Contents
Fruit crops that are unpretentious in care and undemanding to growing conditions are of interest to gardeners. At the same time, it is desirable that fruiting and productivity be at a high level. It is such a culture that Butternut pumpkin is, the features of cultivation and use of which will be discussed today.
Description of Butternut Pumpkin
Butternut squash is an interspecific hybrid of nutmeg squash and African bottle-shaped fruits. The birthplace of culture is called North America. Massively grown in Mexico and other countries with a warm climate. Despite the harsh and sometimes unstable climate of Our Country, the plant quickly adapted to our realities. It can be grown both in private agricultural land and on an industrial scale.
The fruit crop got its name – Butternut – from the English word butternut, which literally means “butter nut”. The etymology of the name is associated with the taste characteristics of the fruit. Butternut pumpkin has a nut butter flavor and a nutty flavor. For this reason, Butternut is often referred to as butternut gourd.

There are two types of Butternut pumpkin: bush (Bush Butternut) and climbing (Waltham Butternut). The main difference is the appearance of the plant. From the names themselves, it becomes clear that a bushy culture is formed in the form of a bush with a diameter of up to 1,5 m, and a climbing one has branched shoots up to 2,5 m long.
It grows both on the ground and on trellises. Since the fruits are characterized by small size and low specific gravity (about 1–1,5 kg), the branches do not fall from the supports. This variety is characterized by large leaf plates of a rich green hue. The leaf shape is standard for representatives of the Pumpkin family.
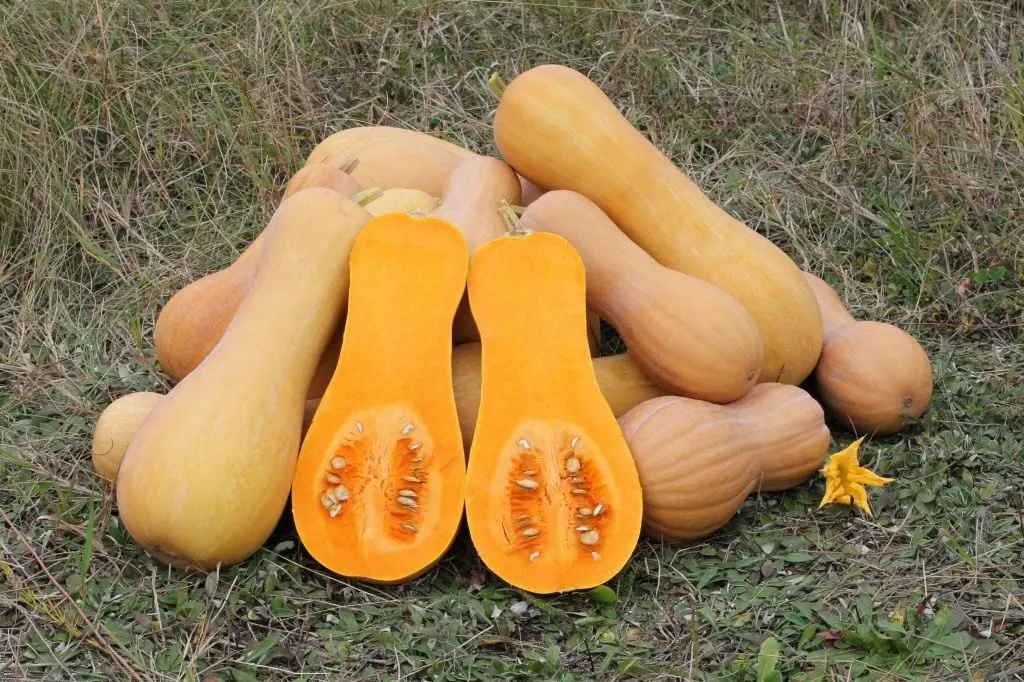
The fruits have a pear-shaped elongated shape. Skin color is light orange. But the pulp of the fruit has a beautiful juicy orange hue. The rind is thin, but very dense. The seed part is located in the lower (expanded) part of the fruit.
Yield and maturity
Butternut refers to early ripe garden crops. With a favorable microclimate and weather conditions associated with high yields, the first fruits can be harvested already 3 months after the formation of ovaries on climbing shoots.
The average yield from one bush is 12–15 kg. In the southern regions, yields can reach 20 kg per plant. If the gardener was engaged in the formation of lashes for growing large-fruited pumpkins (4–5 kg each), then only a few ripe fruits are removed from one bush.
Pumpkin Butternut can be removed unripe. If the weather forecast does not please with warm and sunny days, we recommend removing slightly unripe fruits. Otherwise, pumpkins may start to rot from the middle.
Author’s advice

Taste and aroma of fruit
Pumpkins that have reached technical maturity are distinguished by a pleasant aroma and an interesting taste – oily and nutty. As you can see, garden culture fully justifies its name.
Advantages:
- early fruiting;
- high yield;
- unpretentiousness to care;
- excellent consumer qualities and universal use of fruits;
- long period of storage of the harvested crop;
- small amount of seeds.
Disadvantages:
- exactingness to the soil composition;
- difficulties with pollination;
- loss of taste and commercial qualities when infected with fungal or bacterial infections.
Video “All about Butternut pumpkin”
This video provides a description of the fruits of the culture, and also talks about the features of the use and storage of the product.
Agrotechnics pumpkin varieties Butternut
As you know, the yield of cultivated plants grown in the beds depends not only on weather conditions, but also on a person. Today we will tell you how to plant and grow butternut pumpkin in the open field.
Site Selection
The best place for growing pumpkins is in beds protected from wind and drafts. At the same time, the garden area should be well lit by the sun. The plant does not like wetlands, acidic and alkaline soil. The best soil option is loam with the addition of dolomite flour.
Seed preparation and sowing
The seeds selected for sowing are soaked in a growth biostimulant, spread on a damp cloth and allowed to germinate. After 25-30 days, the seeds can be planted in open ground.
Planting material is sown in the last ten days of May or early June. When forming beds / holes, they maintain a distance of 60 to 70 cm. The seed is planted in such a way that the hatched sprout “looks” up.
Watering and mulching
Butternut loves abundant watering, but at the same time suffers from excess moisture in the soil. The frequency of irrigation should be determined by the degree of drying of the soil and the amount of precipitation. 2–2,5 weeks before harvesting, watering the beds is stopped.
Do not neglect the mulching procedure. In this way, the growth of weed grass can be prevented and the nutritional properties of the soil can be preserved. Hay, straw or dry vegetation is used as mulch.

Top dressing of plants
Beds with fruit crops are fed with mineral fertilizers. During the period of active growth and development, nitrogen-containing preparations are introduced. At the stages of flowering and fruiting, potash and phosphorus fertilizers are added. In one season, the pumpkin is fed at least 2-4 times.
According to the reviews of experienced gardeners, organic matter can be used to feed Butternut. Suitable wood ash, bird droppings diluted with water (1:20) or rotted manure (1:10).
Pollination of culture
For pollination of pumpkin grown in beds, insects, in particular bees, are attracted. If the weather is cloudy and damp, you can pollinate the plants yourself. In the first half of the day, when the inflorescences are open, the “male” flowers are applied to the “female” ones.
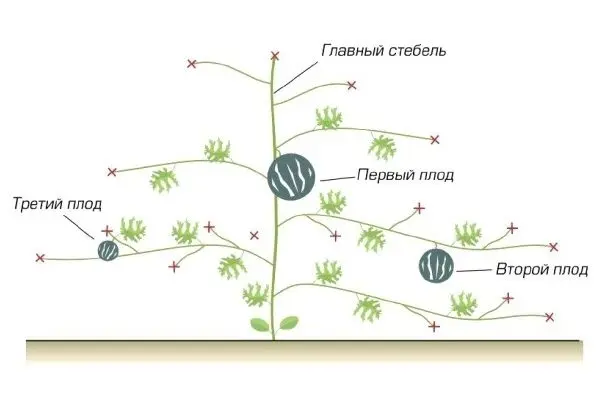
Shrub formation
The formation of culture contributes to the improvement of fruit formation. On one bush, no more than 2 healthy and well-developed shoots are left. But the number of ovaries can be determined at your discretion. When the first fruits appear, you need to cut off the extra leaves.
Diseases and pests
With improper care, the plant suffers from fungal and bacterial infections, which negatively affects the taste and commercial qualities of the fruit. In addition, the pumpkin is often besieged by spider mites and aphids.
Variety Butternut is not recommended to be treated with chemicals. To combat insects and diseases, folk methods are used – soapy water, garlic water, diluted Bordeaux liquid, etc.
Useful properties of pumpkin
The nutritional value of butternut pumpkin is 45 kcal. For 100 g of a ripe product, there are 9,69 g of carbohydrates, 1 g of proteins and 0,1 g of fats. Juicy and fragrant fruits contain a huge amount of vitamins and minerals. So, the chemical composition of the product includes vitamins C, E, K, PP and group B. Pumpkin is rich in potassium, magnesium, sodium, phosphorus, iron, manganese, calcium, copper, selenium, zinc and other micronutrients useful for the human body. and macronutrients.
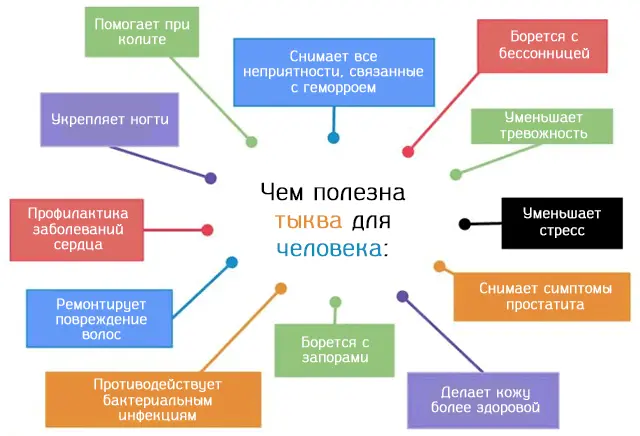
Thanks to such a rich chemical composition, culture has a beneficial effect on humans. With regular use of pumpkin, there is an improvement in the functioning of the digestive, cardiovascular and nervous systems. Also, the product helps to strengthen the nail plates and hair follicles.
Butternut has some contraindications. The product is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance, tendency to allergies and hyperacidity. The use of oily-nut pumpkin is not recommended for diabetes mellitus.
Using Butternut in Cooking
Walnut squash is one of the few products of the Cucurbitaceae family that can be eaten raw. The recipe for a vitamin salad based on pumpkin (300 g), apples (200 g) and liquid lime or acacia honey (100 ml) is popular among housewives.
Butternut retains most of its nutritional and beneficial properties during heat treatment. Therefore, the product can be used for cooking casseroles, first courses, side dishes and warm appetizers. Do not forget about the beneficial and healing properties of nutritious pumpkin juice.
Pumpkin Butternut is famous for its high yield and unpretentious care. Even a novice gardener will cope with the cultivation of this fruit crop.









