Contents
Red moles – These are neoplasms of a benign nature, growing from blood vessels. Red moles are also called hemangiomas.
According to statistics, red moles occur most often in childhood. They are somewhat less common in the adult population.
Until now, scientists have not decided whether hemangioma should be considered a vascular tumor, or a pathology of a congenital nature. However, recent data indicate that red moles are the result of an overgrowth of the vascular endothelium, which makes it possible to consider hemangiomas as vascular tumors.
What is a red mole?
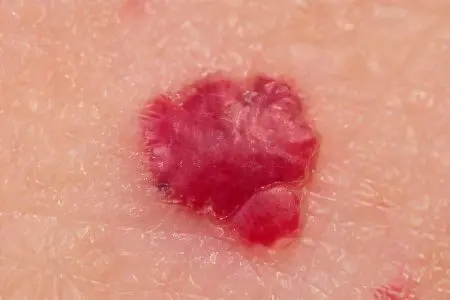
The mole has a red color, as it is an overgrown vascular tissue, inside of which there is blood. While ordinary moles are a skin neoplasm, a red mole is represented by a vessel that has come to the surface of the body. In this case, the hemangioma can be single, or it can be multiple. If the process is expressed to a large extent, then the moles merge and form a burgundy or blue spot.
Prevalence and localization
According to available statistics, hemangiomas are detected immediately after the birth of the child. This happens in 87% of cases. Girls are at risk, they account for about 70% of all diagnosed red moles. By the way, it is hemangiomas that account for up to 48% of all soft tissue formations that are detected in childhood.
A red mole can be found in any part of the body, but 80% of all such defects are localized in the upper body. It is also possible to detect hemangiomas, although extremely rarely, on the bones, in the brain, lungs, and liver.
95% of all hemangiomas are simple formations;
3% – cavernous formations;
2% – formations of a mixed type.
Causes of red moles
The reasons for the development of hemangiomas have not yet been precisely established. It is not known why they appear most in the face area. Scientists attribute this to the fact that it is here that there is an abundant vascular network.
Childhood
Researchers agree that red moles are the result of a pathology in the formation of vascular tissue, which occurs due to disturbances in the development of the fetus.
Vascular tissue passes through all parts of the fetal body along a chain of pericytic cells at the time of organ laying. Pericytic cells with a lack of oxygen to any organ or tissue of the fetus quickly respond to hypoxia and try to eliminate it. To do this, with the help of the production of special proteins, they attract a large number of pericyte cells to the problem area. Cells begin to form new areas of blood supply, eliminating the existing hypoxia. Sometimes, due to the imperfection of the mechanism, the reproduction of specific proteins does not stop even when oxygen starvation has already been eliminated. As a result, the vascular tissue continues to grow, forming a hemangioma.
Red moles are also called vascular hyperplasia, which indicates that they are the result of a violation of the growth process of vascular tissue. It is rather problematic to answer the question of how this happens, since it is necessary to carefully monitor how the intrauterine development of fetal tissues occurs. And there are only data that are obtained from the results of the study of stillborn babies or aborted fetuses.
Adult patients
The appearance of red moles in adulthood is due to hormonal disruptions in the human body. Often this happens during gestation, during menopause, while taking drugs with hormones, when using oral contraceptives, due to pathologies of the endocrine system.
It is possible that viral infections, ultraviolet rays, radiation, chemical agents can provoke the growth of hemangioma.
A lack of ascorbic acid can affect the state of the vascular tissue.
If the capillaries are regularly damaged, then this can provoke the appearance of hemangiomas.
Vascular hyperplasia may indicate diseases of the internal organs, however, the location of red moles does not indicate a problem in the area where there is their maximum accumulation.
Red moles in newborns
During the period of newborn and infancy, red moles in children are very noticeable, but often by the age of 5 they disappear.
Such benign tumors do not pose a danger if they:
Do not itch, do not hurt, do not cause any concern;
They do not become larger, for example, they do not increase in size by 3 times or more in a few months;
Not located under the eye, on the nose, on the face or on the genitals.
It is known that hemangiomas can grow rapidly along the periphery, this is especially true for the first months of a child’s life. Therefore, in 10-12% of cases they are removed, as there are indications for this. The fact is that as it grows, the mole will destroy nearby tissues, provoking defects not only cosmetic, but also functional. This is relevant in the case when hemangiomas are located on the ears, under the eyes, etc. The normal functioning of the organs becomes impossible due to compression by the overgrown formation.
Features of red moles in adults
Red moles, as primary formations, do not occur in adulthood. They arise from previously unidentified vascular proliferations. Most often, they are treated even before the child enters school, so if a hemangioma is present in adulthood, this means that it has either not been treated, or the tumor is located on the internal organs.
The most dangerous location of the red mole is considered to be the body of the vertebra. As the tumor grows, weakening of the structures of the spine will occur, which contributes to the occurrence of fractures.
Classification of red moles
Morphology of hemangiomas
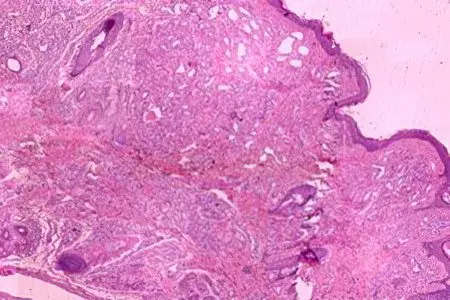
Red moles can be capillary and cavernous. Capillary hemangiomas are represented by layers or a group of vessels that are closely pressed against each other. Each of the vessels has a wall of a membrane, one or more layers of cells similar in structure to epithelial cells. The lumens of these small fused vessels are filled with blood cells. Sometimes fused capillaries form lobules separated by a thin stroma.
As for cavernous moles, they are formed by cavities of different sizes and shapes. The cavities are represented by a layer of endothelial cells, which in their structure resembles the endothelium of capillaries. Possible rupture of the septum of the cavity and the formation of papillae in the resulting lumen.
Location of red moles
On the surface of the skin are simple hemangiomas.
Under the skin are cavernous or cavernous hemangiomas.
The skin and subcutaneous parts have combined hemangiomas.
Mixed moles contain elements of other tissues, such as nervous or connective. These are such hemangiomas as angiofibromas, gemlymphangiomas, etc.
Origin of red moles
Acquired moles are those that appear during a person’s life. However, they can have exclusively percutaneous localization. Complex forms of hemangiomas cannot be acquired. Often they are found during surgery, they are present in the human body from birth, but have not been diagnosed.
Congenital red moles are found either during the neonatal period or in infancy.
The course of pathology
Simple moles do not pose a threat in terms of disruption of the functioning of certain organs.
In turn, complex moles can affect the following organs and systems:
On the organs of vision, on the brain, on the ears;
On the vertebrae, while it is difficult to remove such formations, since they are located in hard-to-reach places;
On large vessels, or on vascular nodes.
Features of red moles
Hemangiomas are somewhat different from other formations. Features of red moles are as follows:
The first 90 days after the birth of the child will be characterized by the accelerated growth of the mole;
In premature babies, hemangiomas grow 2 or 3 times faster than in babies who appeared on time;
Small red moles in the first five years of a child’s life may disappear on their own;
Only simple hemangiomas are capable of spontaneous elimination, other forms of moles require intervention;
What will happen to the mole in the future after its regression or after growth stops is impossible to predict.
Symptoms of red moles
Simple mole. A simple red mole most often looks like a red spot, the sizes can be different. The spot rises slightly above the skin. If you press on the formation from the edge, while capturing a healthy area of u4bu2bthe skin, then the mole will become lighter and smaller. When the pressure stops, the shape, color and size return to their original state. In the first 3 months after birth, the mole will grow along the periphery. You can understand this if you make a stencil on paper and apply it again after XNUMX-XNUMX weeks.
Cavernous hemangioma. A cavernous red mole is located under the skin. The skin above it remains unchanged. A mole can be in a capsule and without it. If there is no capsule, then the boundaries of the formation will not be clear. The color of the mole is blue, it is possible for the blood vessels that feed the mole to show through the skin. Just like a simple hemangioma, the cavernous formation becomes smaller when pressure is applied to it. Sometimes the skin that is located above the mole has a higher temperature. Education does not pulsate. When probing, you can feel the lobules of which it consists. Cavernous formations on the neck, near the ears, on the head are dangerous, as they grow rapidly and are able to penetrate into nearby tissues.
Combined hemangioma. The combined red mole has both a subcutaneous and a supracutaneous part. At the same time, the part that is located under the skin is most often larger compared to the supracutaneous part.
Mixed red mole. A mixed formation has elements not only of the vascular, but also of other tissues – lymphoid, nervous, connective.
Spontaneous problem resolution
Independently, red moles pass if they are superficial or simple. This is possible in no more than 15% of cases. Most often, formations that are localized on closed parts of the body regress.
At first, the tumor becomes not so bright, decreases in size. Six months later, the mole becomes a pale pink spot, located at the level of the skin. In this case, the skin above it atrophies. After another 3-4 years, only a small depigmented area remains on the skin.
Complications
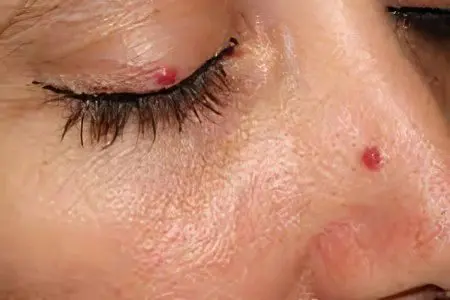
Hemangiomas (red moles) can disrupt the functioning of the organs that are located next to them. This is especially dangerous if they grow in the liver, near the eyes, in the brain.
Perhaps inflammation and the appearance of ulcers on the mole. As the pathological process fades, the spontaneous disappearance of the mole is not excluded.
Bleeding from a mole as a result of trauma. Bleeding is dangerous in the presence of a large mole, if it is a cavernous or combined formation localized on the internal organs.
Infection.
Diagnostics
If the red mole is located on the surface of the skin, then an examination and histological examination is sufficient.
If there is a suspicion of the presence of hemangiomas with a different localization, then angiography and radiography are indicated.
Treatment of red moles
The need to treat red moles is determined by the location and type of hemangiomas. If the formation does not affect the functioning of the organs, does not bleed and does not increase in size, then therapy can be abandoned. Hemangiomas cannot be malignantly reborn.
If hemangiomas are large, located deep, then the doctor offers either conservative or surgical treatment. A combination of these two methods is possible.
Treatment of simple red moles. The cryodestruction method is used to remove small, simple red moles. It is possible to apply crystalline carbon dioxide to the formation for 15 minutes, or to remove the mole by hardware. Treatment is highly effective (up to 96%).
Another method of getting rid of red moles is laser destruction. In this case, the skin is practically not damaged. In this way, you can get rid of both superficial and deep moles. Complications from this procedure are minimal.
Cavernous red moles. The sclerosing method of treatment is indicated for the location of moles on the cheeks, nose, forehead and bridge of the nose. To do this, drugs are injected directly into the mole that contribute to its death with the subsequent formation of a scar, or without it. Cavernous moles are removed surgically if they are located on closed areas of the body.
Combined red moles. In the event that such neoplasms are located on closed areas of the body, they are removed surgically, performing a radical excision. Most often, this operation does not give complications and leads to minimal defects on the skin.
Microwave cryodestruction is considered the best method of getting rid of combined red moles when they are located on the face or on open parts of the body. First, the tumor is affected by an electromagnetic field, and then the cryodestruction procedure is performed. As a result, the formation will be destroyed, but the epithelial cells will not lose their ability to recover.
It is possible to use the following mole removal methods: hormonal therapy, radiation therapy with Buki rays, sclerotherapy.
Deep large red moles located in dangerous places. If the mole grows, is located on the neck, near the ears and on the head, is prone to bleeding and inflammation, then it will not be possible to get rid of it using the above methods.
To remove such formations, embolization of the supply vessel with a hydrogel is carried out with preliminary angiography. This helps to reduce the tumor in size, as its blood supply is disturbed. After that, it will be possible to carry out the procedure of cryodestruction of the mole. The remaining cosmetic defect is leveled with the help of plastic surgery.









