Contents
What is retinal hemorrhage?
Retinal hemorrhage – this is bleeding into the tissue of the retina, resulting from damage to the walls of the eye vessels. Such a hemorrhage may be visually subtle, but it is very dangerous, since visual receptors are located in the retina.
Retinal hemorrhage is quite common and can be the result of both mechanical trauma and some diseases. Any hemorrhage, especially repeated, requires a mandatory medical consultation, since in this case the risk of retinal detachment increases significantly.
Causes of hemorrhages in the retina
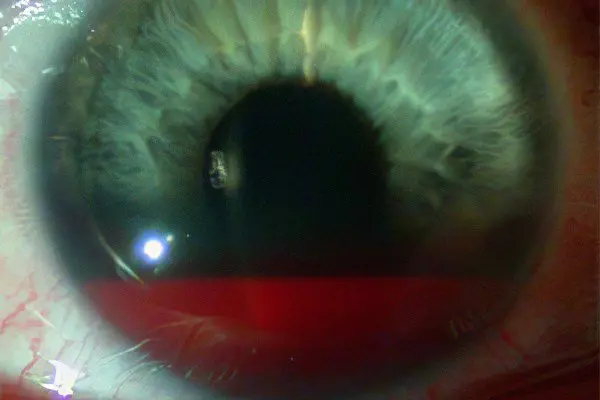
The most common cause of such a hemorrhage is blunt trauma (contusion) of the eye. In this case, an external mechanical force can act both directly on the eye and through the surrounding tissues (a blow to the face, head, or even to the diaphragm).
According to gravity, three degrees of contusion are distinguished:
Lightweightwhen there are almost no visible manifestations, the structures of the eye are not damaged, there is a slight swelling of the cornea and retina, vision can be restored in full;
Average, which is characterized by damage to the tissues of the eye (hemorrhage under the conjunctiva and its ruptures, corneal erosion) and deterioration of vision to light perception;
Heavy, accompanied by irreversible structural changes in the tissues of the eye (ruptures of the choroid and retina, dislocation of the lens) and complete loss of visual functions.
Even slight bruises can lead to serious changes in the structure of the eyeball. Similarly, the symptoms and external manifestations of contusion do not always correspond to the actual severity of the injury. Often, hemorrhages in the visual organs are accompanied by closed brain injuries.
The second, rather numerous group of causes are general diseases:
Atherosclerosis – vessel walls covered with sclerotic plaques lose their elasticity and become more susceptible to influences;
Arterial hypertension – with increased pressure, the risk of rupture of the walls of blood vessels increases;
Diabetes – high glucose levels lead to aneurysms (protrusion) and weakening of the vascular walls;
Systemic connective tissue diseases (scleroderma, vasculitis, lupus erythematosus) – increase the permeability and fragility of blood vessels;
Diseases of the blood (anemia, leukemia, coagulopathy) – clotting disorders and pathological changes in the composition of the blood have a negative effect on the walls of blood vessels.
The third group includes directly eye diseases:
Intraocular tumors that compress blood vessels;
Myopia (nearsightedness) of medium and high degree;
Anomalies of development and inflammatory processes of the choroid of the eye (angiopathy or thrombosis of the retinal veins, uveitis, iritis).
Intense physical activity can be divided into a separate group:
Sports, cardio training;
Attempts during childbirth;
severe coughing or screaming;
Shaking (especially in infants).
Symptoms of retinal hemorrhage
Common symptoms of eye hemorrhage include:
Decreased visual acuity and clarity, blurring, double image;
Restriction of eyeball movements;
Formation of a grid before the eyes;
Flashing “flies”.
Initially, a cloudy spot appears before the eyes, which gradually grows. With a significant extensive lesion, vision may disappear completely.
With contusion of the eye orbit, blood diseases and vasculitis, a pronounced protrusion of the eyeball forward (exophthalmos) is possible.
If the expired blood is localized along the vessels or on the periphery of the fundus, then visual impairment is absent or insignificant. If the hemorrhage occurred in the central part of the retina (macular zone), then vision is reduced quickly and to a large extent.
Hemorrhages outside the macular zone can go unnoticed by a person and be detected only when examined by an ophthalmologist, when diagnosing the fundus.
Treatment of retinal hemorrhage
Retinal hemorrhage is diagnosed by examining the fundus with an ophthalmoscope. It is also necessary to do a complete blood count to clarify the cause of the hemorrhage or the possible identification of the underlying disease in order to take appropriate measures to prevent recurrent hemorrhages.
With extensive hemorrhage and severe damage to the retina, surgery can be performed – vitrectomy. During this operation, cloudy parts of the vitreous body of the eye and blood clots are removed. Vision after surgery is restored within a few weeks. The amount of restored visual function depends on the condition of the retina and optic nerve. If they contain organic changes, then even with positive results of the operation (transparency of the vitreous body, good fit of the retina), vision may remain low.
With moderate hemorrhage, not associated with serious diseases, the main recommendation is maximum rest and rest for the eyes. It is helpful to sit quietly with your eyes closed for a long time, this contributes to the natural sedimentation of blood. It is very important not to allow any foreign bodies (motes, etc.) to get into the eyes at this time so as not to get infected. Vision is restored in about 3-4 weeks.
Of the medications, hemostatic and vasoconstrictive agents can be prescribed; Currently, there are no special drugs for the treatment of retinal hemorrhages. For example, eye drops “Emoxipin” strengthen the blood vessels of the eyes and protect them from excessive lighting. They can be used only after examination and as directed by a doctor. It is also recommended to take vitamins C and K, which strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood clotting.
Preventive measures are reduced to strengthening immunity, timely treatment of common diseases. People at risk should avoid sudden head movements and downward bending.
Author of the article: Degtyareva Marina Vitalievna, ophthalmologist, ophthalmologist









