Contents
Protrusion of the discs of the spine – what is it?
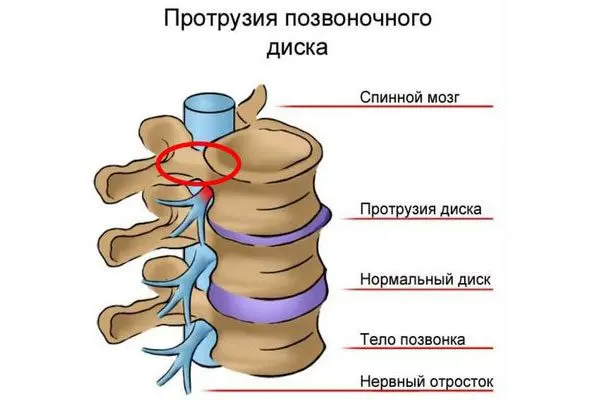
Protrusion of the spinal discs is a pathological protrusion of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal, which is not accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the fibrous ring. Disk protrusion should not be considered as an independent disease. Protrusion is one of the stages of osteochondrosis, which further leads to the formation of a hernia.
It is in the lumbar region that disc protrusion is most often formed, somewhat less often it is observed in the cervical spine. Protrusion in the lumbar region in the vast majority of cases is localized between the vertebrae L4 and L5, or between the first sacral vertebra S1 and the last lumbar vertebra L5. The discs located between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae are less likely to protrude, and the upper lumbar discs are very rare.
The age at which protrusion is most often detected varies from 30 to 50 years. Men are most often affected. Since disc protrusion leads in the future to the formation of a hernia and to possible disability in patients of working age, it is necessary to detect this condition in a timely manner and treat it. In addition, protrusion can cause severe back pain, which worsens the quality of life of a person and affects his well-being. Spinal disc protrusion is the cause of approximately 30% of cases of spinal pain in orthopedic patients.
Symptoms of protrusion of the discs of the spine
Symptoms of protrusion of the discs of the spine primarily depend on the degree of its protrusion beyond the vertebrae, as well as on the location of the pathological focus.
For protrusion of the lumbar disc is characterized by the following clinical picture:
Back pain, which is localized in the lumbosacral region. The pains are chronic and are present almost constantly, with varying degrees of severity. They increase with increasing physical load on the lumbar belt. For example, when lifting weights, when bending over, when staying in one position for a long time (sitting or standing), when performing sudden movements.
When a person takes a comfortable position, the pressure of the disc on the nerve roots weakens, the pain goes away or decreases.
Numbness in the groin and in the lower limbs.
Weakness of the muscles of the lower extremities.
Feeling of “goosebumps” and tingling in the legs.
Development of lumbosacral sciatica.
Feeling of stiffness in the lumbar region.
Decreased range of motion in the lumbar spine. The patient is often unable to sleep on his stomach, fully straighten his lower back, raise his leg high.
All of the above symptoms can have varying degrees of severity. This is especially true for pain symptoms. Often, pain is absent until the protrusion of the spinal disc turns into an intervertebral hernia.
Causes of protrusion of the discs of the spine
The causes of protrusion of the discs of the spine are most often hidden in a disease such as osteochondrosis. The intervertebral disc suffers from degenerative-dystrophic changes that occur as a result of dysmetabolic disorders. The worse the power processes of the disk, the faster it loses moisture and becomes inelastic. Under such conditions, even a minor injury or load on the spinal column can lead to the formation of protrusion. The disc extends beyond the vertebrae and remains in this state until a certain time. After the rupture of the fibrous ring, it makes sense to talk about a hernia of the spine.
The reasons that may affect the formation of protrusion of the intervertebral disc are as follows:
Physical inactivity. Insufficient motor activity always negatively affects the structural elements of the spinal column.
Provoking the formation of protrusion can be uneven loads on the spine, which are the result of factors such as:
Anomalies in the development of the spinal column (splitting of the vertebrae, syndrome of additional cervical ribs, sacralization, etc.);
Curvature of the spinal column (lumbar lordosis, scoliosis);
Long-term static and dynamic loads;
Weight lifting;
Violations of the location of the pelvic bones (hip dysplasia).
Overweight.
Severe spinal injuries can be the cause of disc protrusion. These include bruises, subluxations and fractures of the vertebrae.
It is possible to form a protrusion of the disc against the background of already existing diseases of the spine, for example, with Bechterew’s disease, Calvet’s disease, with tuberculosis of the spinal column, etc.
Various dysmetabolic processes occurring in the body lead to a deterioration in the nutrition of the disk. These include hypothyroidism and diabetes.
It is possible to form disc protrusion against the background of collagenoses and systemic diseases of the connective tissue.
Indirect factors that can affect the formation of disc protrusion are age-related changes in the body and hereditary predisposition to diseases of the spinal column.
Stages of formation of protrusion of the intervertebral disc
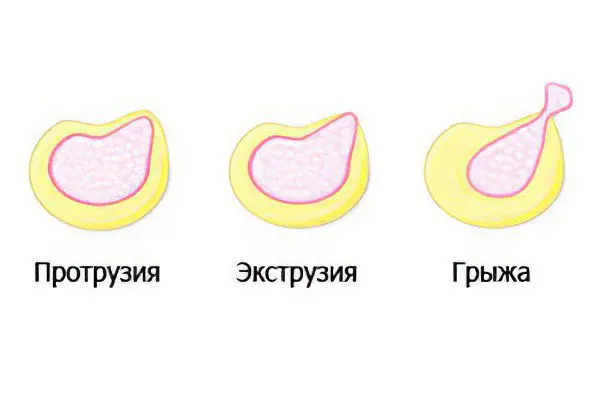
The stages of formation of protrusion of the intervertebral disc can be distinguished as follows:
Destruction of 70% of the disc itself, loss of elasticity, formation of cracks in the fibrous membrane.
Protrusion of the disc with displacement of the nucleus pulposus and with stretching of the annulus fibrosus.
Increased disc protrusion by more than 4 mm, followed by rupture of the annulus.
Formation of a hernia of the spinal column.
Treatment of protrusion of the discs of the spine

Treatment of protrusion of the spinal discs should be timely and comprehensive, which will allow you to control the pathological process and prevent the formation of a hernia.
All patients should follow these guidelines:
For a period of about 4 days, you should adhere to bed rest. Longer rest can negatively affect the effectiveness of therapy. Therefore, if the pain in a person is not too pronounced, then physical activity should be maintained whenever possible.
For some time, the patient needs to completely give up lifting weights, from working in conditions of high vibration. No less dangerous are excessive static loads, being in asymmetric positions, including prolonged sitting. To a minimum, it is necessary to reduce work at the table, at the computer, etc.
Implementation of complexes of physiotherapy exercises. During the first 14 days, the patient should take daily walks, ride a bike or exercise on an exercise bike. In the future, you can move on to aerobics. A set of exercises should be aimed at strengthening the muscles of the spine and the muscles of the anterior wall of the peritoneum.
Well, if physiotherapy exercises will be supplemented with water aerobics and massage. This will prevent the recurrence of protrusion and exclude its formation in other parts of the spine.
Be sure to properly organize a place for a night’s rest. The mattress should be chosen semi-hard, it is best if it is an orthopedic mattress. It is possible to completely refuse the pillow.
With regard to fixing devices, such as lumbar corsets, they can be used for no more than four hours a day. Doctors recommend using such devices before the upcoming dynamic or static load.
Medication
As for the medical correction of disc protrusion, the patient is prescribed the following drugs:
Analgesics. To reduce pain during protrusion of the intervertebral disc, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Muscle relaxants. It is possible to notice an improvement in prima from muscle relaxants only at the initial stages of protrusion formation.
Preparations-chondroprotectors. These drugs do not affect the symptoms of the disease, but its course. Reception of chondroprotectors helps to stop the process of disk destruction. However, they will take a long time to take. The maximum therapeutic effect can be achieved when using third-generation drugs in which Glucosamine is combined with Chondroitin sulfate.
Warming up the affected area gives a good effect: dry heat, electrophoresis with drugs, paraffin applications, exposure to ultrahigh and ultrafrequencies. Procedures based on hyperthermic effects can reduce pain and relieve muscle spasm. Any physiotherapy techniques (magnetotherapy, acupuncture, UHF, etc.) can only be prescribed by a doctor, since they all have certain contraindications.
A good effect is the traction of the spine, due to which there is an increase in the distance between the vertebrae. As a result, the load is removed from the disk, which allows you to stop the progression of the disease, and the hernia does not form.
Surgery
If conservative therapy does not give the desired effect for 8-16 weeks, then the question arises of the need for surgical intervention.
For disc protrusion without rupture of the annulus, percutaneous discectomy or nucleoplasty is used. This is a minimally invasive technique that is performed on an outpatient basis. During the operation, a cannula is inserted into the intervertebral disc, through which a laser is inserted, or an electrode that supplies cold plasma. With their help, the nucleus pulposus is destroyed, as a result of which the pressure inside the disc drops. The annulus fibrosus and the posterior longitudinal ligament pull the protrusion inward and the protrusion is removed. The entire procedure is performed under X-ray control.
In 85-90% of cases, it is possible to refuse nucleoplasty, since conservative treatment in combination with physiotherapy exercises produces a sufficient effect. However, the patient must understand that maintaining physical activity to ensure the normal functioning of the spinal column will be required throughout life. Otherwise, the pathological process will continue to progress, and the patient will form an intervertebral hernia. Therefore, it is so important to engage in physical education, gymnastics and swimming. You should also avoid finding the spine in the wrong position, refuse to lift weights, and monitor body weight.









