Contents
The main symptom of this disease is contained in the very name of the pathology – with replacement hydrocephalus, the substance of the brain gradually loses its volume and is replaced by cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid). Hydrocephalus, or dropsy of the brain, is an excessive production or violation of the movement and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid by various structures of the ventricles and subarachnoid space. Most often, replacement hydrocephalus affects elderly patients. The disease requires mandatory complex treatment.
Causes of the disease
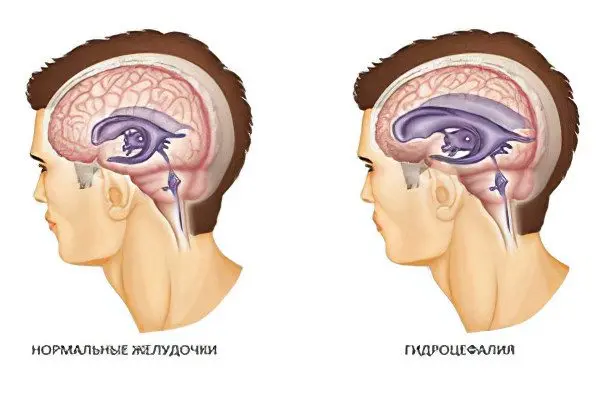
The pathology is based on an imbalance between the production and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid, or the formation of an anatomical obstacle along the CSF circulation path.
Factors that trigger the pathological process:
Inflammatory process in the tissues of the brain, as a result of neuroinfection (neurosyphilis, herpes, toxoplasmosis, rubella);
Pathologies of the vessels of the cerebral circulation system (aortic aneurysm, atherosclerosis);
Cyst in brain structures;
Arterial hypertension;
Alcoholism;
Helminths parasitizing in brain tissues;
Craniocerebral injury.
A small proportion of the causes of pathology is occupied by unexplained factors.
Classification of forms of replacement hydrocephalus

Manifestations of the disease occur in several forms:
External replacement hydrocephalus is a classic variant of the development of the disease, the main symptom of which is a decrease in brain volume, filling the vacated space with cerebrospinal fluid;
Internal replacement hydrocephalus – most of the cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the ventricles of the brain, where it is actively produced by the choroid plexuses of blood vessels;
Mixed replacement hydrocephalus – the cerebrospinal fluid overflows not only the ventricles, but also the subarachnoid space between the membranes of the brain.
Each form of hydrocephalus replacement proceeds with characteristic symptoms. It is not compensated on its own, over time, the symptoms of cerebrovascular accidents necessarily increase, therefore, at the first symptoms, a consultation with a neurologist or neurosurgeon is required.
Symptoms and manifestations

Any form of hydrocephalus shows its most striking symptoms as a violation of the functioning of the central nervous system. Most of the signs of this pathology are associated with an increase in intracranial pressure.
Possible manifestations of replacement hydrocephalus:
Severe headache in the morning after waking up, caused by a long-term horizontal position of the body;
Nausea and vomiting;
Jumps in blood pressure;
Tachycardia, arrhythmia;
Lethargy and drowsiness during the day, insomnia at night;
Increased fatigue, slowing down the pace of doing the usual things;
Irritability;
Decreased visual acuity;
Loss of coordination, unsteady gait.
In the later stages of the disease, symptoms of dementia appear – memory lapses, absent-mindedness, impaired short-term memory, inability to manipulate numbers, perform analysis and synthesis operations, and think logically. The epileptic syndrome becomes a severe complication of hydrocephalus replacement. The patient develops dementia, he can fall into a coma.
How is replacement hydrocephalus diagnosed?
It is difficult even for an experienced doctor to make an accurate diagnosis of this disease based on the patient’s complaints and visual signs.
For a complete examination, the following methods are used:
Magnetic resonance therapy (MRI) is the most informative study that allows you to see the enlarged cavities of the ventricles of the brain, atrophic changes in its tissues, an increased volume of cerebrospinal fluid;
Angiography – X-ray examination of the vessels of the brain;
USG of the brain;
X-ray skull;
Ophthalmoscopy of the fundus;
Carrying out a PCR reaction for the determination of antibodies to the pathogens of herpes, toxoplasmosis, rubella, syphilis in the blood if an infectious cause of the disease is suspected.
If replacement hydrocephalus occurs in a moderate form with minimal symptoms, an examination should be carried out every 6 months to timely detect the negative dynamics of the disease. With severe symptoms of increased intracranial pressure, treatment should be started immediately.
Treatment of replacement hydrocephalus

The choice of treatment tactics depends on the severity of the symptoms of the disease and the degree of brain atrophy. Most often, conservative treatment is used, although with a complicated course, surgical intervention is possible.
The main directions of drug therapy in moderate form:
Improvement of cerebral circulation;
Decreased intracranial pressure;
Improving the general condition of the body.
Treatment methods for replacement hydrocephalus:
Physiotherapy;
Taking nootropics;
Taking diuretics to reduce the volume of cerebrospinal fluid, in combination with potassium and magnesium preparations;
Massage of the temples and collar zone;
The use of therapeutic baths;
Diet using foods rich in trace elements (lettuce, spinach, nuts, bananas, dark chocolate).
Surgical treatment for replacement hydrocephalus is rarely performed, only with a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition.
To facilitate the patient’s well-being, the neurosurgeon performs a bypass operation – the installation of an artificial CSF flow path. The cavity of the ventricles is connected by a shunt to another cavity of the human body, which has the ability to absorb the excreted cerebrospinal fluid.
Most often, the shunt is brought into the abdominal cavity. Once the intracranial pressure is higher than normal, the shunt valve can be opened and some of the fluid drained from the ventricles. The components of the bypass system need to be updated from time to time, because the life of the patient depends on its trouble-free operation.
Another option for surgical intervention is endoscopic ventriculostomy, when an excess volume of cerebrospinal fluid is removed through artificially created holes at the bottom of the ventricles of the brain.
Treatment of replacement hydrocephalus is carried out in a complex manner, in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient.
Prevention

In order not to experience the symptoms of a disease that threatens with serious consequences, you must adhere to the following rules:
Avoid infections, the complications of which lead to brain damage;
Timely treat arterial hypertension;
Avoid increased intracranial pressure;
Do not abuse alcohol, avoid exposure to neurotoxins.
Unfortunately, it is still impossible to avoid age-related changes at the present stage of development of medicine. The prognosis of replacement hydrocephalus, not related to age, is quite good – with timely treatment, the condition of patients improves markedly.









