

Proteins (protein – from the English “protein”) are a complex macromolecular compound consisting of many amino acids connected in a chain by a peptide bond. Protein is the most essential building material for all living organisms.
Protein plays an essential role throughout a person’s life. The body uses it to build new tissues, hair, nails. Protein molecules are involved in the most complex biochemical processes, the synthesis of enzymes, hormones. Bone, muscle, cartilage, skin and blood contain a high percentage of protein (protein).
Proteins play a crucial role in basic vital functions:
Transport molecules throughout the body.
Promote the regeneration of damaged cells, form new ones.
Protect the body from pathogenic bacteria, viruses.
They ensure the normal growth of the body, the development of children and adolescents.
Ensure the normal course of pregnancy.
Lack of protein in the body leads to dysfunction of the internal organs. In a severe case, a person loses the ability to grow, loses muscle mass, and cardiac and pulmonary activity is disturbed. Without adequate complex therapy, protein deficiency leads to premature death.
The value of protein for the body
For normal life, the body requires 22 amino acids – 13 of them it can synthesize on its own, and 9 come with food. Amino acids are formed during the digestion of protein. The variety of amino acids is explained by combinations of proteins, the general list of which consists of more than one hundred thousand items.
Proteins take on the bulk of cellular processes. Thanks to them, the structure of tissues is updated, the internal organs of a person fully function. Proteins are part of every cell, all internal systems, all types of tissues, mucous membranes. Special protein compounds perform enzymatic and hormonal functions in the body.
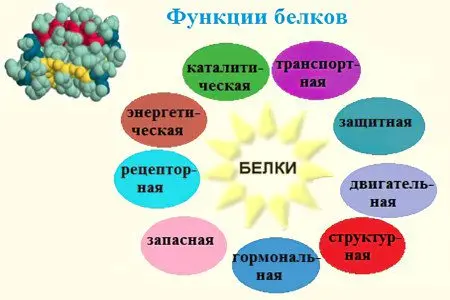
Functions of proteins in the human body
Physiologists distinguish 9 main functions of proteins:
transport. Hemoglobin is a protein compound and is the main component of blood. It ensures the attachment of oxygen molecules and its transfer to all internal organs and tissues. Carbon dioxide is transported back through hemoglobin.
Construction. Proteins are an active component in the formation of new cells and intracellular structures. They are an essential factor in cell membranes, hair, tendons.
Protective. To neutralize pathogenic microorganisms, foreign bodies, antibodies are required – special proteins that are formed as a result of complex immune reactions. In stopping bleeding, the leading role is played by fibrin, a protein formed from fibrinogen.
Regulatory. The metabolism of nutrients is impossible without hormones, which include a variety of proteins. For example, insulin is needed to regulate blood glucose levels, glycogen synthesis. Thanks to him, there is an active transformation of carbohydrates into fats.
Motor. The functioning of muscle fibers is impossible without special contractile elements. This is nothing more than proteins – actin and myosin, which carry out the function of contraction of skeletal muscles and smooth muscles of some internal organs.
Signal. External signals pass through the protein structures of cell membranes. The protein converts the impulses and transmits them directly to the cell nucleus.
The storing. In animals, protein accumulates only in the form of milk casein or egg globulin. In the human hematopoietic system, over time, the breakdown of hemoglobin occurs with the further preservation of iron. This specific process leads to the formation of the ferritin complex. A decrease in ferritin levels is a signal of iron deficiency anemia.
Energy. The assimilation of 1 gram of protein provides the body with 17,6 kJ of energy. First of all, proteins break down into amino acids, and then into final elements – water, carbon dioxide, ammonia. Proteins are included in the process of energy formation only when all other components are used up.
Catalytic. Special protein elements are responsible for accelerating biochemical processes. With their participation, the main processes in a living cell occur.
[Video] Nutritionist, therapist Artut Alekhin will talk in detail about the role of protein in the human body:









