Contents
In autumn, the grapes enter the final stage of vegetation and begin preparations for winter. During this period, it is important to prepare the vineyard for winter so that it can endure frosts and begin to actively develop in the spring. Pruning grapes in the fall and sheltering for the winter are essential care steps.
You need to choose the right time for pruning so as not to damage the plants. The order of processing varies depending on the age of the grapes. Other autumn procedures also include root trimming, treatment for diseases and pests.
Pruning goals
The grape pruning procedure is carried out for the following purposes:
- increase in productivity;
- facilitating plant care;
- stimulating the growth of new shoots;
- grape rejuvenation;
- plant formation, which improves its appearance;
- creating an optimal balance between the root and ground parts of the plant;
- ensuring the flow of nutrients.

Basic pruning rules
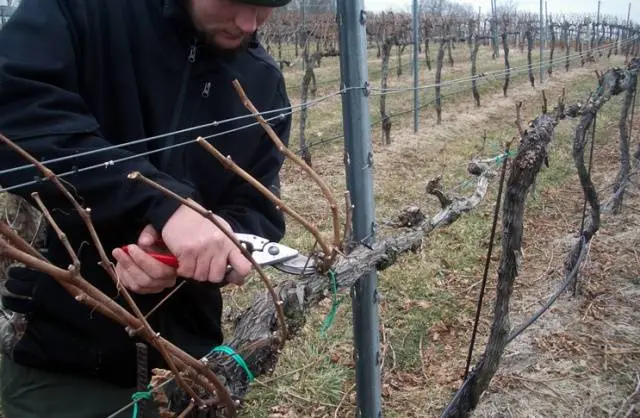
For autumn pruning, you will need a sharp garden pruner. Cuts are made in one motion to get the most even surface. In order for wounds to heal faster, they must be turned inside the plant.
Trimming time
The procedure depends largely on the region where the grapes grow. With the onset of autumn, pruning is necessary in cases where the vineyard takes shelter for the winter. As a result, the plant tolerates winter cold better.
Processing is carried out at the end of October, 2 weeks after leaf fall. If the vine has endured a few light frosts, it will only harden it.

First, it is necessary to process varieties that are characterized by increased resistance to low temperatures. Then they move on to the rest of the landings.
Basic techniques
There are several ways to trim grapes. The choice of technique depends on the degree of growth and plant variety.
- short pruning. This method has another name – “on a knot”. Its purpose is the formation and rejuvenation of grapes. As a result, from 2 to 4 eyes remain on the shoot. Be sure to eliminate the branches growing from the first eye. In total, up to 40 eyes are left on the branches.
- Medium pruning. After the procedure, up to 8 eyes are left on the branch, while their total number on the bush is no more than 50. Thus, frost-resistant shoots are preserved.

- long pruning. This method allows you to increase the fruiting of grapes. 15 eyes are left on each branch, and their total number should not exceed 60. Long pruning is more suitable for Asian varieties.
- Mixed equipment.
The most popular is the mixed cut, which combines short and long techniques. Some of the branches are cut “to a knot”, which contributes to the renewal of the plant. The rest of the grape shoots are pruned to increase the yield.
Pruning according to grape age
The order of the procedure varies depending on the age of the plant:
- Preparation of seedlings. In the first year after planting grapes, it is important to form two vines. We cut the shoots at a height of 40 to 60 cm. Then the plantings are pinned to the ground and covered.
- Pruning a two-year-old bush. In the second year, up to 6 new grape shoots are formed. They formed on branches left in the past year. On each of them leave 2 or 3 kidneys.
- Processing an adult bush.
Grapes pruning aged 3 years and over is carried out in the following order:
- After picking berries, the plant is cleaned of weak shoots and tops that interfere with its development.
- At the beginning of September, on perennial branches, young shoots should be eliminated that have not grown to a wire located at a distance of 0,5 m above the ground.
- Shoots that have outgrown the second wire (it is placed 30 cm above the first) are cut to 10% of the total length. Also eliminate side branches.
- In mid-October, on each sleeve of grapes, the two most developed branches are selected, the length of which reaches the first two wires.
- The lower branch growing on the outer part of the sleeve is cut off so that 4 eyes remain. Thus, a knot of substitution is formed.
- The shoot located on the opposite side and above must be cut off, leaving 5-12 eyes. This branch is called the fruit arrow.
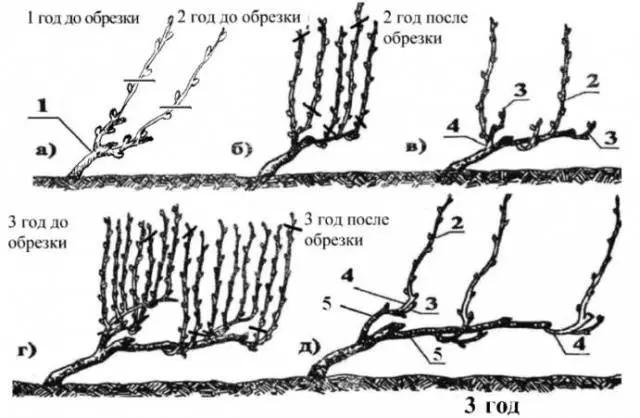
As a result, the most powerful branches and sleeves remain, from which new vines are formed in the spring.
Another stage of the procedure is the elimination of excess mustache. With their help, the grapes are fixed and its development. If the plant is tied up, then it is better to trim the mustache. However, it is better to direct them correctly so that the vine wraps around an arch or gazebo.
Other autumn treatments
Before sheltering the grapes, other procedures must be performed. In autumn, the root system is cut, watered and the plant is processed. After that, the plantings are covered for the winter.
Root cutting
Katarovka allows you to destroy the roots of grapes that are on the surface of the earth. They do not perform important functions and only take away the strength of the plant.
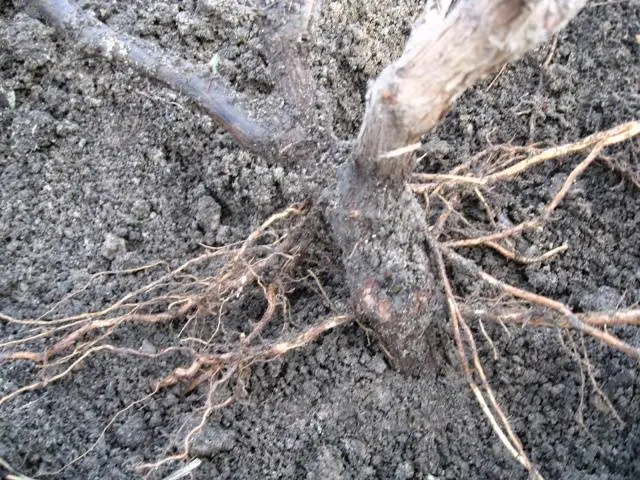

To eliminate excess roots, a ditch is dug under the trunk to a depth of 20 cm. Branches located above the main rhizome are eliminated.
Sections are disinfected with a solution of copper sulphate. Then the pit is covered with sand, and the bush is spudded and watered with warm water.
Pest control
To protect the vineyard from diseases and pests, a number of preventive measures are taken. Pest larvae and fungal spores often find shelter under the bark of the shoots. Their activity begins in the spring.
The most effective remedy is a solution of copper sulfate. A bucket of water requires 0,1 kg of the substance. The consumption of funds is 2 liters per bush.
For the processing of grapes, special preparations are used: “Topaz”, “Ridomil”, “Avixil”. To obtain a working solution, they are diluted with water in the ratio indicated in the instructions.

Shelter
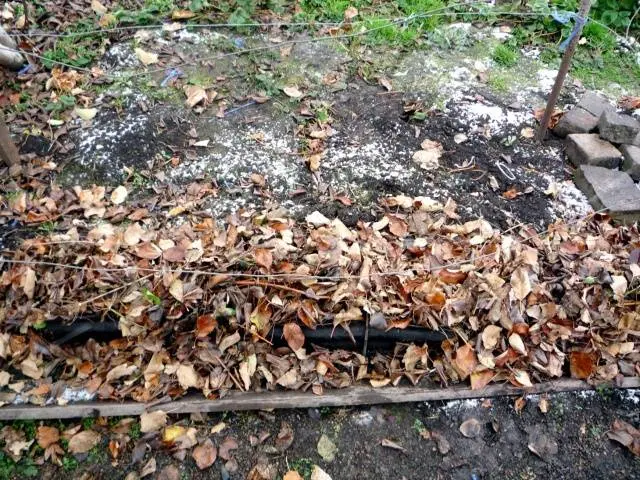
After pruning, you need to cover the grapes. Along the landings, you need to dig trenches, after which the vine is tied up and placed in them. From above, the plants are covered with earth with a layer of 15 cm. The soil must be slightly moistened to avoid freezing. This technique is suitable for regions where there are no severe frosts.
Additionally, the vineyard is covered with a film, straw, thick cloth or slate. Above the grapes should remain a snow cover that protects the plants from freezing. To prevent the snow cover from being blown away by the wind, it is necessary to put up shields. In the spring, they are removed, and the earth is discarded so that the plant dries.

Conclusion
Pruning and sheltering are mandatory stages of vineyard care. Such procedures protect plantings from winter frosts, rejuvenate the vine and increase yields. The pruning order varies depending on the age of the grapes. Be sure to eliminate the roots that are selected on the surface of the earth. To protect plantings from pests and diseases, they are treated with special preparations.










