Contents
A gardener’s dream is a lush, healthy rose bush. But roses, like all other plants, are affected by pests and diseases that can occur even with good care. Do not be afraid if you suddenly notice a damaged leaf – this does not mean that the rose will die. What are the diseases of roses and how to protect yourself from them in this article.
The reason may be a lack of nutrients or bad weather conditions. For the successful cultivation of roses, you need to be able to recognize the signs of disease damage in order to take the necessary measures in time and help the plant cope with the scourge.
Diseases
When choosing varieties of roses, gardeners pay attention to their characteristics. Of course, you need to understand that if it is written that a variety is resistant to diseases, this does not mean that this specimen will never get sick. Therefore, it is important to be able to distinguish the signs of rose diseases and carry out processing in a timely manner. The main diseases of roses:
- A dangerous fungal disease is mučnistaâ rosa. It usually infects plants in summer and early autumn. When infected, a white coating appears on the leaves and buds, the leaves begin to curl up and fall off. Contribute to the appearance of this disease dense plantings, dry soil, lack of calcium and excess nitrogen fertilizers. It is important to start processing plants at the first sign of the onset of the disease. Spraying with foundationazole or phytosporin is carried out several times until the symptom of the disease disappears. If the treatment does not help, you need to remove the affected bush along with part of the soil. Do not leave fallen leaves.
Powdery mildew on roses - Rust. The causative agent of this disease is a rust fungus. Orange dust appears first near the buds and root collar, then brown spots can be seen on the leaves. The fungus takes away nutrients from the rose, which can lead to the death of the plant. Affected shoots and leaves must be removed. Bordeaux liquid is used for prevention and treatment.
The appearance of small yellow formations on roses indicates rust damage. - The most dangerous disease black spot. The leaves very quickly become covered with large black spots and fall off. The plant may lose all leaves and die. Complicating the fight against this disease is the fact that it affects the plant in early spring, and visible signs of damage become noticeable only in the middle of summer. To prevent the spread of infection, all fallen leaves must be collected and burned. In the spring, as soon as the leaves begin to bloom, it is necessary to treat with copper-containing preparations, such as copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture. If signs of disease appear, re-treat in the summer. You also need to spray the ground around the plant, as the pathogenic fungus can persist in the soil.
Yellowing leaves of a rose with the appearance of black spots indicate black spot - purple spotting. This is not such a dangerous disease. When it appears, which is manifested by irregularly shaped spots, it is enough to improve drainage, mulch the soil and feed the plant with complex fertilizer.
Purple spotting on rose leaves - Bacterial cancer. Another dangerous disease. It appears as a brown spot that appears on the stem. The bark cracks and the shoot dies. Diseased stems must be cut and burned. The fungus that causes this disease usually enters when the stems are mechanically damaged. Therefore, it is very important to keep the secateurs clean and treat the cutting edges with an alcohol solution. After you have carried out sanitary pruning, feed the bush with complex fertilizer. Before sheltering roses for the winter, leaves and unripened shoots should be removed, the bushes should be sprayed with copper-containing preparations.
Intractable cancer of the stem of a rose - Withering. There are several reasons why, starting from the tip, the shoot fades. Such a phenomenon can begin after stem frostbite, powdery mildew or black spot disease, with a deficiency of nutrients – potassium, calcium and phosphorus. Top dressing should be carried out according to the schedule starting in early spring. Affected shoots should be cut to a bud located below the affected area.
The table shows common rose diseases, their pathogens and treatment.
| Name | Symptoms | How and what to treat |
|---|---|---|
| gray mold | The disease appears in the spring after storage of seedlings and after shelter for the winter, brown spots appear on the leaves and stems, turning into gray fluffy rot. The causative agent of the fungus is Botrytis cinerea Pers. | Remove leaves and stems damaged by the disease, spray the rose, seedling and storage place with fungicides – Fundazol, Benlat, Teldor, Maxim. |
| Antraknoz | The leaf is covered with small black spots, in the initial stage it is easy to confuse with black spotting. In the process of the development of the disease, the color of the spots changes to red or purple, in the future, holes may form at the sites of the spots. The causative agent of the fungus is Sphaceloma rosarum. | Remove and destroy diseased parts of the rose and spray with fungicides. The most suitable: Ridomil Gold, Fundazol, Profit and Topaz. Reprocessing may be required. |
| Cerkosporoz | One of the varieties of spotted roses, small numerous brown spots with a dark border form on the upper side of the leaf. As the disease progresses, the center of the spots becomes grayer and the edges become dark purple. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus – Cercospora rosiola Pass. | It is treated similarly to black spot, by removing the infected parts of the rose and spraying. |
| septoriosis | The disease is in many ways similar to other spotting, the leaf is covered with numerous dark brown spots, which brighten in the center over time, leaving a thin dark border. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus – Septoria rosae Desm. | It is treated similarly to black spot, by removing the infected parts of the rose and spraying. |
| Pestalozziosis | Brown spots appear on the edges of the leaves, growing towards the middle, the border of healthy and affected leaf tissue often has a characteristic yellow color. The causative agent of the fungus is Pestalotia rosae West. | Remove stems with diseased leaves, spray the entire rose with fungicides: stems, leaves, buds. Bordeaux liquid, Topaz, Abiga-Peak are suitable. |
| Downy Mildew | The shoots are covered with small red-brown spots, the leaves become creamy white and develop poorly, gradually deform and fall off. The disease can be confused with chemical burns. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus – Pseudoperonospora sparsa. | It is necessary to remove parts of the rose damaged by the disease (leaves, stems). Spray the rose bush and the soil around it with fungicides. Profit, Ridomil Gold, Fundazol. |
| Mučnistaâ rosa | Parts of the rose are covered with gray powdery spots. Usually the disease damages the leaves, stems and buds of roses. The causative agent of the fungus is Sphaerotheca pannosa | It is necessary to remove the parts of the plant affected by the disease. Spray with fungicides – Bactofit, Skor, Topaz, Fitosporin. Provide access to fresh air to the rose. |
| Black spot | The rose bush is covered with black or brown spots, most often the disease damages the leaves of roses. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus – Marssonina rosae | It is necessary to remove parts of the rose bush damaged by the disease and spray with fungicides. Ridomil Gold, Fundazol, Profit are suitable. |
| Rust | Rust-like growths form on the stems and leaves. The leaves weaken, brighten and fall off. The leaves, stems and buds of roses are most susceptible to disease. The causative agent of the fungus is Phragmidium | It is necessary to remove the affected parts of the rose, circulate fresh air and spray. Topaz, Abiga-Peak are suitable for processing, Bordeaux mixture and a solution of copper sulphate can be used. Multiple processing required. |
Viruses
In addition to fungal diseases, roses can be affected by viruses. These include:
- Mosaic blotch virus. You can recognize it by light spots on different parts of the plant.

Mosaic blotch virus on rose - Rose streak virus. The leaves around the edges seem to be surrounded by a burgundy border.

Banding virus appears on the tips of rose leaves
Viral diseases of roses are not treated. It is necessary to remove diseased plants along with the roots and part of the soil. Removed bushes need to be burned. Shed the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate, they should also process garden tools. Neighboring plants need to be treated with agents for the prevention of bacterial diseases. Carry out feeding.
To avoid the occurrence of these and other diseases, you need to inspect the plants before buying seedlings and / or before planting a rose. And carry out regular processing of the rosary.
Disease control
Proper care of roses helps them resist disease, but cannot completely protect them. The main method of protection against the appearance of, for example, black spot or powdery mildew is the treatment of plants with pesticides. When using them, it is important to observe simple precautions.
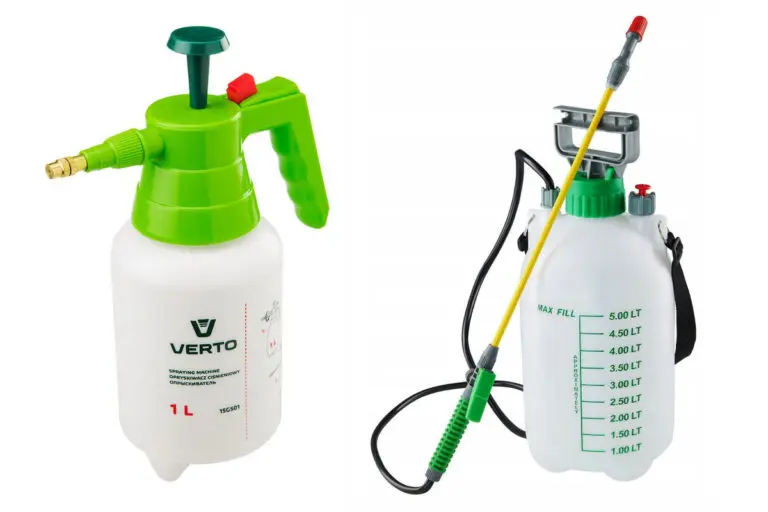
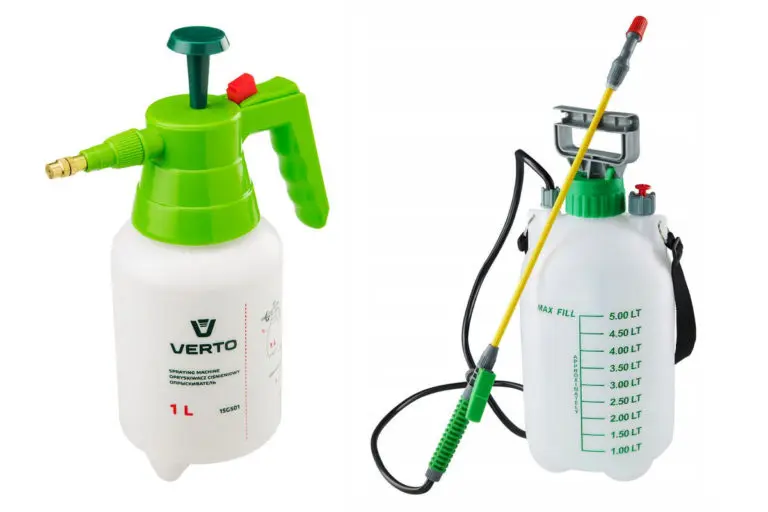
Spray equipment
If the damage is minor, a hand sprayer can be used. If you need to treat a large area, then it is better to use a sprayer with a pump. To make it comfortable to carry it, choose a volume of 5 liters. It is necessary to maintain the recommended distance to the plant when spraying.

Spray preparation
Fungicides are needed to prevent diseases, especially fungal ones. Typically, fungicide treatment is carried out several times. Before starting the treatment of plants, you need to carefully study the instructions for the use of drugs. It is important to follow the recommendations for the dosage of the drug.
Important! Do not forget that you can not use dishes that have previously been used for herbicide treatment.
When and how to spray
There are certain rules, following which you will not harm your roses and increase the effectiveness of the procedure:
- Spraying is carried out on a cloudy and calm day.
- The leaves of the plant must be dry.
- During the flowering period, spraying is carried out in the evening so as not to harm the bees.
- You need to spray both the upper and lower sides of the leaf until the liquid begins to drip from them.
- Adjust the sprayer so that a strong jet of mist is directed at the roses.
- Make sure that the drug does not get on your skin. Spraying should be carried out in protective clothing and gloves.
Beginning gardeners usually process the rose garden as needed when they notice signs of disease when examining roses. With this approach, you need to have a small set of tools on hand. So for the prevention of the most common diseases, you can use “Derozal” or “Terminator”, containing carbendazim.
Specialists prefer to process roses according to the schedule throughout the season, and use special tools only in emergency cases. The main treatments are carried out in May, June and September. The bushes are sprayed with a mixture of permethrin (an insecticide against pests) and carbendazim (a fungicide). Between these treatments, additional sprays with carbendazim are possible in case of black spot or powdery mildew.
| Group | Characterization | Names of fungicides |
|---|---|---|
| Benzimidazoles | They have a systemic effect, it is recommended to apply by irrigation, they are well distributed throughout the plant with nutritious juices. Excellent for the treatment of many fungal plant diseases. Can be used as a seedling and seed dressing agent. | Ferazim, Terminator, Derozal, Shtefazal, Bavemtin; Benlat, Fundazol, Agrocyte, Vial, Vincit, Tekto (fungicides contain different active ingredients) |
| Triazole | Penetrate deep into the leaf of the plant, moving behind the point of growth, well protect young shoots from diseases, excellent for the treatment of many types of fungal diseases of plants. | Quick, Split, Topaz, Impact, Vincite, Vectra, Bayleton, Tosonite, Vial, Lospel, Real, Premis25, Raxil, Terrasil, Tilt, Sumi8, Falcon combined fungicide, Folicur combined, Shavit combined, Rex, Allegro Plus, Bumper, Alto (drugs contain different active ingredients). |
| Carbamates | They have a systemic effect, it is recommended to use an irrigation agent as a prophylactic agent, it spreads well through the vascular system of the plant. | Previkur, Tatu, Topsin-M, Cabrio Top (have different active ingredients) |
| Hydroxyanilide | It has a protective systemic effect, is not phytotoxic to humans and animals, and is an excellent remedy for rot and powdery mildew. | Teldor |
| Piperazine derivatives | They have a protective and healing effect, it is good to use against powdery mildew, rot and gray mold | Saprol |
| Pyrimidamines | It has a systemic effect, it is well used against powdery mildew. | Rubigan, Milgo, Horus (fungicides with different active ingredients) |
| Imidazoles | Effective against powdery mildew and mold. | Mirage, Sportak, Trifmin. |
| Derivatives of hydroxycarboxylic acids | They have a systemic effect, they are used as a seedling and seed dressing agent. | Vitavax, Carboxin |
| Dithiocarbamates | They have a contact action, are effective in between treatments for combination with other fungicides. | Polycarbacin; Ditan, Acrobat (mancozeb); Antrakol; Ridomil-Gold combined (mancozeb, metalaxyl); Cabrio Top (fungicides with different active ingredients). |
| Organophosphorus | Effective against downy mildew, powdery mildew and gray mold. | Allett, aluminum fosetil, Efal, Mitsu Alufit Afugan |
| Amino acid derivatives | It has a systemic effect, a single application is recommended. Effective in the treatment of downy mildew. | Metalaxil, Ridomil, Alacid, Apron, Creptan, Sandofan, Arceride, Maxim, metalaxyl-M |
| Acetamides and oxazolidine derivatives | Effective against late blight, Alternaria, mildew. | Thanos – combined |
| Strobilurins | It has a systemic effect, penetrates well into the tissues of the plant, is able to move behind the growth point, protecting the shoots. It has a high resistance to temperature extremes, it is recommended as an excellent prophylactic agent. It has a wide spectrum of action, applicable to many fungal diseases. | Strobi, Flint, Quadris, Cabrio Top (fungicides contain different active ingredients) |
After spraying
After finishing the processing of plants, you need to thoroughly rinse the equipment used, and then wash your hands and face. The remains of the mixture for spraying plants can not be stored. Each time it is necessary to prepare a fresh solution.
It is important to store the chemicals used for spraying in a safe place out of the reach of children. Do not store them in jars or bottles with poorly legible labels or without them. Crockery after use of the contents must be disposed of.
Problems in growing roses similar to diseases
If, when growing roses, you saw a deterioration in the growth of a bush, the appearance of spots on the leaves, this does not always indicate a plant disease. This may be due to the wrong planting site or micronutrient deficiencies. Let’s take a closer look at what problems you might encounter.
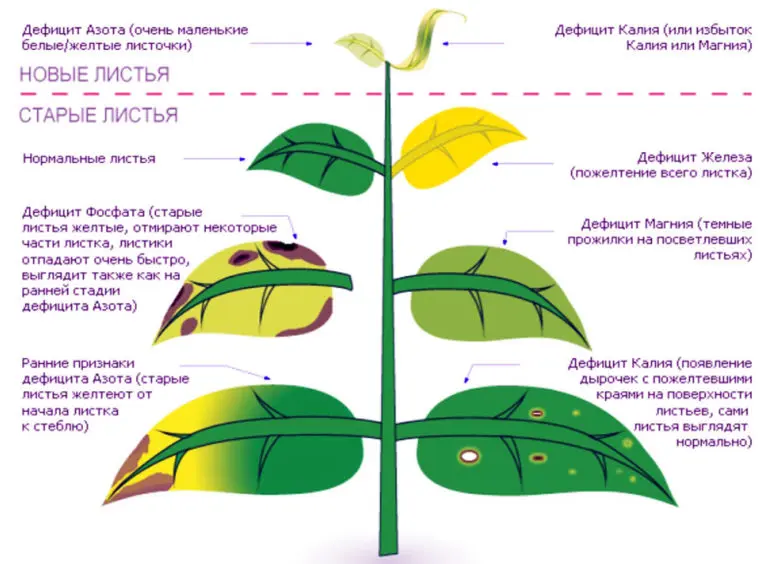
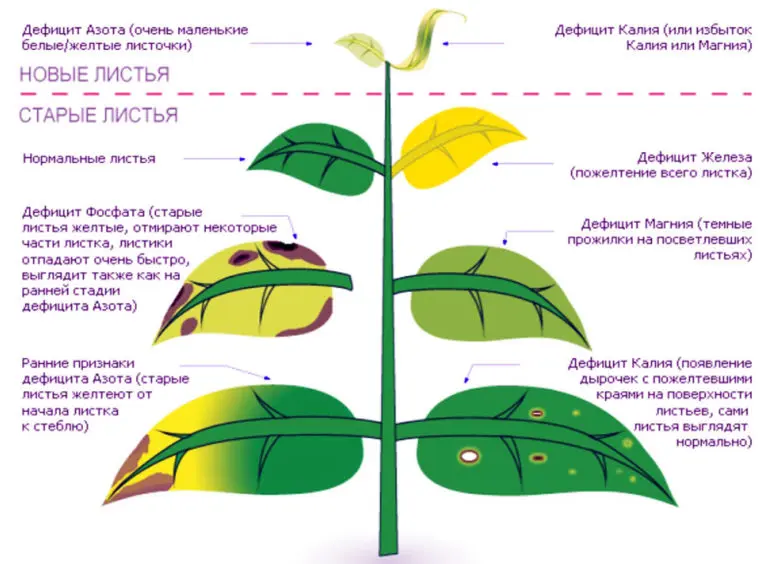
- Nutrient deficiencies. An experienced gardener can determine by the appearance of the plant which element the plant lacks and adjust the feeding schedule.
- Nitrogen deficiency. Young leaves become small, their color is paler, they fall off ahead of time. Sometimes you can see reddish spots on them. The stems weaken and bend.
- Phosphorus deficiency. Young leaves become dark green with a red-violet tint. Stems are twisted.
- Potassium deficiency. Often seen in sandy soils. Young leaves take on a reddish tint, and adults dry out at the edges. The flowers are shrinking.
- Magnesium deficiency. The leaves, starting from the middle, turn pale, the tissue dies, and the leaf falls off.
- iron deficiency. The leaves are covered with yellow spots, young shoots turn completely yellow. In this case, special measures are needed. It is necessary to reduce the level of lime in the soil. The “MultiTonic” fertilizer will perfectly cope with the task.
- Freezing plants. To determine that your bush is damaged by frost, you can by its appearance. Affected leaves shrivel, become thin, tear, and brown spots appear on the edges. In areas with frosty winters, plants need shelter, which is removed only after the frost has passed, but before the start of the growing season (budding).
- Stagnant water at the roots. External signs are similar to those that indicate a lack of manganese, but in this case, the veins of the leaves begin to turn yellow, and then the stain spreads along the leaf. Roses need good drainage, which must be taken care of when planting a bush.
- Herbicide damage. If herbicides are accidentally applied to the roses while working on the lawn, you may see the leaves of the plant begin to curl in a spiral, and the stems turn red and bend. These shoots must be removed. To prevent such damage, do not use weed killers on a windy day, do not use the same watering can to herbicide the lawn and water the roses.
- Non-opening of buds. Sometimes you can notice that a normally developed bud does not open, its petals begin to turn brown. The reason may be excess moisture, lack of sun.
Tips for Growing Roses
Of course, it will not be possible to completely avoid the difficulties in growing this beautiful flower. Compliance with simple rules and the implementation of preventive measures will save you from many problems that arise during the growth and flowering of the bush:
- Carefully inspect the seedlings before buying. A strong root system and strong shoots are important. Seedlings should not show signs of diseases or pests.
- Plant roses only in places suitable for them. Roses love light, do not like north and northeast winds, cannot stand the close occurrence of groundwater and the strong acidity of the soil. The right place will save you from problems associated with wetting, freezing, lack of lighting and swaying of the bush by the wind.
- Always remove fallen leaves and removed shoots. Affected leaves and shoots must be burned. You can’t put them in compost.
- Prepare the soil well. It is necessary to provide drainage and availability of nutrients in the soil.
- Feed your roses the right way. At different times of the year, bushes need a different set of minerals. Don’t add too much lime to the soil.
- Check your plants regularly. Take action at the first signs of illness.
- Cover and uncover roses in time. Before wintering, remove all leaves and diseased shoots. After removing the shelter, carry out preventive treatment with preparations containing copper.
Conclusion
With proper care, rose bushes will remain the main decoration for a long time and will delight with a beautiful shape and lush flowering.