Contents
What is a rib fracture?
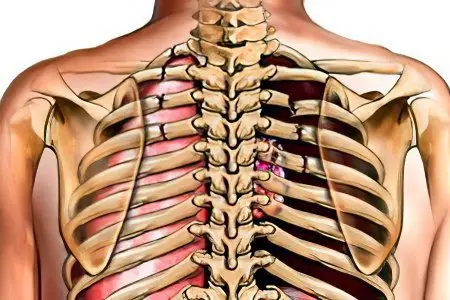
Rib fractures are the most common chest injury. Among the total number of fractures, about 16% are fractures of the ribs. In people of a fairly advanced age or with certain chronic diseases, rib injuries are much more common, since the elasticity of important bone structures of the chest decreases with age.
Fractures without complications are usually fractures of one or two ribs. They do not pose a danger to human health and life and usually grow together quite well. The greatest danger associated with this injury is serious damage to the internal organs and significant respiratory failure. Uncomplicated fractures occur in about 40% of chest injuries. In the remaining 60%, internal organs are noticeably affected – the lungs, pleura, and organs of the cardiovascular system are damaged.
Multiple rib fractures are an incredibly serious injury that poses a great threat, since in this case the likelihood of serious life-threatening complications increases dramatically.
Signs and symptoms of a broken rib
When the ribs are fractured, many victims complain of quite noticeable pain at the site of injury, they also have difficulty breathing, they cannot breathe freely. Even the slightest cough causes sharp pain. Victims move very carefully, afraid to feel increased pain, slowly undress and dress. Also, because of the fear of experiencing severe pain, the victims become superficial and breathing itself. If, due to a broken rib, a lung is affected, blood spitting appears.
After the injury has occurred, the victims almost immediately indicate the classic signs of injury: a sharp pain appears in the chest, which, when talking, coughing, breathing and moving, noticeably increases and, accordingly, decreases when the patient lies or is in a sitting position. In this case, breathing is rather shallow, and the entire chest of a person on the side of the fracture lags far behind when breathing.
Signs of a fracture of the ribs from the side and front are especially difficult for the victims to endure, and breathing is disturbed. If a rib fracture occurs at the back, the signs of this damage are not so pronounced, and significant impairment of pulmonary ventilation, as a rule, does not occur.
If the patient has damaged several ribs, his condition becomes much worse. Breathing becomes very shallow, the skin becomes pale, acquiring a bluish tint, while the pulse increases significantly. The patient tries not to move, preferring to sit still. The main signs of a rib fracture are severe bruising, noticeable swelling of soft tissues. When listening, it is not always possible to determine breathing.
One of the dangerous complications of a rib fracture that can develop is dangerous post-traumatic pneumonia. Usually this complication makes itself felt a few days after the injury. The development of this complication directly depends on the state of health and age, as a rule, patients of elderly and senile age are susceptible to it.
If the condition of the victim worsens, pronounced symptoms of intoxication are observed, the body temperature rises greatly, and breathing becomes difficult and difficult. In this case, we can talk about the development of dangerous pneumonia. However, one should not forget that in debilitated elderly patients, post-traumatic pneumonia does not always occur with a noticeable increase in temperature, sometimes there is only a general deterioration and weakness.
Post-traumatic pneumonia often occurs due to a significant decrease in the level of ventilation in the lungs on the side where there is damage to the ribs. The victim usually experiences severe pain during a fracture, so he tries to take shallow, superficial breaths. There are cases when a rather painful swelling forms in a certain area of the fracture.
If the victim tries to take a deep breath, there is always severe pain, and therefore the attempt ends unsuccessfully. This particular symptom is referred to as “halved inspiration”. This sign is not observed when there is a contusion of the chest.
Another significant sign of a rib fracture is the so-called axial load symptom. They try to determine it by alternately squeezing the entire chest. Since the chest is a bone ring, when some of its sections are compressed, the load on other sections is significantly increased. When the damage occurs, the victim feels pain at the fracture site, and not at the place where the compression occurred.
With proper palpation, there is always a sharp local pain. A specific deformity in the form of a step at that point of maximum pain also indicates a fracture of the rib. Then, to exclude possible complications, you can palpate not only the chest, but the entire abdominal cavity, determine the heart rate and blood pressure. A good aid in diagnosing a fracture is radiography.
True, there are reasons due to which it is not always possible to determine a fracture of the rib. Therefore, a specific clinical picture usually plays a dominant role in establishing a diagnosis. If all the signs point to the presence of damage to the chest, it is possible in some cases not to conduct an x-ray examination. To reduce the risk of complications, a urinalysis and a complete blood count are performed to reveal a more complete picture of the damage.
First aid for broken ribs
You should not engage in any self-treatment for fractured ribs, but first aid is necessary:
Give the person a pain reliever (such as ibuprofen);
Make the necessary fixing bandage from a towel and bandage;
The affected area must be kept in the cold (it is best to apply ice)
After that, see a doctor as soon as possible. If the victim is being transported to the hospital, it is necessary to carry out transportation in a prone position or in a half-sitting position.
Rib fracture classification
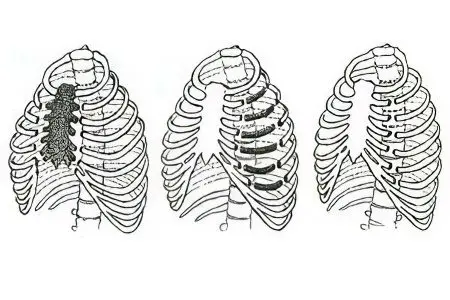
Impacts on the ribs of a person are divided into indirect and direct. With indirect impact, the chest is compressed, so the ribs break on both sides of the place of compression. As a rule, several ribs break at once. In the case of direct impact, fragments of the rib can damage various internal organs, the lung when the ribs bend inward.
There are bilateral fractures, as a result of which the chest loses the necessary stability, and a dangerous violation of lung ventilation occurs. So-called fenestrated fractures also occur, i.e. fractures in two places on one side. Most often, rib fractures occur in people over 40 years of age. This is due to changes in bone tissue that occur in the human body due to age. In childhood, rib fractures are extremely rare, because the children’s chest has great elasticity.
There is also the following division of rib fractures: rib fracture, bone fracture (so-called subperiosteal fracture) and complete rib fracture. The latter most often occurs at the site of the bending of the ribs. All these cases are characterized by the same symptoms of a fracture.
Rib fracture treatment
If there is a fracture of one or two ribs, treatment can be carried out at home or in a clinic under the supervision of a specialist, the patient must be put in plaster. If complications occur or a multiple fracture of the ribs occurs, the patient must be treated in a hospital.
As modern medicines, 10 ml of a 1-2% solution of procaine is used, which is injected into the fracture site. Further, without removing the needle, quickly add 1 ml of 70% alcohol. In the case of a properly administered drug, the pain syndrome practically disappears, and the patient is able to breathe deeply, and coughing does not cause such severe pain.
Also, in the treatment of rib fractures, an expectorant mixture is prescribed, and ordinary mustard plasters must be placed on the chest. It is necessary to perform breathing exercises with caution, and UHF (ultra-high-frequency therapy) procedures are prescribed from the third day after the injury. Further, at the fracture site, electrophoresis of procaine and obligatory calcium chloride is used as a treatment, and then special therapeutic exercises are prescribed.
In particularly difficult cases, surgical treatment of the fracture is necessary. To release the accumulated blood, on the recommendation of the attending physician, if necessary, a puncture is performed. As a rule, for recovery in simple cases, the patient needs about four weeks, while strict bed rest and complete rest are required. With multiple fractures, the duration of treatment depends on the general condition of the patient himself.









