Contents
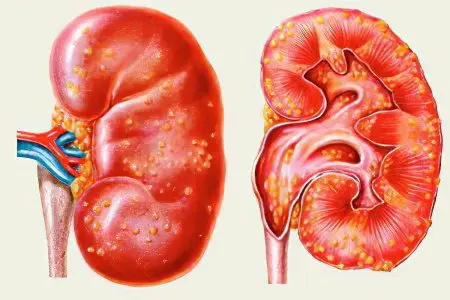
Pyelonephritis is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the kidneys. The disease develops as a result of the spread of pathogenic microorganisms penetrating the kidneys from the lower parts of the urinary system. The most common cause of pyelonephritis is Escherichia coli – E. Coli. It is found when performing a urine test in sick women in large numbers. Less commonly, the causative agents of the disease are other gram-negative bacteria, staphylococci and enterococci. In 20% of cases, pyelonephritis occurs as a result of a mixed infection.
Pyelonephritis is a serious disease characterized by a severe course. Patients suffer from severe pain, general well-being is disturbed. Experts are unanimous in the opinion that the disease is much easier to prevent than to get rid of it.
Pyelonephritis refers to infections of the urinary system. If pathogenic bacteria capture its lower sections, and antibiotic therapy is selected incorrectly or is completely absent, then microorganisms begin to multiply rapidly with spread to the kidneys. This leads to the symptoms of pyelonephritis. The nephrologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Facts and statistics about pyelonephritis
It has been established that female representatives suffer from pyelonephritis more often than men by 5 times. The acute form of the disease is diagnosed more often in women of reproductive age who have an active sex life.
In the United States of America, 1 out of 7000 people gets sick every year. 192 patients need and receive this care every year.
With adequate treatment, up to 95% of all patients notice a significant improvement in the first two days.
Pyelonephritis affects children, both girls (in 3% of cases) and boys (in 1% of cases). In childhood, the disease is dangerous for its complications. Thus, cicatricial changes in the kidney parenchyma are diagnosed in 17% of children who have been ill, hypertension in 10-20% of children.
Abundant fluid intake is an essential condition for the treatment of the disease. For drinking, it is necessary to use clean water, which normalizes the balance in the body, thins the blood, promotes the speedy removal of pathogenic microorganisms and toxic products of their vital activity. The effect is achieved by increasing the number of urination as a result of heavy drinking.
You should not refuse to drink plenty of water because of pain during bladder emptying, as this is the only way to remove bacteria from the body. You should urinate as often as possible so that there is no such serious complication as blood poisoning, as a result of which a person may die.
Alcoholic drinks, coffee, carbonated water – all this is prohibited in pyelonephritis. It is believed that cranberry juice can help in the fight against the disease. It is consumed in its pure form, or diluted with water.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis
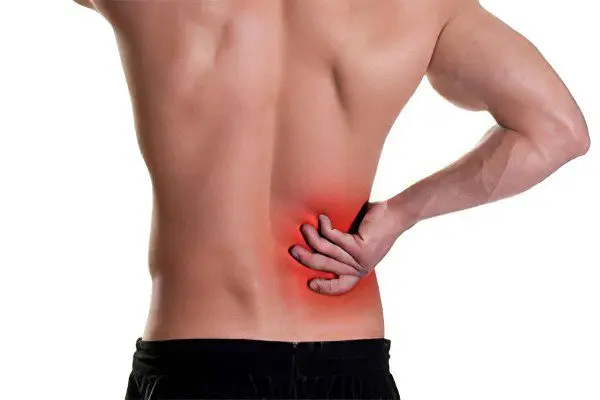
Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis are as follows:
The occurrence of a feeling of nausea, which may be accompanied by vomiting.
High body temperature with chills. Sweating increases, appetite disappears, headaches occur.
Increased fatigue, malaise and weakness.
Painful sensations with localization in the side from which the kidney is damaged. Pain can also be girdle in nature with predominant localization in the lower back. “Spillage” of pain occurs with a bilateral inflammatory process. An exacerbation of the disease is characterized by Pasternatsky’s symptom, which boils down to the appearance of pain when tapping in the lumbar region and, for a short time, an increase in erythrocyturia. When changing the position of the body, the intensity of pain does not change, but they increase during deep breathing and palpation of the abdomen.
An increase in the number of urination, regardless of the sex of the patient.
Slight swelling.
Laboratory tests of urine and blood indicate inflammation. Pathogenic bacteria and leukocytes are found in the urine.
If pyelonephritis is purulent, then the body temperature can manifest itself abruptly – rise to high values and fall to subfebrile levels several times a day. Most often, the fever lasts for a week.
Bacteriemic shock is typical for 10% of patients.
There are also non-specific symptoms for acute pyelonephritis that may indicate the disease:
An increase in body temperature to high values, up to the development of a feverish state.
Tachycardia.
Dehydration of the body.
If the disease has become chronic (which often occurs with an untreated acute stage of the disease, although sometimes chronicization of the process without a previous exacerbation is possible), then the symptoms of pyelonephritis may be less pronounced, but they persist for a long time period. When donating blood for analysis, signs of inflammation may not be detected. Leukocytes are present in the urine, but the bacterial component may be absent. When remission of pyelonephritis occurs, then all laboratory parameters will be normal.
In addition, every third patient notes the following symptoms (characteristic of inflammation of the lower urinary system):
Pain during emptying of the bladder of the type of pain.
The presence of blood impurities in the urine.
Constant desire to empty the bladder even when it is not full.
Darkening of urine, the presence of turbidity in it, the presence of an unpleasant fishy smell.
Causes of pyelonephritis
Ascending entry of bacteria into the kidneys
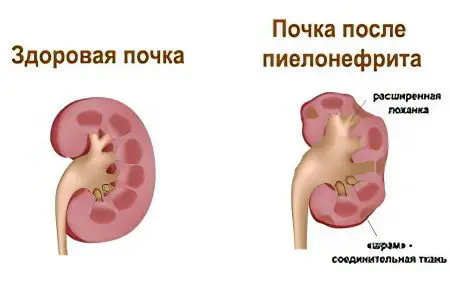
The development of the disease is provoked by bacteria. They, through the urethra, enter the urinary system and inseminate the bladder. If the infection is not eliminated, then gradually it will rise higher and higher, capturing the organs located in its path and eventually affecting the kidneys. In 90% of cases, the disease occurs due to the penetration of Escherichia coli into the bladder. She, having begun her vital activity in the intestines, penetrates into the urethra from the anus. Most often this happens during the emptying process. Due to the fact that the urethra and anus in women are located nearby, and the main source of infection is Escherichia coli, they suffer from pyelonephritis much more often.
In addition, the urethra in women is short, and the anatomy of the external genital organs is such that it is not difficult for E. coli to penetrate the bladder and then the kidneys. Therefore, the ascending route of infection is the most common cause of infection, resulting in acute pyelonephritis.
However, not always only E. coli leads to inflammation of the kidneys.
Other causes of pyelonephritis include:
Staphylococcus;
Enterococci;
Mycotic microorganisms;
Pseudomonas;
Klebsiella;
Proteus;
Enterobacter.
Vesiculourethral reflux (vesicoureteral reflux)
This pathology is characterized by the fact that from the bladder, urine flows back into the ureters and is partially thrown into the renal pelvis. When the disease remains undetected at an early stage, it leads to regular stagnation of urine, reflux and reproduction of pathogenic agents in the tissues of the kidney, which leads to an inflammatory process.
The more exacerbations of pyelonephritis the child suffers, the more the structure of the kidneys is disturbed. As a result, normal tissue is replaced by scar tissue and the organ is unable to perform its functions in the same volume. This development of the disease is typical mainly for young children who have not reached the age of five. However, scarring of kidney tissues is also possible in adolescence against the background of the disease.
It is children’s kidneys that are more prone to scarring, since:
Backflow or reflux in childhood occurs under less pressure than in adults.
The immune system of children is more vulnerable to the pathogenic influence of bacterial agents than in adulthood. This is especially true for children under one year old.
Pyelonephritis is more difficult to detect at a younger age, especially in infancy.
Vesico-dream reflux is found in most children under six years of age suffering from pyelonephritis (from 20 to 50% of all patients), while in adults this pathology is diagnosed only in 4% of cases.
Pyelonephritis, transferred at an early age, leads to irreversible changes in the tissues of the kidneys. So of all patients on hemodialysis, 12% were sick with acute pyelonephritis in childhood.
As for other causes of pyelonephritis, they are of low prevalence. It is possible for the pathogen to penetrate not from the bladder, but through the blood flow from other organs.
The possibility of developing the disease increases against the background of urolithiasis, when the ureter is blocked by a stone. As a result, urine is not excreted in full, it stagnates, which is a favorable environment for the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. (Read also: Urolithiasis – causes and symptoms)
Risk Factors
There are risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease, among them:
Deposition of stones in the kidneys in nephrolithiasis.
Pathologies of the development of the organs of the urinary system of a congenital nature.
Changes in the urinary system due to age.
Neurogenic dysfunction of the bladder, which is observed in diabetes mellitus. This condition requires re-insertion of the catheter, which increases the risk of developing the disease.
Spinal cord injury as a result of trauma.
AIDS.
The period of bearing a child, which can lead to a decrease in tone and a decrease in ureteral perylstatics. This is due to their compression by the growing uterus, with polyhydramnios, with a narrow pelvis, with a large fetus, or against the background of existing insufficiency of the vesicoureteral valves.
Full or partial displacement of the uterus outside the vagina.
The introduction of a catheter into the bladder, which leads to its obstruction.
Pathology of the prostate gland in men.
Sexual activity of a young woman. During intercourse, the muscles of the urogenital diaphragm contract as a result of massaging the urethra, which increases the risk of infection along the ascending pathway.
Operations on the organs of the urinary system.
Diagnosis of pyelonephritis

Diagnosis in a typical case is not difficult. The patient’s complaints about pain in the lumbar region, intoxication syndrome become the basis for taking tests and undergoing an instrumental examination, which makes it possible to diagnose pyelonephritis.
Instrumental research is reduced to:
Ultrasound of the kidneys, which allows you to detect the presence of stones in them, provides information about the size of the organs, about changes in their density. In the chronic course of the disease, the echogenicity of the parenchyma increases, and in the acute course it decreases unevenly.
CT makes it possible to assess not only the density of the parenchyma, but also the state of the perirenal tissue, vascular pedicle and pelvis.
Excretory urography provides information about the limitation of the mobility of the affected kidney, the tone of the urinary tract, the condition of the calyces, etc.
Cystography is performed to detect intravesical obstruction and vesicoureteral reflux.
Angiography of the arteries of the kidneys is used more often with the already diagnosed chronic pyelonephritis, since this method is not routine for detecting the acute stage of the disease.
Women should definitely undergo a gynecological examination.
What tests are given for pyelonephritis?
With pyelonephritis, it is necessary to pass the following tests:
Oak
OAM.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko.
Trial of Zimnicko.
Bacteriological examination of urine.
It is possible to perform a prednisolone test, which allows you to identify the latent course of the disease. Why is a special drug (Prednisolone with Sodium chloride) administered intravenously, after which, after an hour, after two and after three hours, and then, after a day, urine is collected and analyzed.
Urine indicators for pyelonephritis
A general urinalysis for pyelonephritis will give an alkaline reaction, where the pH varies between 6,2 and 6,9. Changes occur as a result of bacterial waste products entering the urine and due to disruption of the functioning of the tubules. The color of urine changes to a darker side, its reddish tint, cloudy suspension is possible. Possible protein detection.
Urine analysis according to Nechiporenko will detect a significant increase in the number of leukocytes over erythrocytes.
The Zimnitsky test will detect a decrease in urine density. Nighttime diuresis will prevail over daytime.
Bacteriological examination will detect in 1 ml of urine the number of bacteria exceeding 10 to the fifth degree. To determine their type and establish sensitivity to a particular drug, a culture study is performed.
The prednisolone test will indicate the presence of pyelonephritis by increasing the number of leukocytes.
Complications and consequences of pyelonephritis

Complications and consequences of pyelonephritis can be very serious. The disease is especially dangerous for women who are carrying a child, as well as for people with diagnosed diabetes.
Among the possible complications of the disease:
Renal failure;
Blood poisoning;
Kidney abscess.
Sepsis as a complication of pyelonephritis
Most often, diagnostic errors lead to the fact that pyelonephritis cannot be cured. Although it happens that the disease acquires a severe course until the moment of contacting the doctor. Mostly these are people who have various injuries of the spine and do not have the natural ability to feel pain in its lower part.
If treatment is not performed in full, or is completely absent, then the inevitable progression of the disease occurs. Pathogenic microorganisms multiply when their number reaches the limit point, they penetrate the bloodstream and spread throughout the body through its channel. This is how sepsis develops, which often ends in the death of a person.
Pyelonephritis is essentially a mild disease from which people should not die. It responds well to antibiotic therapy. However, with complications such as sepsis, septic shock, end-stage pyelonephritis, the risk of death increases many times over. After all, statistics clearly indicate that sepsis becomes a fatal complication for every third person affected by it. But even those who, after blood poisoning, remain alive are often doomed to disability, since it becomes necessary to remove certain parts of the body and organs of the patient in order to save life.
Famous people who were sick with pyelonephritis with sepsis:
Jean-Paul II – the Pope died of sepsis in 2005, which was a complication of pyelonephritis.
Marianne Bridie Costa died of sepsis due to pyelonephritis in 2009. The famous Brazilian model had her arms and legs amputated in an attempt to stop the progression of the disease, but the death could not be prevented.
Etta James, singer and Grammy winner, suffered from pyelonephritis complicated by sepsis.
Emphysematous pyelonephritis
This complication in 43% of cases leads to the death of the patient. The complication is characterized by a severe course, since as a result of the accumulation of gas in the kidneys, necrosis of the organ occurs and renal failure develops.
In addition, pyelonephritis, in addition to the above complications, can lead to such consequences as:
kidney abscess;
Development of apostenomatous pyelonephritis;
Kidney carbuncle.
Answers to popular questions
How many live with pyelonephritis? With pyelonephritis, you can live a full life, which will not be limited by any time frame. However, an important condition is timely adequate treatment of the disease and prevention of exacerbations. In addition, it is possible to completely get rid of chronic pyelonephritis if it is detected during early diagnosis and passes against the background of persistent treatment. In general, the prognosis depends on the duration of the disease, on the damage to one or two kidneys, on the microflora that led to inflammation. According to statistics, if a person does not change his lifestyle and does not start treatment, after the diagnosis of pyelonephritis is made, the life expectancy does not exceed 10 years
How long does the temperature last with pyelonephritis? With pyelonephritis during an exacerbation, the temperature lasts up to one week.
How much water to drink with pyelonephritis? During an exacerbation of the disease, the body needs as much fluid as possible. The patient is advised to drink more than 2000 ml of pure water per day. Only a doctor can reduce volumes if there are appropriate contraindications.
Is it possible to warm up, go to the bath with pyelonephritis? During an exacerbation of the disease, it is forbidden to visit the bathhouse, as well as perform other warming procedures. The patient’s condition may worsen. In the stage of remission, the bath is not contraindicated, but you must be completely sure that the disease has receded. For this, tests are taken and ultrasound of the kidneys is performed.
Is it possible to have sex with pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis, as a disease, has no contraindications to sexual activity.
How many lie in the hospital with pyelonephritis? In the hospital with pyelonephritis are from 10 days or more. It all depends on the condition of the patient and the presence of complications.
How and how to treat pyelonephritis?
How and how to treat pyelonephritis depends on how the disease proceeds. In the event that an exacerbation of a chronic disease, or primary acute pyelonephritis occurs against a background of high temperature, is accompanied by a drop in pressure, severe pain, suppuration and a violation of the normal outflow of urine, surgical intervention will be required.
The patient must be hospitalized if it is impossible to carry out drug therapy at home (vomiting after taking pills for pyelonephritis), as well as with severe intoxication. In other situations, at the discretion of the doctor, treatment can be carried out on an outpatient basis.
Pyelonephritis is treated with antibacterial and symptomatic therapy in combination.
To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, the following conditions must be met:
It is important to observe the drinking regimen throughout the entire period of treatment.
For the first few days, the patient must observe bed rest, that is, be warm in a horizontal position.
To reduce body temperature and eliminate pain, the use of NSAIDs is necessary.
Moist cold is most dangerous for inflamed kidneys. This applies to both exacerbation of the disease and the chronic course of pyelonephritis. During the period of remission, it is important to take a horizontal position of the body at least once a day for half an hour and empty the bladder more often.
Treatment with antibacterial drugs in adult patients. After confirming the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a broad-spectrum antibacterial drug. After the results of the bacterial culture are obtained (more often this occurs after 5 days), the antibiotic can be replaced with another one that is more effective in this case.
When the effect of the therapy is absent in the first 2-3 days, it is advisable to perform a CT scan of the abdominal cavity. This procedure is necessary to rule out hydronephrosis of the kidney and to rule out an abscess. In addition, a bacteriological analysis of urine is required to determine the sensitivity of microorganisms.
Sometimes, after the completed antibacterial course, it is necessary to repeat it, but with drugs of a different group. If the disease has become chronic, then it is necessary to take antibacterial agents for a long time. Difficulties in the treatment of the disease lie in the resistance of the bacterial flora to antibacterial agents.
The prognosis is favorable when the disease is detected at an early stage and with timely treatment. If the pathogen is not detected in the urine all year after therapy, then the person is considered healthy.
Therapy of pyelonephritis caused by fungi. If the disease is provoked by mycotic microorganisms, then treatment with antifungal drugs is indicated. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the dynamics of the removal of fungi from the kidneys, for which CT, retrograde pyelography, and X-ray contrast urography are performed. Surgery will be required if the urinary tract is clogged and urine stagnates in the kidneys. In this case, patients impose a nephrostomy. This method leads to the normalization of urine outflow and makes it possible to administer antimycotics directly into the kidney.
Nephrectomy. Removal of the kidney is necessary against the background of sepsis, which cannot be corrected with drugs. It is especially important to perform a nephrectomy for renal failure, which tends to increase.









