Contents
When constructing any drywall construction, a base is needed – a frame on which the GKL sheets are attached. This frame is assembled by technology from special products – profiles. About what a drywall profile can be, its types and sizes, scope – in this article.
Materials: what profiles for GKL are made of
A profile for drywall of any kind is made of steel and aluminum. Steel (plain or galvanized) are more common, since aluminum, although they have excellent characteristics, are very expensive.
Steel can be ordinary or with a protective layer – galvanized. Ordinary – made of black steel – have a lower cost, suitable for rooms with normal operating conditions. With their help, they make a false ceiling, walls and partitions, arches in living rooms, corridors. In rooms with high humidity – bathrooms, kitchens, etc. – it is better to use galvanized steel or aluminum.
Types and sizes of drywall profiles
In any place that sells materials for drywall, there are profiles of various types and sizes. To choose and not be mistaken, you need to know how they differ.
To create wireframes
There is a profile for drywall of the following types:
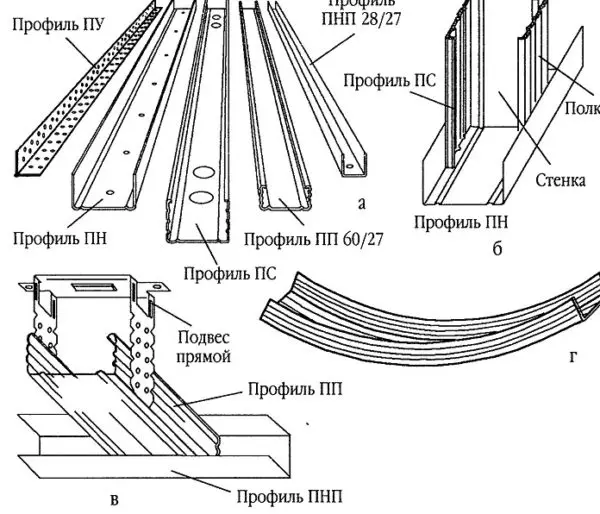
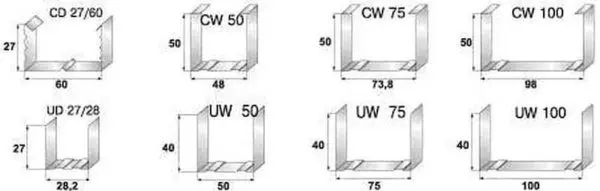
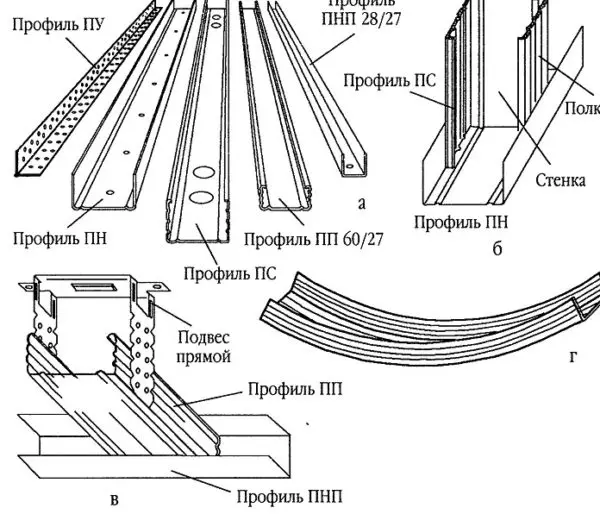
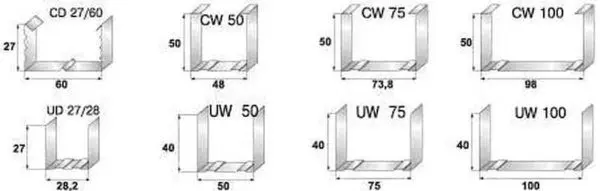
- guide. It is designated as PN (UD) (decoding – guide profile). U-shaped in cross section, with smooth sidewalls. It is used as a base-support for racks and lintels. It is attached along the perimeter of the structure, then all other elements of the system are installed into it. Dimensions:
- 28*27mm;
- 50*40mm;
- 65*40mm;
- 75*40mm;
- 100*40 mm.

The guide profile for drywall can be distinguished by smooth shelves
- Rack-mounted. Designated PS (CD) – rack-mount profile. It is inserted into the guides, and the plasterboard is attached to it. Accordingly, it bears the main load and must have high rigidity. It has a U-shaped structure with additional shelves and stiffeners, which give it greater rigidity. Dimensions:
- 50*50mm;
- 65*50mm;
- 75*50mm;
- 100*50 mm.

Rack profile for drywall has additional stiffeners and shelves
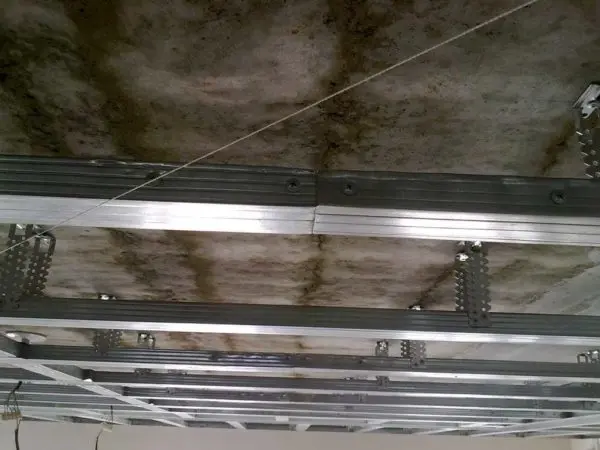
- Ceiling. Designated PP and PPN. Accordingly – the guiding and supporting ceiling profile. The ceiling guide has a section in the form of the letter “P”, has a smaller section than the wall guide. Ceiling bearing profile – has shelves and stiffeners, but differs in shelves of a lower height. A lower height, in order to “take away” less height from the room and that the plasterboard ceiling is thinner, creates less load on the frame.
- 60*27 mm – PP;
- 28*27 mm – PPN.

The ceiling profile is also guiding and supporting. Differ in smaller sizes (compared to wall-mounted)
- Arched. It has a complex structure – with cuts on the side faces for increased flexibility. Needed to create curved surfaces.
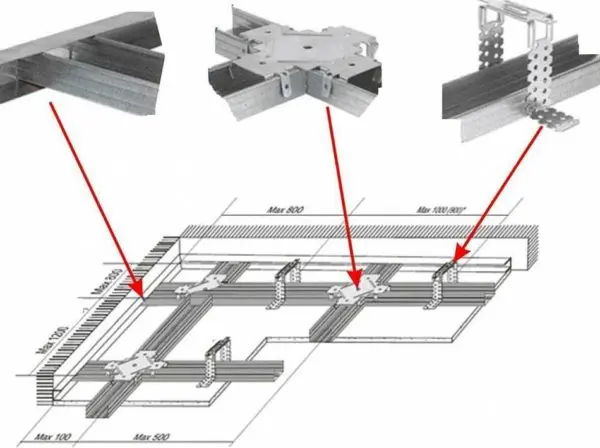
These are all types of drywall profiles that are used to build a frame. A “frame” is assembled from the PN guides, PS racks are inserted into them, which are then connected by jumpers (usually from PN) – for greater structural rigidity.
Additional profiles and accessories
There are several types of additional profiles that are used in finishing work, when creating a suspended frame for the ceiling, for attaching rack profiles to walls, etc.
- Angular. In section – a right angle with a slightly protruding central part. Used to decorate the corners of plasterboard structures. There are several types:
- Both shelves are perforated with large holes – so that the corner becomes part of the plaster, due to which they are held.
- Corner profile for plasterboard with mesh. A strip of mesh can be glued to the edges of the perforated corner – for better adhesion with subsequent finishing.
- On a paper basis – two metallized strips are pasted on thick paper. They are used in unloaded places – they make out window openings, the edges of niches, shelves and other similar products.

Corner profile – to form and protect the corners of drywall constructions
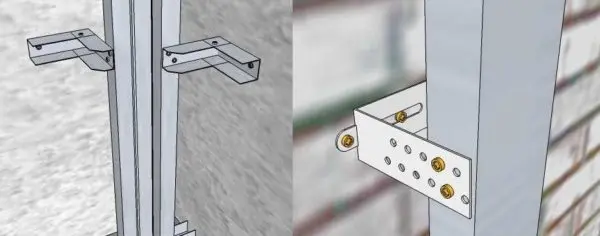
- Perforated hangers. This is a fastener in the form of a tape 125 * 60 mm. It is divided into three parts. The middle one is used to fix the suspension to the ceiling / wall, the outer ones are perforated, bent at 90 °, profiles are attached to them.

Perforated hangers and how to use them - Anchor hangers for PP (ceiling profiles). There are several types. Used in the installation of suspended ceilings. A distinctive feature is that it is easy to adjust the height, which is necessary when setting the ceiling plane.

Anchor hanger – for easy adjustment of the false ceiling height - Single-level and two-level connector for software (crab). Plate with fixing elements for fastening crossed profiles. It is used in the construction of frames for suspended ceilings.

Connectors – single-level and double-level - Profile extension. Small staple (110*58 mm) for splicing two pieces of the same type and size.
Most of these devices can be dispensed with. For example, two profiles are spliced using a piece of a guide profile of a suitable size. It is inserted inside, the shelves are crimped with pliers, screwed with self-tapping screws. The connection is more rigid than with special devices.

When creating a frame located along the wall, it is fixed not with perforated hangers, but with boots – sections of profiles bent in the form of the letter “G” (called “boot” – according to its characteristic shape).
This is not so much a way to save money, but an opportunity to get a more rigid mount, since perforated hangers were originally developed for suspended ceilings and the load from wall drywall, and even laid in two rows, is difficult to withstand.
Profile length
Profile for drywall of each type may vary in length. Standard length – 2,4 and 2,8 meters. but there are up to 4 m.

Should I look for long profiles? It doesn’t make much sense. Unless the assembly of the frame will speed up a little. The profiles under the GKL are perfectly spliced, while the strength of the structure does not suffer. Only when assembling the frame, it is necessary to make sure that the joints on adjacent racks are not at the same level. Usually joints are made alternately at the top, then at the bottom.
How to choose a profile for GKL
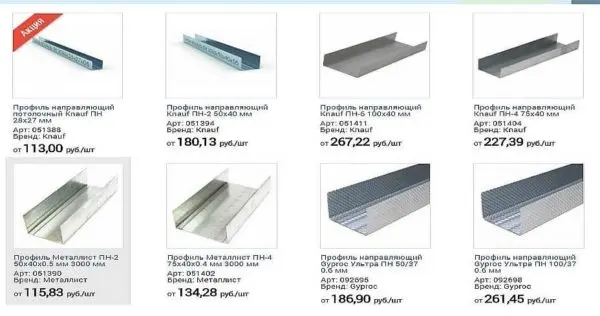
In a more or less large hardware store or even on the market, there are drywall profiles of the same type and length, but with a significant difference in price. The cost can vary twice, and sometimes more. Moreover, the most expensive ones are usually Knauf, the cheapest ones are unnamed China, the middle range is domestic manufacturers.
Metal thickness
The difference will become clear as soon as you take the profile in hand. Some are strong, rigid, made of steel with a thickness of 0,5 mm, 0,55 mm, 0,6 mm and more. Others are made of such thin metal that they change their geometry even if the profile is lifted by one edge.
With this parameter, everything is more or less simple and clear. The thicker the metal, the stronger and stiffer the profile, but the price is also higher. It is optimal to create partitions with a standard wall height to take profiles with a metal thickness of 0,5 or 0,55 mm. If possible, you can take 0,6 mm.
It makes sense to take a greater thickness of the metal only if the height of the partition is large – the load will be more significant and additional strength will not hurt. But in this case, you need to look at what will cost less – a profile for drywall made of thicker metal or more often installed racks and crossbars. Just keep in mind that racks are usually installed in increments of 60 cm – so that the joint of the GKL sheets falls in the middle of one of the rack profiles. With a decrease in the step, the same thing is required – the joint of drywall sheets should not hang in the air. So it will be possible to put them only after 40 cm. So the seam will also have to be on the profile. But this is too many racks and is unlikely to be cheaper. In general, consider.
Manufacturer selection
Choosing a manufacturer of drywall guides is both simple and difficult at the same time. All experts unanimously claim that the best are Knauf (Knauf). They always correspond to the declared parameters, have an ideal geometry: the racks fit perfectly into the guides, do not hang out and do not burst them. In general, working with Knauf drywall profiles is easy, simple, work is progressing quickly. But, this is just the most expensive of the entire range. Despite this, the advice is this: if you have no experience with drywall, you better buy Knauf.
There are several Russian firms in the middle price range. These are Giprok (Giprok) and Metallist. There are also regional little-known campaigns. Here’s how lucky. Trust your feelings and feedback. It is not always possible to focus on the words of sellers. Domestic manufacturers have good batches, there are unsuccessful ones. In most cases, there is such a problem as a mismatch in the dimensions of the rack-mounted PS and guide PN profiles. Racks must be accurately installed inside the guide. To do this, with the declared width, for example, 50 mm, the actual width should be 1,5 mm less. Here, with the accuracy of observing this difference, problems arise. In addition, the declared thickness of the metal must be checked (with a micrometer). In general, it will work out to save money, but you will spend a significant amount of your nerves and time.

Giprok has a profile with a corrugated surface. All sides of the profiles – both the back and the shelves – have extruded “pimples”. They increase the rigidity of the profile. This is true – the design is more rigid. But the connection of the racks and guides is more clumsy – due to the mismatch of the “pimples”, they are not attracted closely like the smooth walls of the metal. There is a second point – structures from such profiles creak more. With all this, such profiles cost a little less than Knauf, but working with them is more difficult. In general, it’s up to you.
How to count the number of profiles
Knowing what type and type there are profiles for drywall, their dimensions are not enough. It is necessary to calculate the number of each type. It will be easier to count if you draw a frame plan on a piece of paper, sign the names of the profiles, put down the dimensions. This will not take much time, but it will help to more accurately determine the quantity.

Calculation of the number of guides for one wall
If the walls are very uneven, you can level them with drywall. A parallel wall is arranged, but set strictly according to the level. In this case, the calculation of the number of drywall profiles will be as follows:
- Guides – PN. They are mounted around the perimeter. To find the footage of guide profiles for wall sheathing, we measure its length and height, add and multiply by 2. If there are windows / doors on the wall, the guide profile is mounted around the perimeter of these openings. To the resulting figure we add twice the height of the opening and its width.

This is what the frame for the partition looks like - Rack profiles for GKL – SP. As already mentioned, they are placed in increments of 60 cm. Moreover, the extreme opening cannot be more than 60 cm. Even if 10 cm remains, an additional stand is placed. First, we count the number of racks: divide the length of the room by 60 cm, add one more – the corner one. For example, the length of the room is 4,75 meters. 475 cm / 60 cm = 7,91 pcs – this will be 8 racks + 1 corner, total – 9 pcs. Next, we look for the footage – the figure found is multiplied by the height of the room. We get the required length for the racks: 9 m * 3,2 m = 28,8 m.
- Jumpers. Rack profiles are used. They are placed in increments of 60-80 cm, but at the same time, the vertical joints of drywall sheets should also fall on such a partition. Here you will have to count depending on the selected step, and then add the figure found to the one that was calculated in the previous paragraph.
If all the walls in the room are sheathed with plasterboard, a similar calculation is carried out for each wall, then the results are summarized.
Number of drywall profiles for false ceiling – PP and HDPE
The calculation here is a little simpler: the frame is assembled “in a cage”, so it’s easier to calculate it. The rest of the approach is the same as described above. So we consider:
- The footage of PP profiles for suspended ceilings is equal to the perimeter of the ceiling. We measure the length and width of the room, add and multiply by 2. This will be the desired number. For example: a suspended ceiling will be made in a room measuring 3 * 4 meters. Calculation of the footage of PP profiles: 3m + 4 m = 7 m, 7 m * 2 = 14 m. For this room, you will need 14 meters of the PP profile.

First, guide ceiling profiles are mounted - PNP profile footage. It is better to place load-bearing profiles along a short wall. In this case, we divide by 60 cm the size of the longer wall: 400 cm / 60 cm = 6,66 pieces, rounded up – 7 pieces. It is not necessary to add a corner post, since a guide profile will be filled around the perimeter and the posts are tucked into it. Carriers from the PNP profile are located along the short side (in this example, it is 3 meters), that is, the required length of this type of profile is 7 pcs * 3 m = 21 meters.
- Next, we consider the number of PP profiles for partitions – segments 60 cm long, which are installed between two adjacent carrier profiles. In this case, the partitions will be located along a long wall. Therefore, we consider this: 300 cm / 60 cm = 5 pcs, and the total length will be 5 pcs * 4 m = 20 m.
In total, for a false ceiling in a room measuring 3 * 4 meters, you will need 14 m + 20 m = 34 m of the PP profile, 21 meters of the PNP profile.