Contents
Proctosigmoiditis is a dangerous inflammatory bowel disease. Even after treatment, a relapse of the disease is possible from simple stress or malnutrition – the risk is about 15%. Properly selected treatment and compliance with all recommendations for several years reduce the risk of exacerbations by almost half.
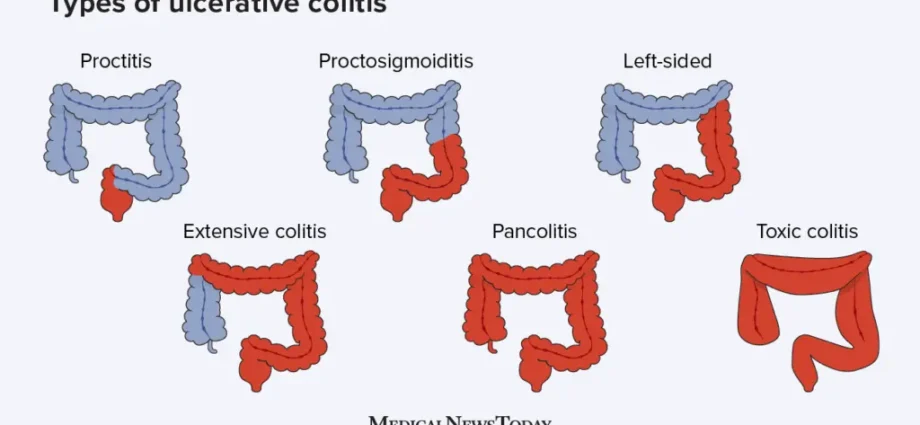
What is proctosigmoiditis
Proctosigmoiditis is an inflammation of the rectum and sigmoid colon. The mucous membrane is affected, as well as the submucosal layer. In this case, the functioning of the intestine is disturbed.
Unlike inflammation of the rectum – proctitis, proctosigmoiditis is more dangerous. The digestive tract ends in the rectum, so there are only muscles and fiber around it. Even if the inflammation spreads to these parts, the risk is less. The sigmoid colon is already in the abdominal cavity, above the rectum. The inflammatory process in it is potentially dangerous for all neighboring organs.
Proctosigmoiditis occurs at any age in any gender. It develops very intensively, and without treatment it quickly becomes chronic. And this means that it will be almost impossible to completely recover – the patient will be tormented by periodic exacerbations of prostosigmoiditis.
The mucosa is the outer lining of the intestine. It is damaged by various external factors. Allergic reactions increase, and immunity is pathologically activated. The production of a special protective enzyme lysozyme, which is capable of destroying the membranes of bacterial cells, is disrupted. As a result, inflammation increases.
Proctosigmoiditis is acute – it begins quickly and brightly, the symptoms are very pronounced. But it can also go into a chronic relapsing form, in which exacerbation and temporary improvement constantly alternate. In a severe case, a chronic continuous form develops – the disease proceeds more weakly, but there is no improvement in the condition at all.
A severe form of the disease reduces the quality of life, people lose their ability to work. Other parts of the intestine are also affected, and the person constantly suffers from unpleasant symptoms.
Causes of proctosigmoiditis in adults
Various aggressive factors affect the mucous membrane, which serves as a barrier between the intestine and the external environment.
Often it is infections and parasites that cause proctosigmoiditis. Pathogenic flora and helminths affect the intestinal mucosa with their toxins, and also damage it mechanically.
The toxic effect of medicines is also possible: heavy antibiotics, constant use of laxatives, alcohol, and other substances. They support chronic inflammation.
Sometimes the body’s own immunity attacks the body: autoimmune intestinal pathology, as well as allergies. Constant eating of food that the body does not tolerate leads to damage to the intestinal mucosa and an increase in the permeability of the membrane.
Poor blood supply affects the condition of the mucosa. In older people, atherosclerosis of the vessels of the mesentery, the organ that attaches the intestines to the walls of the abdominal cavity, is often observed. Often the elderly suffer from constipation. Excess stool stretches the intestines, damages the mucosa. Intoxication with food decay products also occurs.
Violations in the work of other digestive organs affect the state of the underlying departments. For example, with pancreatitis or cirrhosis of the liver, a lack of enzymes leads to poor digestion of food even at the stage of the small intestine. Thus, unprocessed substances pass down to the large intestine, and inflammation develops.
Oncology, as well as the treatment of this disease, can also provoke proctosigmoiditis. Tumor cells release toxins into the intestine, causing a pathological immune response. And radiation therapy injures the intestine itself, and not just the tumor.
Symptoms of proctosigmoiditis in adults
The severity of symptoms depends on the cause of the disease. But the symptoms themselves are quite similar: all patients feel pain in the lower left side of the abdomen. The pain can “give” to the lower back, groin, during defecation, it intensifies. The anus itself also hurts and itches.
At the same time, the urge to defecate is frequent and false; after going to the toilet, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the intestine persists. The stool is upset, diarrhea and constipation alternate. In the feces, impurities of mucus are visible, and even pus with blood. Sometimes mucus is secreted from the anus involuntarily, even outside of going to the toilet.
With a severe degree of proctosigmoiditis, general well-being worsens, the temperature rises, the patient eats little, he is shivering, and weakness develops.
Treatment of proctosigmoiditis in adults
The proctologist and gastroenterologist are engaged in the treatment of this disease. Severe forms of proctosigmoiditis require hospitalization.
First, the cause of the disease is found out, and the main treatment depends on this. After it, all patients with proctosigmoiditis are prescribed complex therapy. It is aimed at reducing inflammation and improving the healing processes of the intestinal mucosa.
Regardless of the cause, all patients adhere to a strict diet. The food is cooked soft, steamed and water, they eat fractionally in small portions. Pureed dishes are good. All food that irritates the mucous membrane and causes gas formation is excluded: fried, spicy, smoked, fresh fruits, etc.
Microclysters with special therapeutic solutions, as well as warm sea buckthorn oil, also help well. They reduce inflammation and help mucosal cells regenerate. Sometimes sitz baths are used with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, which has an antiseptic effect. There are many rectal suppositories that a doctor prescribes depending on the cause of proctosigmoiditis. They fight pathogenic flora, soften the mucous membrane, relieve inflammation.
Diagnostics
The proctologist collects an anamnesis: interviews the patient, finds out when the problem arose and how it manifests itself. It is important to remember these details and tell your doctor.
Next, the doctor palpates the abdomen – usually there is pain on the left, rumbling in the sigmoid colon.
An important, but unpleasant moment in the diagnosis is a digital examination of the rectum. Up to 80% of all rectal tumors are diagnosed by this method, it is extremely effective. The doctor feels the affected area. The sphincter at the same time spasms, so the examination is unpleasant. The rectal mirror helps to examine – you can assess the condition of the mucosa for 10 cm.
To examine a larger area, sigmoidoscopy and fibrocolonoscopy are used. A special tube with a camera is inserted to determine the extent of the lesion. Tumors are excluded, suspicious areas are taken for a biopsy.
Stool tests are prescribed: there are a lot of leukocytes, inflammatory cells in it, helminths or bacteria can be detected if they are the cause of the disease. It also turns out which antibiotics the bacteria are sensitive to.
Additionally, a blood test may be required. It has all the signs of inflammation – increased leukocytes, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, etc.
Modern treatments
Antibiotics and antiparasitics are effective if proctosigmoiditis is caused by infection or helminths. Antibiotic therapy is adjusted when test results are obtained and it is known which drugs the bacteria are most responsive to.
Antispasmodics and carminatives help reduce pain. They reduce cramps, reduce bloating. The intestinal wall is less stretched and the pain is also reduced.
If digestive problems are found, enzymes are prescribed. Their enzymes are sometimes not enough for the normal digestion of food, they are replaced with artificial ones. The affected beneficial microflora is helped to restore probiotics.
In severe cases, corticosteroids are prescribed. They suppress the immune system if it is activated more than necessary and “hit” its own cells. This helps relieve inflammation.
Prevention of proctosigmoiditis in adults at home
Compliance with the diet and diet most effectively helps to avoid such problems. It is also important to observe the drinking regime, to avoid constipation.
It is necessary to play sports, to prevent stagnation of blood in the pelvic area, especially if you sit a lot.
To avoid infections, you need to maintain hygiene and exclude anal sex. In case of unpleasant symptoms, do not be shy, consult a doctor – delay can cost you your health.
Popular questions and answers
About why it is impossible to treat proctosigmoiditis with folk remedies, and how important it is not to start the disease, will tell surgeon of the highest category, proctologist, Ph.D. Vasily Gavrilov.
Local complications of proctosigmoiditis include bleeding, suppuration, perforation of the colon with the release of feces into the abdominal cavity and a threat to life. A violation of the stool may also develop, such as frequent trips to the toilet or strong urges with abdominal pain, which can significantly reduce the quality of life of the patient.
Common complications include intestinal need, intoxication against the background of excessive absorption of toxic substances from feces, vitamin deficiency states.
Therefore, the meaning of calling a doctor at home or an online consultation is rather doubtful. It is worth contacting a coloproctologist in a hospital, and not calling him at home.
The treatment of ulcerative proctosigmoiditis is a “creative” process, and is a rather difficult task, requiring a doctor-patient tandem with the same interest in the cure.
Ulcerative colitis is really not an appendicitis that has been removed and will not appear again in a person. In the treatment of ulcerative colitis, it is more about remission, the attenuation of the disease for a certain period. And in most cases, with timely access to a coloproctologist or gastroenterologist, you can choose adequate therapy, in which the patient will have a stable long-term remission, that is, the absence of symptoms.