In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Reye’s syndrome is an acute encephalopathy with fatty degeneration of the liver and internal organs.
It occurs worldwide with equal frequency in boys and girls. The age at which the disease occurs is within wide limits – from infancy to adolescence, the highest incidence is recorded in the autumn and winter seasons of the year.
The hypotheses about the causes and development of the syndrome include:
• insufficiently documented role of viral infections in the course of which a genetic metabolic error is revealed; the most frequently isolated viruses causing infections preceding Reye’s syndrome are the following viruses: influenza, parainfluenza, smallpox, rubella, common parotitis (mumps), adenoviruses, reoviruses, rhinoviruses, Epstein-Barr, CMV, Herpes simplex, Herpes zoster,
• defect of lipid and amino acid metabolism,
• exogenous toxins that alter the host’s response to viral infection, the most frequently mentioned of which are: salicylates, pesticides, insecticides, aflatoxins, latex paints, and sometimes paracetamol.
symptoms
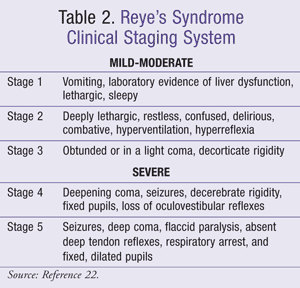
The disease has a two-phase course. It begins with catarrh of the respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract, not always with fever. After a short-term improvement, there is rapid vomiting followed by rapidly increasing neurological symptoms associated with brain edema, such as agitation with characteristic screaming, delirium, disturbed consciousness, convulsions, coma. Muscle tension increases, respiratory and heart dysfunction join. The course of the disease is electrifying, most often fatal, and if the child survives, severe neurological defects remain. Very rarely we observe recovery without neurological damage.
Treatment: in a hospital setting.
The content of the medTvoiLokony website is intended to improve, not replace, the contact between the Website User and their doctor. The website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. Before following the specialist knowledge, in particular medical advice, contained on our Website, you must consult a doctor. The Administrator does not bear any consequences resulting from the use of information contained on the Website.