Contents
The vesicle is distinguished by its decorative effect, unpretentiousness of cultivation, and frost resistance. These advantages are a good reason for planting it to decorate the garden plot. It will not be superfluous to know how to propagate the vesicle using various methods.
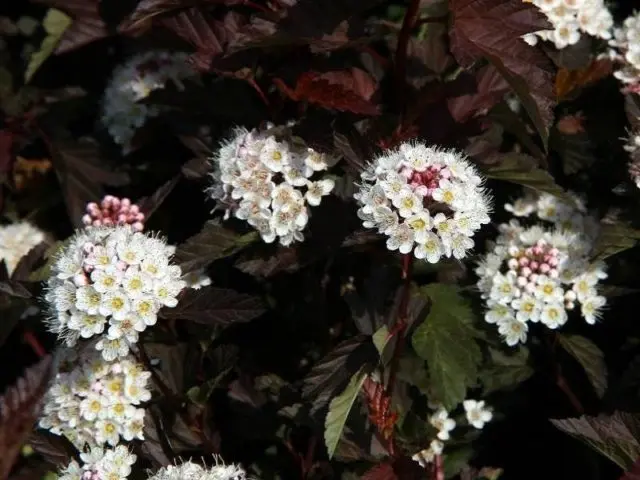

The plant looks great in separate plantings on the lawn, in composition with conifers. Very effective hedges from it, neatly and interestingly trimmed. The shrub tolerates pruning and shaping well. By propagating the vesicle, you can create elegant alleys, compositions for gardens, squares, parks. This is especially true for red-leaved varieties.
How does the vesicle reproduce?
Decorative vesicles with raspberry-purple foliage are very fond of open and sunny places. In shaded areas, they lose their bright color and individuality and become green.
You can propagate the red-leaved vesicle by cuttings, dividing the bush, layering. Seeds germinate well, but seedlings grown in this way will not receive all varietal qualities. Their leaves are most likely to be green. Plants obtained from seeds bloom somewhat later than usual. For this reason, the seed method is more suitable for species vesicles.
More reliable and effective is the vegetative method of reproduction.
Layers are laid in the spring, at the beginning of the season. The rooting process is completed by winter, but care is needed for future seedlings.
Cuttings give good results. Reproduction requires green young shoots and the implementation of all stages of their rooting. Seedlings obtained by layering and cuttings should be securely covered in the first winter.
Reproduction of the vesicle by dividing the bush is possible in spring, summer and autumn. In the summer, planting should be done as quickly as possible so as not to dry out the root system of the plant.
The success of all methods depends on the quality of the planting material and the thoroughness of further care.
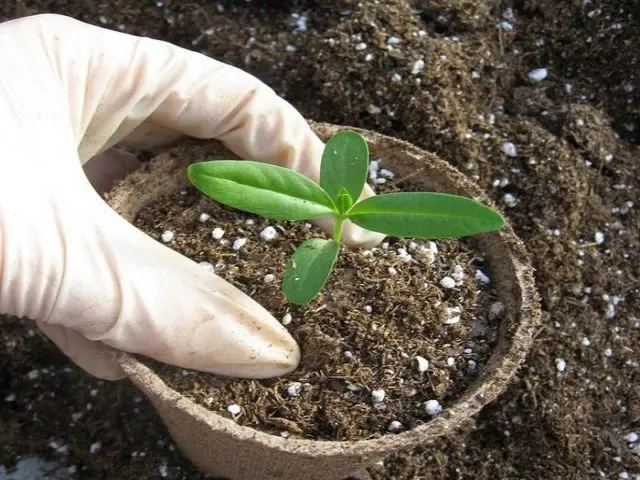

Propagation of the vesicle by seeds
Propagation by seeds is rarely used, more often for non-varietal plants with green foliage. Varietal seeds will produce red leaves only one in five times.
If it is decided to propagate the viburnum vesicle with seeds, the best time for sowing is autumn. In the spring, seed material needs stratification to accelerate germination. To this end, they are placed in the refrigerator for 2 months or in the snow, after placing them in a bag. Sowing in autumn is carried out in open ground to a depth of 3 cm, after which it is covered with a film. In spring, the seeds are placed in containers with light soil at the same depth. After the appearance of three pairs of true leaves, the seedlings dive. Before planting, they should be hardened by taking them out daily to fresh air and gradually increasing the hardening time. It is possible to propagate by seeds with spring sowing directly into the ridges. The seed is laid out on the surface of the soil and lightly mulched with peat or humus. In dry weather, sowing is covered with non-woven material to create a microclimate. After the appearance of shoots of the vesicle, they are thinned out, leaving no more than 1 seedlings per 20 m. For planting in a permanent place in the fall or next spring, neutral or acidic soil in partial shade or a sunny place is needed. The pit for planting the vesicle should be much larger than the earthen coma of the seedling. Peat, compost, leaf humus fall asleep at the bottom. A young plant is placed in the middle and its roots are covered, deepening the root neck by 5 cm. When planting single vesicles, keep a distance of 2 m between the bushes. For a hedge, a distance of 40 cm is enough. Further care of the seedlings consists in cutting and forming a bush, abundant watering ( 40 l under an adult plant twice a week), double feeding (at the beginning of the season and after flowering).
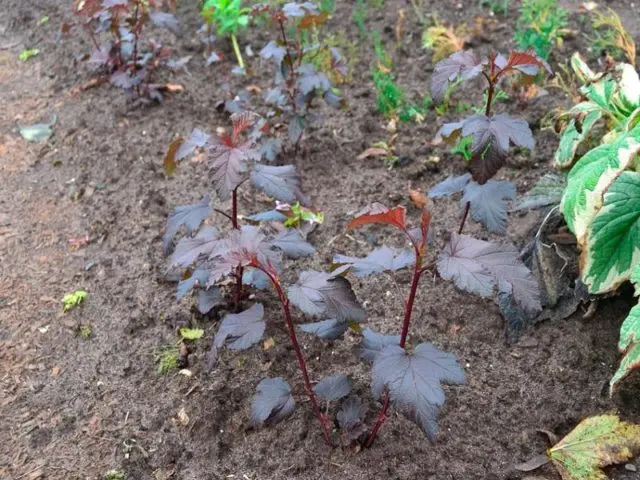

Propagation of the vesicle by cuttings
The method of propagation of the vesicle by cuttings is the most popular of all. Shoots of the current year are taken as planting material. For their preparation use a sharp disinfected knife. The procedure for propagation by cuttings is as follows:
- Cut shoots containing up to 5 buds (2 of them form roots, 3 shoots).
- The prepared cuttings are placed in a solution of a root formation stimulator.
- Prepare a soil mixture of sand and peat.
- Warm it up and moisturize.
- The vesicle cuttings are placed in the ground to a depth of two buds.
- To create favorable conditions and successful reproduction, the entire planting material is covered with a film or each individual cutting is covered with a cut plastic bottle.
- Watering and airing regularly.
- For the winter, the cuttings are carefully covered or transferred to grow indoors.
- In the spring, seedlings are planted in a permanent place.
Reproduction in this way is not difficult. Subject to all the rules, it is easy to get the required number of vesicle seedlings for the garden.
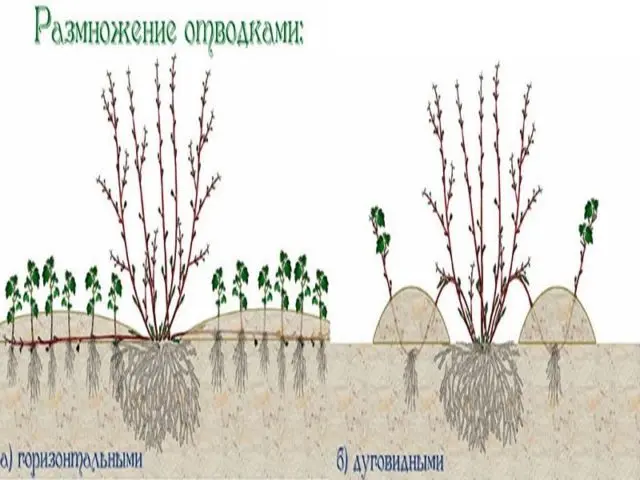
Reproduction of the vesicle by layering
One of the oldest and most proven methods of propagation used by gardeners is layering. It consists in stimulating root formation on the stem of the mother plant – before separation from it. The simplicity of the method consists in the absence of the need to create a microclimate to maintain the viability of the shoots. The method originates from ancient times, when people, observing the reproduction of plants in this way in natural conditions, began to reproduce it, changing and improving the technique. It is necessary to choose the right shoots and soil composition for successful rooting.
Reproduction from an old vesicle bush is difficult if all of its shoots are lignified and young branches are absent. To stimulate the formation of shoots, pruning of old ones is recommended. The ground around the mother plant should be prepared. The growth of the roots is facilitated by moist, loosened, warmed soil, the absence of light at the place of their formation. The best time for propagation by layering is April, after the leaves bloom. Certain steps must be taken:
- Find a young side branch that can reach the ground.
- Remove the leaves from the shoot, leaving 10 cm at the top.
- Under the bush, dig a furrow up to a depth of 15 cm.
- Bend down the shoot of the vesicle and lay the leafless part into the groove.
- Anchor the branch to the ground with wooden or metal studs.
- Give the end of the shoot with leaves a vertical position with a small support (peg or garter).
- Watering and loosening is necessary throughout the season.
- You can separate the plant in autumn or spring.
- In the first winter after rooting, the seedling needs shelter from spruce branches.
After separation from the mother plant, the vesicle is not immediately transplanted to a permanent place, so that it gets used to living autonomously, and its root system has developed to the desired volume.
The method of propagation by layering cannot immediately produce a large number of seedlings, but it is simple and has a guaranteed result.
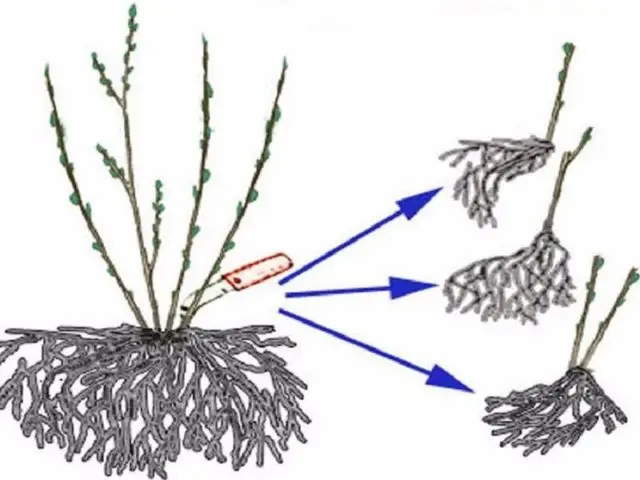
Reproduction of the vesicle by dividing the bush
The method of dividing the bush is not complicated; it does not require special skills from gardeners. It will take quite a lot of physical effort to dig up the plant and divide it into parts. The best time for the procedure is spring, before the development of the kidneys and sap flow. In this way, reproduction of the vesicle is also possible in the fall. The plant easily tolerates division, quickly recovers. But in the summer this should not be done, since there is a high probability of the roots drying out and the death of the ornamental bush.
The method does not give a large number of new plants, which is worth remembering when choosing this method of reproduction. From a lush bush you can get no more than 5 – 6 parts, which are planted as separate ones.
Before dividing, you should take care of preparing planting pits for plants by choosing the appropriate site for the site and preparing a soil mixture of peat and sand.
The division of the vesicle bush is performed according to the scheme:
- First, all branches of the mother plant are pruned at a height of 70 cm from the ground. The procedure will serve as an incentive for the formation of new young shoots.
- The bush is dug out entirely.
- Gently release the fibrous roots from the ground.
- The vesicle is divided into several parts so that each has a good rhizome and healthy branches.
- The separated parts are treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate to disinfect them.
- Place the parts in the landing pits.
- Sprinkle with soil.
- Tamp the soil a little.
- Deepen the root neck 5 cm into the ground.
- After abundantly watered.
- The soil is mulched with peat.
- If the bushes remain weak by winter, they need shelter.
When propagating by dividing the bush, a sense of proportion is required. You can not divide the mother plant into too small parts. They may stagnate and die. As a result, the number of ornamental bushes will not only not increase, but the existing vesicle bush will be destroyed.
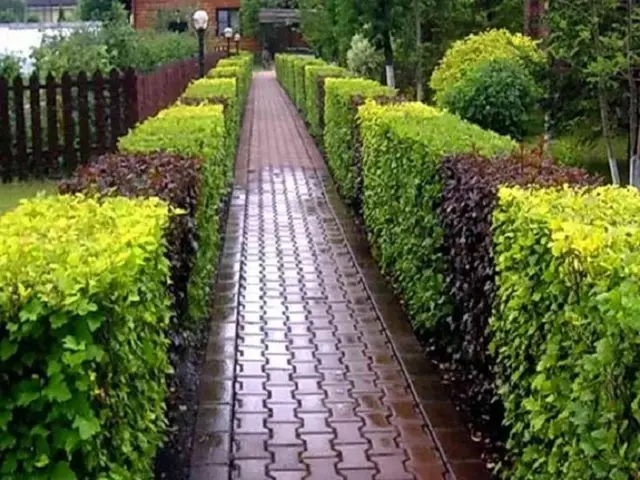

Conclusion
It is not difficult to propagate the vesicle in one of four ways. Each gardener can choose the most suitable, according to their capabilities and goals. The high decorativeness of the foliage and flowers of the shrub allows you to decorate any area with it. Unpretentiousness, vitality, the possibility of rapid reproduction make the vesicle one of the most popular decorative species used for landscaping. It easily tolerates a haircut, if desired, you can achieve any shape, which is often used to frame garden paths and alleys.









