Contents
Otitis in children is an inflammatory process that affects various parts of the ear. Pathology can be exposed to the outer, middle and inner space. The disease has a variety of symptoms, the severity of which depends on the form, stage and nature of the course of otitis media.
It is known that children suffer from this disease much more often than adults, this is due to the peculiarities of the structure of their hearing aid. At an early age, up to 80% of children have a history of this disease, and by the time they enter the first grade, otitis media has been diagnosed at least once in 95% of all children. Often in childhood, the disease tends to recur and in advanced cases leads to serious complications. Therefore, timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease at the initial stages of its development is so important.
Otitis media in children
Otitis media in children is the development of an acute infectious process in the ear cavity of a child, with damage to the middle part of the ear. As for the peak incidence, it falls on the age of six months to one and a half years. After the frequency of parents visiting the doctor about the occurrence of otitis media decreases. This is explained by the fact that acute respiratory viral infections are common among the child population of the planet, which in most cases lead to the development of the disease. According to statistics, 63% of children at least once suffered from acute otitis media. Provoking factors in the development of the disease are acute respiratory viral infections, measles, diphtheria, scarlet fever, proliferation of adenoids, sinusitis, rhinitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis. Through the external auditory meatus, the infection can get inside only when the eardrum is damaged.
As for newborn children, they may develop otitis media due to the fact that microbes are transmitted to it from a mother with pyelonephritis, mastitis, endometritis, etc. As for the pathogens of otitis media, pneumococci, hemolytic streptococci, fungi are most often found during sowing , Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella.
Otitis media can develop against the background of a general decrease in immunity, due to the fact that the child was not full-term, in the presence of allergies, rickets, vitamin deficiency and other provoking factors. In addition, the auditory tube itself in babies is wider and not curved, which makes it easier for pathogenic bacteria to enter the middle ear cavity.
Recent data prove that the lack of breastfeeding negatively affects the ability of the child to resist the disease. More often suffer from otitis media children who started attending kindergarten, as well as those whose parents abuse bad habits, and in particular, smoking.
Doctors also argue that an additional risk factor for the development of otitis media is the frequent use of nipples, autumn and winter, and the unfavorable environmental situation in which the child lives.
Symptoms of otitis media in children
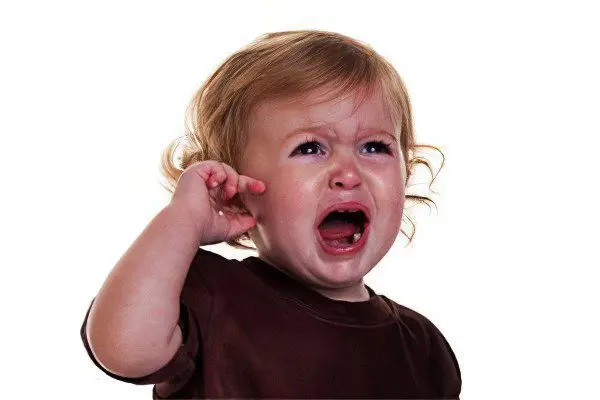

Among the symptoms that characterize the development of otitis media in a child, the following can be distinguished:
An increase in body temperature, which can be more than 38 ° C, however, it rarely reaches significant figures.
A child, like an adult, will experience pain in the ear, however, at a younger age, except for loud and incessant crying, he is not able to show this symptom.
Increased anxiety. If the child is small, then he will not be able to fall asleep, or will sleep for short periods of time. The baby often turns his head, trying to find a more comfortable position.
The motor activity of the child is reduced.
Appetite disappears. Infants begin to refuse the breast, or take it only on one side. In this case, the diseased ear will be lower than the healthy one.
When pressing on the protrusion on the ear (on the tragus), the crying intensifies.
Often in childhood, against the background of otitis media, diarrhea and vomiting develop.
If a perforation of the tympanic membrane has occurred, then a secret of one nature or another will be separated from the ear.
At an older age, children can verbalize anxiety and point out which ear is causing them discomfort. If parents suspect that the baby is developing otitis media, it should be immediately shown to the pediatrician or an ambulance team should be called to the house. It will be possible to determine the presence of the disease using standard otoscopy. This procedure is absolutely painless and will not cause unnecessary discomfort to the child.
Treatment of otitis media in children
Therapy of acute otitis media in childhood is aimed primarily at relieving pain and lowering body temperature if it exceeds acceptable limits. When otitis media is caused by a bacterial flora, the child is given antibiotics. It is worth knowing that otitis media most often, namely in 80% of cases, passes without their use.
As for the use of antibacterial agents, doctors give preference to drugs of the penicillin group. As a means of relieving pain and inflammation in childhood, Nurofen and Paracetamol are used in the form of a suspension. It is important to visit a doctor after suffering otitis media and make sure that the child does not have a persistent hearing loss. This is especially true for children under the age of 2 years, since the parents themselves will not be able to understand that a complication has arisen.
The prognosis is usually favorable, but only if therapy was started in a timely manner.
Therefore, competent actions of parents are so important in case of suspicion of the development of otitis media in a child:
For any of the above symptoms, you should seek the advice of a specialist.
If discharge is observed from the ear, then this is an occasion for an immediate visit to the doctor.
If your child is very anxious, you can give him paracetamol or ibuprofen, in age-appropriate dosages. This should be done before visiting a specialist. You should not independently bury any, even the most famous drops, in the child’s ear.
You should not use folk remedies for the treatment of childhood otitis without consulting a doctor.
Purulent otitis in children
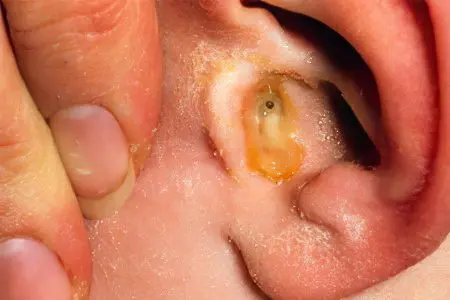
Purulent otitis in a child is characterized by the fact that the mucous membrane of the middle ear becomes inflamed and purulent exudate forms in its cavity. Also, like other varieties of the disease, purulent otitis media most often develops in a child at an early age.
This form of the disease is the most dangerous, since untimely treatment can lead to the entry of purulent masses into the cranial cavity and result in serious complications, ranging from hearing loss to death. The risks of such consequences are also high due to the fact that the eardrum of a child is thicker than that of an adult, which means it is less prone to rupture. Therefore, purulent masses, even with their high accumulation, rarely come out.
Most often, the pathology develops against the background of the fact that acute otitis media was incorrectly diagnosed or its treatment was not effective enough. Also, the transition of a milder form of the disease into a purulent form can provoke hypothermia, a decrease in the body’s immune forces, a lack of vitamins, and an irrational intake of antibacterial agents.
Less often, the development of purulent otitis becomes the result of acute respiratory infections and influenza. The cause may also be a congenital anomaly in the structure of the ear cavity or nose of the child. It is important to correctly toilet the child’s ear. It is unacceptable to use a cotton swab or other devices to try to clean the earwax from the baby’s ear canal. It is enough to remove it only from the auricle with light and non-traumatic movements.
As for the possible complications of purulent otitis media in childhood, among them are otoanthritis, meningitis, heart and kidney disease, and mastoiditis.
A characteristic feature of purulent otitis in childhood, especially up to a year, is that it occurs bilaterally, that is, both ears are involved in the pathological process. Purulent masses in the ear cavity are more often formed in childhood, also due to the fact that the mucous tissue lining it is still too loose, which makes it more vulnerable to the pathological effects of viruses and bacteria.
Symptoms of purulent otitis media in children
Symptoms of suppurative otitis will vary depending on the age of the child.
If he was recently born, then the main signs of purulent otitis media include the following:
Increased moodiness and excessive tearfulness of the baby, for no apparent reason. The child cannot be calmed or rocked. The crying of the newborn does not stop and is of high intensity.
The child refuses to eat. Doesn’t take breasts or bottles of milk into her mouth. This is due to the fact that sucking movements increase pain.
The cry of the child is not monotonous, but shrill, indicating that something is bothering the child.
The baby is restless, cannot lie motionless in bed even when he manages to fall asleep.
No response to toys. This is due to hearing loss, so the child stops turning his head and looking towards the outgoing sound.
Because of the increased pressure in the ear cavity, the child often vomits. It is worth being able to distinguish it from regurgitation.
Sometimes there are short-term convulsions.
When trying to take the breast, the newborn rotates his head all the time, trying to find the most suitable position.
An increase in body temperature up to 38 ° C, and sometimes even higher.
Instinctively, the child tries to press the sore ear, so he tries to roll over or turn his head in the direction where the inflammation is localized.
During otoscopy, the doctor sees a swollen and hyperemic eardrum.
As for older children, the symptoms of purulent otitis media are somewhat different. These include signs such as:
Decreased physical activity of the baby.
Excessive and unreasonable fatigue of the child.
The manifestation of apathy in all actions and movements.
Pale skin.
Congestion in the ears.
An increase in body temperature, sometimes to very high values.
The appearance of secretions from the ear, of various consistency, which are formed during the rupture of the eardrum.
Child’s attempts to point out or talk about a problem that is bothering him. Children as young as 2 years of age can verbalize that their ear hurts.
Decreased appetite and sleep disturbance.
Treatment of purulent otitis media in children
Purulent otitis in a child should be treated only by a doctor. Self-therapy is unacceptable. This is due to the fact that the disease is fraught with serious complications. Do not use traditional medicine and experiment on the baby. It is also important to refrain from instilling any, even medicinal solutions into the ear until the doctor arrives. Until the child’s ear is examined by a doctor, it is possible to give him an antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drug, it can be either Paracetamol or Nurofen, produced in a special children’s form.
One cannot count on the fact that purulent otitis media can be cured by just instillation of some drops. Treatment should be comprehensive and prescribed by a doctor. Otipax, Sonopax, Otinum are often prescribed as ear drops. If the treatment does not have the desired effect, a puncture of the membrane is required in order for the purulent exudate to come out. However, this is fraught with consequences such as hearing impairment and even loss. Therefore, it is so important to contact a specialist at the first suspicion of otitis media.
The child is shown drinking plenty of water and attending physiotherapy procedures.
Catarrhal otitis in children
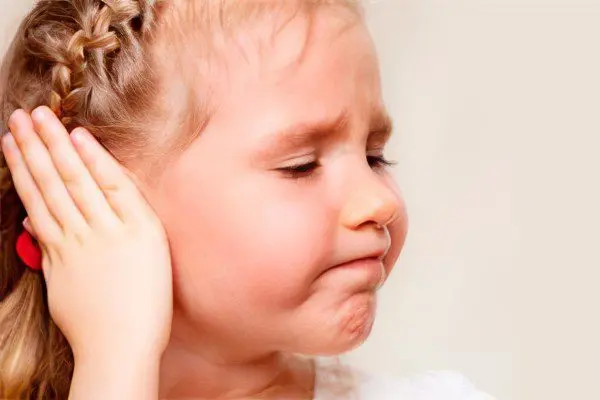

Catarrhal otitis in children is an infectious disease common in childhood, in which inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear occurs. Often it is this form of otitis that precedes the development of a purulent form of the disease. This happens due to unqualified or untimely treatment.
The factors influencing the development of catarrhal otitis include, first of all, frequent acute respiratory viral infections and influenza, as well as overgrown adenoids and other chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract. In addition, catarrhal otitis occurs more often in children due to the fact that their auditory tube has certain anemic features. All this becomes a fertile ground for the reproduction of pathogens.
Symptoms of catarrhal otitis in children
Symptoms of catarrhal otitis are manifested brightly. Among them are:
Pain that is always very intense. Older children can express their feelings in words, and in younger children, they signal pain to their parents with the help of incessant screaming.
The child may complain of a headache and even a toothache, which is determined by its ability to radiate to these areas.
The baby’s hearing is reduced, which is easy to see by the reaction of infants to a bright ringing object, such as a rattle. An older child can independently say that he is worried about some hearing impairment.
Often with catarrhal otitis, the body temperature rises, sometimes to high values. The general condition is disturbed, the baby refuses to eat, becomes lethargic and weak.
Redness may occur in the ear area.
Most often, newborn children suffer from catarrhal otitis media. Even improperly organized breastfeeding can lead to its development. At an older age, there are frequent cases of infection of the middle ear due to an injury to the eardrum received by the baby. This is due to the fact that children often try to place a foreign object in the ear canal.
Treatment of catarrhal otitis in children
Treatment should be carried out only after the diagnosis is established. Only a doctor can correctly determine the form of otitis media and the stage of its course.
In general, the treatment of catarrhal otitis is reduced to the following activities:
Local treatment, for its implementation will require the use of ear drops. There are many drugs, but Otipax is most often prescribed for otitis media in childhood. This remedy helps relieve pain and reduce inflammation. They can be used even in newborns.
If the doctor indicates that there are no contraindications, then dry compresses can be applied to the ear, which will help improve blood circulation and relieve inflammation.
To relieve swelling from the nasal mucosa, the use of vasoconstrictor drops is indicated. It can be children’s Tizin, Nazivin, Sanorin, etc.
In some cases, antibiotics are required, but most often they are used to treat purulent otitis media, which can occur against the background of catarrhal otitis media with inadequate therapy.
Paracetamol-containing drugs will help reduce the temperature.
Exudative otitis media in children

Exudative otitis media in childhood is characterized by the fact that exudate begins to accumulate in the child’s ear cavity. This happens against the background of the inflammatory process. The peak incidence of this form of otitis occurs in the age group of children from 3 to 7 years. A similar diagnosis is made to them in 60% of cases of common ear diseases. In primary school age, the incidence of exudative otitis media is on the decline and the number of cases of this pathology is reduced to 10%.
Symptoms of exudative otitis media in children
Symptoms of the disease do not appear clearly. This makes it difficult to diagnose the disease. However, parents should be aware that even a slight hearing loss may indicate the development of the disease, and the child must be shown to the doctor. As a rule, children do not pay attention to the fact that their hearing is deteriorating, considering this a variant of the norm. Sometimes they may complain of emerging tinnitus. Therefore, so often exudative otitis media is detected only during a routine examination.
However, this disease is dangerous in that if left untreated, it will become chronic. In this case, the risk of developing serious complications is significantly increased. Among them, one can distinguish the development of adhesive otitis media, as a result of the progression of which adhesions form in the ear, which can significantly reduce hearing, up to its complete loss. Moreover, these adhesions cannot be eliminated with the help of conservative treatment. In addition, against the background of exudative otitis media, purulent or acute inflammation often occurs in the middle ear. These otitis media tend to recur and cause a lot of problems for the child and their parents, reducing the quality of life of a small patient.
In addition, exudative otitis media can cause a decrease in school performance, lead to a delay in psycho-emotional development. When the chronic form develops in early childhood, the child may develop speech disorders.
Treatment of exudative otitis media in children
In order to start treating the disease, it is necessary to find out the cause of its occurrence. It is imperative to exclude the growth of adenoids, choanal polyps, and conduct a thorough sanitation of the sinuses.
Only after these measures can you start cleaning the ear canal and restoring its functionality. In this case, physiotherapeutic procedures help to cope with the problem, in particular, electrical stimulation of the soft palate, magnetotherapy, diadynamic currents, blowing the ear according to a certain method. Antibiotics are not used to treat exudative otitis media.
When otitis media has flowed into a chronic form, and conservative methods of treatment do not help, then they resort to surgical treatment. This may be paracentesis of the tympanic membrane, tympanotomy, shunting of the tympanic cavity. At an early age, general anesthesia is used for the operation, and at an older age, local anesthesia can be used.
Otitis treatment in children
Therapy of otitis that occurs in a child should be handled by an otolaryngologist. When a child complains of pain in the ears, you should immediately seek the advice of a specialist.
However, sometimes it happens that it is not possible to quickly show the child to the doctor. In this case, you can try to relieve the pain by giving the baby medicine to eliminate it. These include ibuprofen and paracetamol. Both of these drugs are allowed in childhood and act not only as an anesthetic, but also as an antipyretic.
Helps reduce swelling of the nasal mucosa and auditory tube various vasoconstrictor drops. These include Galazolin, Nazol, Tizin, Afrin, Xylometazoline, Sanorin and others.
It is important to remember the only fundamental rule – when a child complains of pain, in no case should you instill any drops in his ear canal before an ear examination by a doctor. Anesthesia agents such as Otinum and Otipax have some contraindications, and first of all, this is a rupture of the eardrum. Through the perforation, they can enter the ear cavity and damage the auditory nerve, which will cause permanent hearing loss.
The treatment that a doctor prescribes for a child with otitis media most often comes down to the following aspects:
We will take antiviral drugs. They contribute to the speedy disposal of the common cold and allow you to eliminate the symptoms of SARS.
Nasal drops with a vasoconstrictive effect. They have been listed above.
NSAIDs, ibuprofen is most commonly used in childhood. This remedy helps to eliminate both pain and lower the temperature.
Combined ear drops. They eliminate swelling and itching, reduce inflammation.
Ear drops with antibacterial effect. They are prescribed for purulent otitis, and for varieties of the disease that are of a bacterial nature.
Antihistamines. They help eliminate swelling from the mucous membranes, both the nasopharynx and the auditory tube.
Antibiotics that are prescribed for bacterial and purulent otitis media.
In most cases, childhood otitis is treated at home, but with a mandatory visit to a medical facility to monitor the child’s condition.
Antibiotic for otitis in children
Antibiotics for otitis in a child are most often prescribed immediately when the child has not reached the age of 2 years, or he has a high body temperature with severe symptoms of intoxication, as well as severe pain that is not relieved by painkillers. Only a doctor can decide on the choice of the drug, as well as set its dosage.
Ампициллин has a wide spectrum of action and is often prescribed for otitis media in childhood. This semi-synthetic penicillin is most often used in childhood in the form of a suspension or in the form of water-soluble tablets. Up to 10 years, it is best to use a suspension that is easily and accurately dosed and the child has no difficulty in taking it. It should be understood that the drug has serious contraindications and side effects from almost all organ systems. The gastrointestinal tract suffers the most. However, this powerful tool is able to cope with even the most severe infection.
Clarithromycin. A safer and more effective drug than penicillin drugs. It has an antibacterial effect and is prescribed in the form of a suspension in childhood. The doctor calculates the dose, depending on the weight of the child and the stage of the disease. During use, side effects may occur on the part of the senses, digestive and nervous systems. Also, do not forget about allergic reactions.
Cefriaxone used as an intramuscular injection. It is used only in the conditions of inpatient treatment.
Roxithromycin can be used in children after they reach 4 years of age. The weight of the child must exceed 30 kg. The advantage of this remedy is the complete absence of contraindications, with the exception of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. In some cases, there may be side effects from the nervous and digestive systems. The development of superinfection is not excluded.
Sofradex – ear drops containing antibiotic and hormones. Can be used to treat chronic and acute otitis externa.
[Video] Dr. Berg – Best NATURAL Otitis Remedy:









