Contents
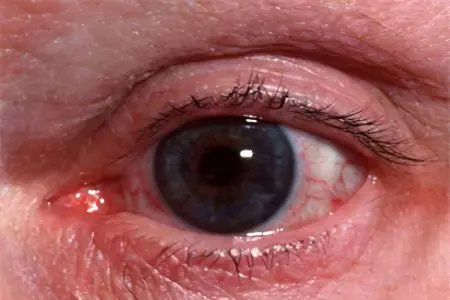
Rosacea of the eye is an erythema that moves from the face to the organs of vision. The disease is characterized by damage to the cornea, iris, eyelids and conjunctiva. Eye rosacea has a chronic course and in 30% of cases accompanies the skin form of rosacea. The disease is most often bilateral.
The anterior tissues of the eye during fetal development of the child are formed from the same germ layer as the skin. Therefore, they are characterized by similar pathologies. But since the eyes have a higher sensitivity and innervation, their inflammation is very noticeable for the patient.
Eye rosacea usually affects people between the ages of 40 and 60, although it can also occur in children.
The disease cannot be ignored. If left untreated, rosacea can lead to complete blindness.
Causes of eye rosacea
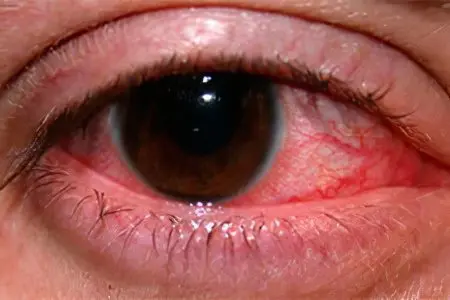
The causes of eye rosacea can be identified as follows:
Alcohol abuse and smoking. These bad habits contribute to capillary damage, disrupt their normal tone, and lead to congestion. All this becomes favorable factors for the manifestation of the disease.
Frequent visits to the solarium, prolonged exposure to the sun without the use of eye protection. Ultraviolet light triggers a number of pathological reactions that damage the skin vessels and intercellular substance, provoking the development of eye rosacea.
Sharp temperature changes.
A connection has been established between the development of eye rosacea and diseases of the digestive system.
An indispensable condition for the occurrence of a pathological process in the organs of vision is the presence of rosacea on the skin of the face. The inflammatory process leads to translucence of blood vessels through the epidermis and severe erythema. Venous outflow suffers, blood stagnation is present on an ongoing basis, which is the basis for the development of eye rosacea.
Meibomian gland dysfunction causes instability of the tear film, excessive evaporation of the tear fluid, and the formation of dry eye syndrome. All of these become key mechanisms in the development of the ocular form of rosacea.
Scientists tried to establish a link between the disease and infection with an eyelash mite, however, it was not possible to trace it. However, Demodex follicularum is quite common in patients with eye rosacea.
Eye rosacea symptoms
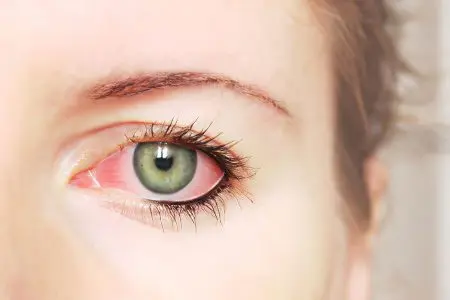
Symptoms of ophthalmic rosacea are most often mild, although it all depends on how severely the eyes are affected. When the disease is just beginning to develop, the patient complains of pain in the eyes, increased lacrimation, and a burning sensation. There may be a feeling that a foreign body is constantly present in the eye. Visual acuity may suffer already in the early stages of the disease.
The conjunctiva and the white of the eye become engorged, swollen and red. During a visit to the ophthalmologist’s office, the doctor visualizes telangiectasia of the edges of the eye, persistent inflammation of the eyelid, the presence of chalazions in the thickness of the eyelids.
For a long time, a person may unsuccessfully try to treat conjunctivitis.
Meibomian gland ducts are sometimes blocked by yellow plugs. If you press your finger on the edge of the eyelid, then a thick, opaque secret will stand out from the duct. Sometimes it looks like a slurry.
As the cornea is damaged, phenomena of keratitis and germination of blood vessels into the stroma of the cornea itself are observed. At this time, vision drops sharply, up to complete blindness. Vessels in the eye resemble twigs. This stage of the development of the disease is characterized by the addition of cutting pains, severe photophobia. Ulcers and infiltrates may appear on the cornea.
Ignoring the symptoms of ophthalmic rosacea leads to the development of serious visual complications. The most dangerous of them are phlyctenular keratoconjunctivitis, corneal neovascularization, peripheral keratitis, conjunctival fibrosis, ulcerative scleritis.
Diagnosis of eye rosacea
Diagnosis of eye rosacea begins with a standard examination of the patient. The doctor evaluates the visual acuity of the patient, conducts biomicroscopy and tonometry of the eye. It is imperative to interview the patient in detail, to clarify whether there was a history of skin form of rosacea.
As for additional examination methods, it is possible to carry out the Schirmer test and the Norn test. They allow you to determine the stability of the tear film and the quality of tear production.
During the examination, it is necessary to conduct a differential diagnosis with dry eye syndrome, allergic and toxic conjunctivitis.
Eye rosacea treatment
Most often, the treatment of rosacea of the eyes is not difficult. Only in the case when the disease has a running course, a long therapeutic course may be required. To prevent this from happening, you should seek help from an ophthalmologist already in the early stages of the development of the disease. In addition to the main treatment, symptomatic therapy is carried out.
Metronidazole Gel
Rosacea of the eye, accompanied by demodicosis, requires the use of drugs based on Metronidazole. With ophthalmic rosacea, the parasite is found in the ciliary bed in 90% of cases. It is not difficult to identify it, it is enough to conduct a standard microscopic examination with the collection of eyelashes from both eyelids.
The following drugs can be used to eradicate the parasite:
Ointment Demalan.
Gel Stop Demodex.
Gel Metrogil.
The duration of treatment and the choice of drug should be determined by the doctor. If the drug was chosen correctly, then the inflammation process will fade away, and the control microscopic examination will not find traces of the parasite in the ciliary bed.
Antibacterial drugs for topical use
If eye rosacea is accompanied by the addition of a bacterial infection, then the patient is prescribed antibiotics. Bacteria that provoke skin inflammation in rosacea easily colonize the mucous membrane of the eye and conjunctiva. Therefore, bacterial conjunctivitis is a frequent companion of eye rosacea.
To get rid of inflammation, you will need to use the following drugs:
Eye drops: Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Tobramycin.
Ointments: Erythromycin, Tetracycline.
These drugs have a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity and can cope with most microorganisms that affect the mucous membrane of the eye. When the ongoing therapy does not give the desired result, it becomes necessary to perform an antibiogram. This study allows you to identify which drugs the pathogenic flora is sensitive to. Then the patient is prescribed a second course of local antibiotic therapy.
Hydration of the mucous membrane of the eye
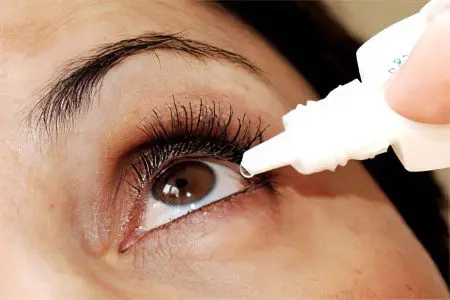
Dryness of the mucous membrane of the eye is one of the common symptoms of rosacea. Insufficient hydration is caused by disturbances in the work of the meibomian glands, which overlap due to a number of factors (mucosal edema, parasitism of mites, hypertrophic changes in the skin of the eyelids). As a result, the tear fluid quickly evaporates from the surface of the eye, causing dryness. To get rid of this phenomenon, it is necessary to use special moisturizing drops. They need to be installed until rosacea can be completely eliminated.
These drugs include:
Oxyal.
Systane.
Hilo chest of drawers.
Stimulation of metabolic processes
The natural metabolic processes that occur in the organs of vision, with rosacea, are disturbed, as there is chronic inflammation. Any defects and injuries of the eyelid and conjunctiva regenerate longer, which negatively affects the patient’s well-being.
To normalize metabolic processes, it is necessary to use drugs such as:
Emoxipine.
Solcoseryl.
Tauphone.
Removal of inflammation
If you do not get rid of the inflammation, then the person will experience severe discomfort. During an exacerbation of the disease, the use of hormonal drugs is permissible. However, only a doctor can prescribe them, evaluating the full benefits of the treatment. Preparations with a hormonal component are used for several days, but not for too long.
To eliminate a chronic inflammatory reaction, which is not associated with the risk of developing serious complications, you can use the following drugs:
Indomethacin (Indocollir).
Diclofenac (Diclo-F).
VisiDol.
Disinfection of the skin around the eyes
To treat the skin around the eyes, ointments and creams with an antibacterial component are used. It can be Tetracycline or Erythromycin. They should be used from the very beginning of the therapeutic course. This is an excellent prevention of the addition of a bacterial infection and other complications. In complex therapy, it is possible to use decoctions and compresses based on medicinal herbs.
Laser therapy for eye rosacea is rarely prescribed. The laser can be used to eliminate a cosmetic defect and remove the hypertrophied layer of eyelid skin. The decision on the need for laser therapy is made by the doctor.
Prophylaxis and prognosis
If the patient complies with all the appointments of the ophthalmologist, then the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Although in some cases, treatment lasts for several months.
In order to prevent the development of ophthalmic rosacea, the impact on the eyes of negative factors should be minimized. All people over the age of 45 should be examined by an ophthalmologist every year. Basic recommendations come down to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, and regular exercise. All diseases of the digestive system must be treated qualitatively. If the inflammation of the skin of the face with rosacea is stopped in time, the disease will not spread to the organs of vision.
Author of the article: Degtyareva Marina Vitalievna, ophthalmologist, ophthalmologist









