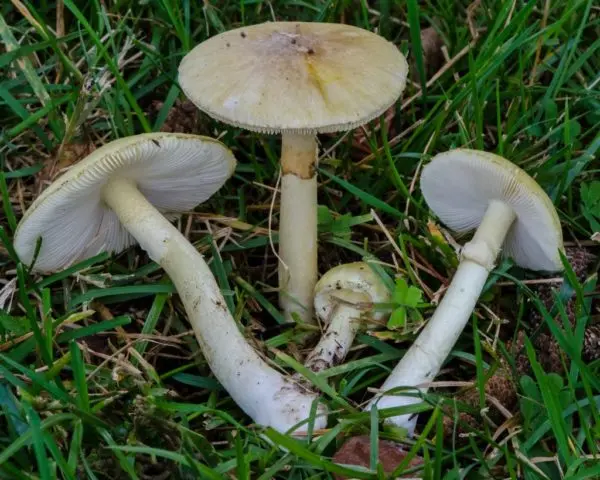
You can confuse the Gulden row with inedible mushrooms, for example, toadstool.

Collection rules
Ryadovka Gulden is a rare specimen, about which there is very little information. Therefore, if it is found, it should not be plucked, but it is recommended to inform the environmental authorities.
Use
Row Gulden is not consumed raw. Pre-boiled, it is fried. You can pickle and pickle this mushroom.
Conclusion
Row Gulden is a mushroom whose properties are poorly understood. It was first described in the writings of Copenhagen mycologists. This species is conditionally edible, sometimes it is found in northern forests, not far from spruces, on loamy and calcareous soils. There is no reliable information about the influence of representatives of this species on the human body.















