Contents
Currant is one of the few berry bushes that can be propagated by cuttings at any time of the year. In many ways, this quality contributed to its wide distribution in our country. Propagating currants with cuttings in summer or spring is quite simple if you follow certain rules.
Features of propagation of currant cuttings in spring and summer
Cutting currants in spring and summer is one of the vegetative ways of propagating this plant. It is widely used not only for berry bushes, but also for fruit trees. For propagation of currants, annual shoots are best suited.
When to cut currants
In winter and early spring, lignified cuttings are used to propagate blackcurrants. These are parts of annual shoots cut in autumn. In spring and summer, namely from May to July, currants can be propagated using the so-called “green” cuttings. They are non-lignified shoots of the current year, or rather their flexible tops, which have a bright green color. For propagation of currants by cuttings in summer, the most leafy endings of shoots with a length of at least 10 cm are chosen.
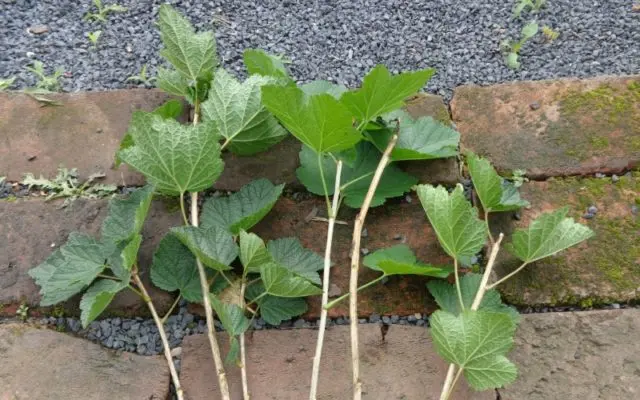

At the end of summer, semi-lignified stem cuttings are used to propagate currants. These are parts of the shoots of the current year, on which the bark has already formed. Semi-lignified cuttings are light brown in color and do not have much flexibility.
Rules for cutting cuttings
Currant cuttings for propagation are harvested in cool weather, usually in the early morning. For work, you will need scissors or pruners. Non-lignified green cuttings are cut relatively easily and do not require significant effort. For cuttings of currants in spring and summer, well-bearing young bushes are chosen that do not have signs of disease and are not affected by pests. The cut parts of the plant are immediately wrapped in wet burlap, preventing them from drying out. After harvesting a sufficient amount of material for propagation, they proceed to the direct cutting of the cuttings.
For cutting cuttings for propagation of black or red currants in the summer, it is most convenient to use the same scissors or a sharp clerical knife. Cut shoots are divided into parts 12-15 cm long with an oblique cut so that each cutting contains 3-4 internodes. 2-3 leaves are left in the upper part, if the lower sheet is more than 6 cm, it is cut off with scissors in half to reduce the evaporation of moisture from the leaf plate. Leaves are completely removed from the bottom of the cutting. Finished cuttings, if necessary, are sorted into varieties and tied into bundles with twine or elastic.
How to propagate currant cuttings in spring and summer
Having prepared currant cuttings for propagation, you can immediately begin to root them. To form your own root system, you can first use water or immediately plant them in a nutrient substrate or prepared soil.
Reproduction of currant cuttings in the spring in the water
The formation of the root system of cuttings in water allows you to visually follow the entire rooting process. The method is extremely simple and effective. In early spring, cuttings harvested from autumn are placed several pieces in containers with water in such a way that 2 lower internodes are submerged. After 1-1,5 weeks, the growth of the root lobe will become noticeable, tubercles will appear in place of future roots. After that, the cuttings are moved to individual larger containers, making sure that the roots are always in the water. As the root lobe grows, leaves will begin to bloom on the handle, but if flowers appear, then they must be cut off.

The whole process of forming your own root system in water can take from 1,5 to 2 months. All this time, you need to regularly monitor the water level in containers with cuttings, updating it from time to time. Sprouted cuttings are planted in open ground in a permanent place, usually in May, after the soil has warmed up sufficiently.
How to root currant cuttings in the substrate
In addition to the water method, blackcurrants can be planted with cuttings in a special substrate. In this case, the root system is formed in a loose, moisture-absorbing material that retains water well and at the same time has good air permeability, which is important for root development. The substrate can be:
- moss-sphagnum;
- perlite;
- peat;
- river sand;
- coconut fiber;
- small sawdust.
To root the cuttings, the planting container is filled with a substrate – a wide, shallow container that can be covered with a transparent material, glass or film. The lower part of the cutting with a cut is treated with Kornevin or any other root growth stimulator, and then planted in a container with a substrate at an angle of 45 °, deepening by 8-10 cm. The distance between adjacent cuttings should be about 10 cm, too frequent planting can adversely affect root system growth.
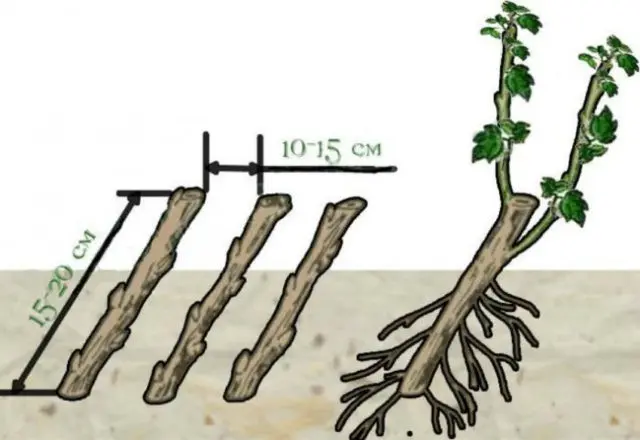
After planting, the container with the cuttings is covered with a film or any transparent material, simulating greenhouse conditions, and placed in a well-lit place. At the same time, direct sunlight on seedlings should be avoided. The whole process of rooting currant cuttings in the substrate can take 3-4 weeks. All this time, the substrate needs to be moistened, gradually reducing the frequency of watering from 5-6 times a day in the first week to 2-3 times in the last. Seedlings should be monitored regularly. If the buds turn black and dry, then the cutting has not taken root and must be removed.
How to plant currants in spring with cuttings in open ground
Currant is good because the rooting of its cuttings is very good. Therefore, some gardeners, when propagating it, do not use the intermediate formation of the root system of the future seedling in water or substrate, but immediately plant currant cuttings in open ground. In this case, rooting will be slower, the probability of rooting cuttings will decrease, and in case of a successful result, the start of fruiting will be postponed for a year. Therefore, it is more expedient to use already germinated cuttings for propagation. They are transplanted into open ground in May, when there is no threat of return frosts.
For planting, it is necessary to prepare the soil in advance, dig it up and fertilize it by applying organic and mineral fertilizers. The first year in open ground, seedlings grow, so they are usually planted in rows, in special shallow grooves, at a distance of 0,25 m from each other. In autumn, the condition of seedlings is visually assessed. If they are healthy, strong and well developed, then they are transplanted to a permanent place. Weak specimens are left for the winter. Such seedlings are transferred to a permanent place only next spring, since immature plants may not withstand the stress of transplanting, take root insufficiently and die in winter.
How to care for cuttings after planting
After planting in open ground, young seedlings require increased attention. If nighttime temperatures drop drastically, it is necessary to provide shelter for protection, at least for the first time. It is best to use a greenhouse or greenhouse to grow cuttings, but not all gardeners have the opportunity to use these facilities for a crop such as currants. Therefore, to protect against low night temperatures, a film, covering material is used. Often, planted cuttings are covered with cut plastic transparent containers from drinking water.

At first, the seedlings need to be shaded, avoiding direct sunlight on them. It is regularly required to moisten the soil, the trunk circles need to be cleaned of weeds and mulched.
Transfer to a permanent place
For planting currants on a personal plot, you need to choose places illuminated by diffused sunlight. Sites along fences, areas in the immediate vicinity of buildings and structures, and places near large fruit trees are well suited in this capacity. The site should not be low-lying or swampy, if groundwater approaches the surface closer than 1 m, then it is necessary to artificially increase the height of the soil at the site of the future planting.
The soil is dug up in advance, removing weeds, stones, and other debris. At the same time, fertilizers are applied to the soil. Compost and rotted manure are best suited for this purpose, while a small amount of phosphorus and potassium additives can be added at the same time. Currant prefers to grow on soils with neutral acidity. However, not all soils have such pH characteristics. If the acidity of the soil exceeds the permissible values, then slaked lime, chalk or dolomite flour are additionally included in the fertilizer composition.

A seedling is transplanted to a permanent place in early spring, before the start of the vegetation processes in the plant, or in early autumn. The second option is considered more preferable, however, in regions with an early onset of winter, it is unacceptable. From the moment of planting to the onset of frost, at least 2 months must pass, otherwise there is a very high risk that the plant will not be able to adapt to a new place and will die in winter. In other regions, it is better to plant currants in the fall, since this shrub enters the growing season very early, which means that there is a high risk of being late with the deadlines, which will greatly delay the rehabilitation process in a new place.
It is better to dig a planting hole for a currant seedling in advance, 2-3 weeks before the expected time of work. Its size must be guaranteed to accommodate the entire root system of the transplanted bush. The standard size of the landing pit is 0,5 m in diameter. The depth should not be more than 0,5 m, since the currant root system has a surface structure. The soil taken out of the pit is mixed with humus, for additional nutrition, superphosphate and potassium sulfate are added to its composition. If the soil is clayey, river sand is added to the composition of the soil.
For planting, it is better to choose a cloudy, but warm day. At the bottom of the planting hole, a small mound of nutrient soil is poured. The seedling is planted at an angle of 30-45 ° to the surface, while its direction does not matter. This method of planting stimulates the growth of a large number of lateral roots, the plant adapts faster and produces a large number of root shoots. However, if it is planned to grow currants in a standard form, then the seedling is installed in a pit strictly vertically. Gradually, the root system is covered with nutrient soil, periodically watered and compacted to prevent the formation of voids. After all work, the root neck should be 5-6 cm below the soil surface.
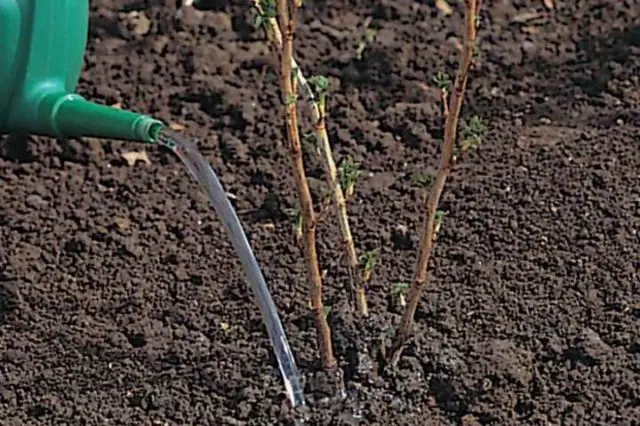

After the planting hole is completely filled with soil, an annular groove is formed around the seedling and abundant watering is carried out (usually 2 buckets for each bush). Then the soil in the root zone is mulched with peat, compost, tree bark. This measure retains moisture in the soil and prevents the growth of weeds.
Conclusion
To propagate currant cuttings in summer or spring, you do not need to make significant efforts. Working with this shrub is very simple, it is unpretentious and often forgives the gardener many mistakes. Currant cuttings are a great way to propagate them, applicable in spring, summer and even winter. When using it, you can get any amount of planting material in a short time. This is especially true for economical gardeners, as well as for those who grow currants on an industrial scale.









