Contents
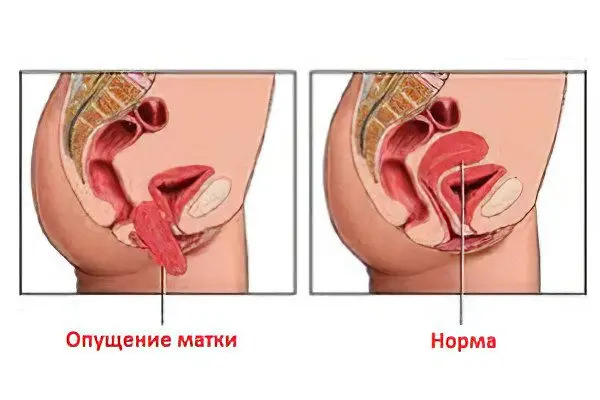
Prolapse of the uterus is the incorrect position of the uterus, the displacement of its bottom, as well as the displacement of the cervix below the level of the normal border due to the weakness of the muscle fibers of the pelvic floor and ligaments. Pathology is accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms: a feeling of pressure, a feeling of discomfort, patients are disturbed by pulling pains in the abdomen and vagina. Patients may experience difficulty urinating, vaginal discharge. The disease is complicated in some cases by partial or complete prolapse of the organ.
The prolapse of the uterus or its prolapse is the most common variant of the abnormal location of the internal genital organs. The prolapse of the uterus is accompanied by a displacement of the cervix of the organ and its bottom below the normal border, however, the cervix is not visible from the genital slit even with attempts. If the uterus extends beyond the genital slit, then this is regarded by experts as one of the symptoms of uterine prolapse. The downward displacement of the uterus serves as the first harbinger of partial or complete prolapse of the organ. In the advanced stage of the process, the uterus or part of it may be outside the vagina.
Prolapse of the uterus is one of the frequent pathologies of the abnormal location of the pelvic organs in women of any age. The frequency of diagnosing uterine prolapse increases in older age populations. More than 50% of all recorded cases are found in women who have crossed the fifty-year milestone.
The correct position of the uterus in the small pelvis is provided by the ligamentous-muscular apparatus. To maintain the anatomically correct position of the organ, the tone of the muscular walls of the uterus is important. The pathology is based on weakness of the ligaments and muscle fibers. The clinical picture of uterine prolapse includes symptoms such as a feeling of pressure on the lower abdomen and pain of similar localization. In addition, a woman is diagnosed with dysmenorrhea, bloody discharge from the vagina. Possible violations of the activity of the lower intestine, urinary incontinence.
Causes of uterine prolapse

Prolapse of the uterus is very common in patients of any age, but if at the age of 30 years the pathology is determined in 10% of women, then over the age of thirty and under forty the disease worries 40% of patients. In patients older than 50 years, 50% of women suffer from uterine prolapse. Of all the operations that are performed in gynecology on the genitals, 15% are operations for the prolapse or prolapse of the uterus.
The reason for the prolapse of the uterus is most often the weakening of muscle tone and the ligamentous apparatus of the pelvic floor, which is accompanied by a displacement of the rectum or bladder. Often the disease is accompanied by a violation of the work of these internal organs.
Uterine prolapse may begin in youth and progress over time. When the organ is lowered, functional disorders become more pronounced, which is accompanied by moral and physical suffering and is the cause of complete disability.
The failure of the ligaments and muscles that hold the uterus can be caused by various reasons.
Factors leading to uterine prolapse:
Genetic predisposition;
Congenital anomaly in the formation of the pelvic organs;
Incorrect management of childbirth, complications of labor activity;
Age-related dystrophic changes;
Hormonal imbalance during menopause;
Surgical intervention on the pelvic organs in history;
Irregular weight lifting;
Formation of neoplasms affecting the anatomy and functioning of the uterus (cyst, myoma, fibromyoma);
Pathology of the connective tissue of the ligaments holding the uterus.
To damage the muscles that hold the uterus, lead to perineal ruptures in the breech presentation of the fetus. Muscles and ligaments can be damaged when using a vacuum extractor or obstetrical forceps during delivery.
Risk factors include frequent childbirth, excessive physical labor, heavy lifting, age of patients, hereditary factors, high intraperitoneal pressure, obesity, tumors, constipation, severe cough.
Fibroids and other neoplasms provoke uterine prolapse due to an increase in the load on the ligaments of the small pelvis. A long-term strong cough can also contribute to the displacement of the uterus due to the constant tension of the muscles of the diaphragm.
In most cases of the disease, the clinical picture of prolapse develops with a combination of several prerequisites.
Degrees of uterine prolapse
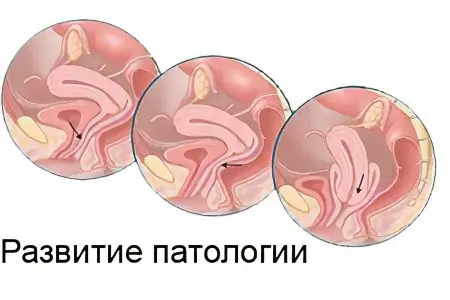
In its development, the disease goes through several stages.
There are 4 degrees of pathological changes:
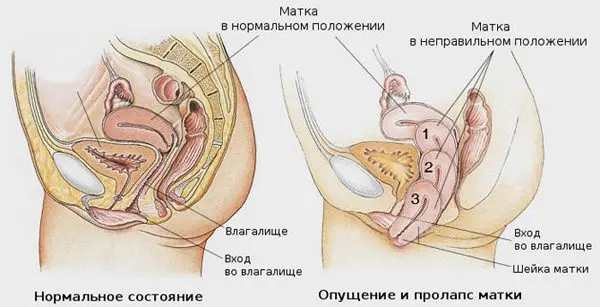
First degree – the uterus or its cervix are mixed relative to the norm by an insignificant distance. The walls of the vagina are slightly lowered. The lower border of the neck is not visible during physical exertion. The genital slit may gape.
Second degree – the uterus partially falls out, with physical exertion, the cervix exits through the genital slit.
Third degree – incomplete prolapse of the uterus is diagnosed, when straining, both the cervix and part of the uterus come out of the vagina.
Fourth degree – the uterus completely falls out.
Symptoms of prolapse of the uterus

The clinical picture is manifested by a large number of vivid sensations, so the diagnosis is not difficult.
Symptoms of pathology:
Feeling of pressure on the bottom of the pelvis;
Pain in the lower abdomen, “gives” to the lower back and sacrum;
Sensation of a foreign body in the vagina;
Bloody vaginal discharge (does not always appear);
Impaired urination;
Soreness during sexual contact, the inability to carry it out in the last stages of the development of pathology;
Painful and heavy menstruation, leading to the development of anemia;
Violations of the menstrual cycle.
Without treatment, the symptoms of uterine prolapse progress. Initially, the disease is manifested by pulling pains, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, in the region of the sacrum, lower back; in the vaginal area there is a sensation of a foreign body. During sexual intercourse, patients are concerned about pain and spotting. In patients, the menstrual function changes, the discharge becomes abundant or scarce. Pathology is accompanied by infertility, but the onset of pregnancy is not excluded.
Over time, disturbances in the functioning of the urinary tract join the manifestations of the disease, they are observed in half of the patients. With a prolonged course, prolapse of the uterus provokes stretching of the walls of the ureters and kidneys. The downward displacement of the uterus may also be accompanied by enuresis.
In every third case, women have complications from the rectum: constipation, colitis, incontinence of feces and gases occur.
In the later stages of the development of the disease, a woman can independently feel the uterus protruding from the vagina.
Consequences of uterine prolapse

Violation of urination during uterine prolapse causes the development of an infectious process due to the addition of a bacterial component – inflammation of the kidneys, bladder, urethra.
Approximately 30% of patients are diagnosed with proctological pathologies:
Colitis;
Constipation;
Fecal incontinence;
Flatulence.
The surface of the uterus protruding from the vagina is covered with cracks. When walking, the body is subjected to mechanical stress, the risk of infection, bleeding ulcers, pressure sores increases. The tissues of the uterus swell, become bluish in color, cyanosis appears. The cyanosis of the organ is due to stagnation of blood due to a violation of microcirculation in the vessels of the uterus.
Severe complications of uterine prolapse – varicose veins of regional veins, infringement of the organ in the last stages of prolapse, infringement of part of the intestine.
Treatment of uterine prolapse
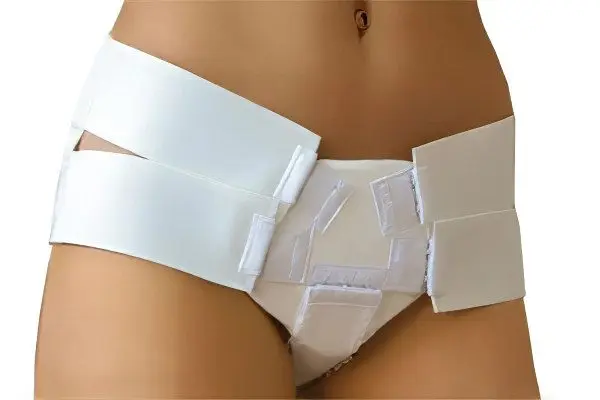

The tactics of treating uterine prolapse, chosen by the doctor, depends on how far the pathological process has gone, whether the woman plans to have a child in the future.
The use of drugs. Conservative therapy can be effective at the stage of slight displacement of the uterus and its cervix. To improve the blood supply to the organ, ointments and drugs with estrogen for oral use are prescribed.
Gynecological massage. At the beginning of the disease, gynecological massage is used, conducted in courses with a break. Massage is performed by a specialist on a gynecological chair for 10-15 minutes. Pain during the procedure is a reason to stop the manipulation.
Physiotherapy. At the first stage of the development of prolapse, gymnastics according to Yunusov is prescribed. Kegel exercises should be done to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
Wearing a bandage. The method is used as a preventive measure at the initial stage of the disease. Properly worn bandage supports the uterus in an anatomically correct position, allows you to get rid of pain and discomfort. The bandage is widely used to restore the elasticity of the pelvic tissues after childbirth and after operations to restore the ligamentous apparatus of the uterus.
The use of pessaries. If a woman is contraindicated in surgical correction of uterine prolapse, at stages 3-4 of the pathological process, the doctor recommends that she install a pessary – rubber or PVC rings to hold the uterus in the correct position. After a month, the ring is removed, as you need to take a break. Every 3-7 days of wearing the pessary, it is briefly removed for aseptic processing and protection of the vagina from bedsores. Cons of wearing a pessary – the vagina is stretched, the uterus drops even more.
Operative therapy
If possible, the doctor tries to save the uterus, because when it is removed, the risk of other organs being missed increases.
Groups of operations for the treatment of uterine prolapse:
Colpoperine levatoroplastika – strengthening the muscles of the pelvic floor;
Plastic surgery of the ligaments of the uterus – shortening and suturing them to the anterior wall of the organ;
Strengthening the cardinal and sacro-uterine ligaments that fix the uterus – the reproductive function may be impaired;
Suture of the uterus to the walls of the pelvis – to the sacrum, to the pubic joint;
Implantation of endoprostheses;
narrowing of the vagina;
Removal of the uterus if there is a good reason.
These operations are performed in several stages, by laparotomy, through the vagina, by the method of abdominal surgery. In 30% of cases, a recurrence of pathology occurs.
After surgery, carrying weights over 5 kg, sexual contact, and any physical activity are limited for a month and a half.
Prevention

Although uterine prolapse is rare in young women (only 10%), the onset of the disease should be prevented from adolescence. Prevention consists in strengthening the muscles of the press and small pelvis, dosed physical activity. To prevent uterine prolapse, significant physical exertion should be avoided.
Women suffering from constipation must follow a special diet, take laxatives.
To prevent prolapse of the uterus, it is necessary to conduct a qualified pregnancy and childbirth. Women should promptly follow all the recommendations of the doctor leading the pregnancy, give birth exclusively in maternity hospitals and perinatal centers.
Immediately after the birth of a child, it is necessary to limit physical activity, apply a set of exercises to maintain the muscles of the pelvic floor and abdominal wall. It is desirable that the optimal load, the frequency of exercises and the start of training be determined by a specialist in physiotherapy exercises.
During menopause, the risk of developing uterine prolapse increases, so the following measures should be taken:
Engage in physical therapy;
Take drugs to increase the tone of the ligamentous apparatus of the uterus and improve its blood supply;
As prescribed by the doctor, use hormone replacement therapy.
Exercises to prevent uterine prolapse
There are simple exercises to prevent the development of prolapse:
“Lift” – the execution begins with a smooth tension and relaxation of the muscles of the perineum for 4-5 seconds alternately. Then the time of tension and relaxation is increased to 20 seconds. After that, the rate and duration of stress cycles is increased by the maximum possible duration in time.
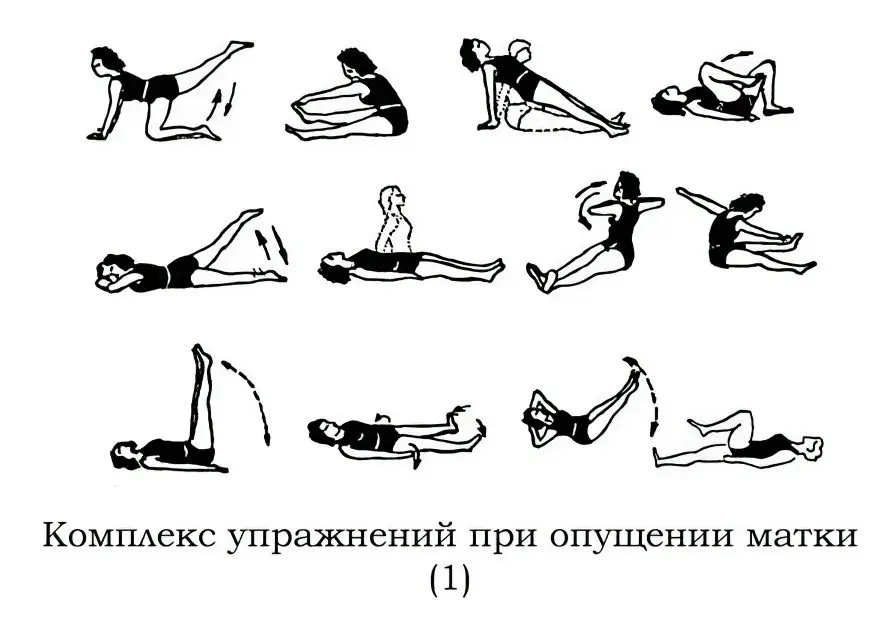
“Bicycle” – lie on your back, bend your knees, “pedal” as if riding a bicycle.
Lie on your back with your legs extended. Alternately raise them at an angle of 45 °, holding in an elevated position for 5-6 seconds, constantly extending the time (up to 20 seconds).
Lie on your back, bending your knees. Lean on your elbows, raise your pelvis, tighten the muscles of the perineum. Hold in this position for 4-5 seconds, relax, repeat the exercise several times.
Lie on your stomach, alternately raise and lower your limbs, bending your back.
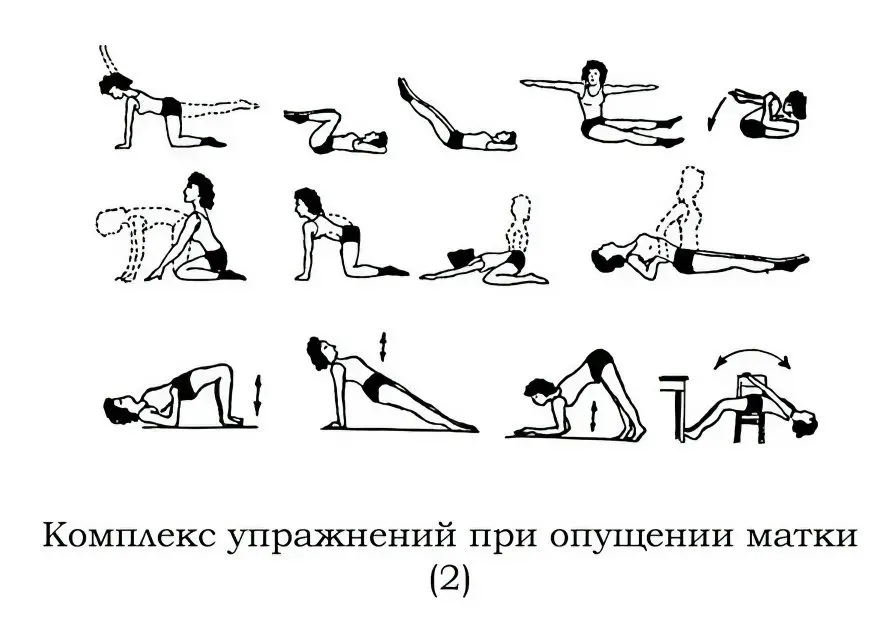
Gradually, the number of approaches increases from 6-7 to 20-22 in one session.
The duration of a daily workout is 30-40 minutes. Such care for your health will reduce several times the risk of uterine prolapse, the development of pathologies of the pelvic organs and lower intestines.









