Contents
If vegetables grow on the site, then most likely it also has potatoes. Large areas are allotted for this root crop, so it is not always possible to arrange the necessary crop rotation. As a result of planting potatoes in one place, she may develop any disease; the most common of the entire list is potato scab. When it occurs, vegetable tubers are affected.
Diseased tubers do not threaten human health, they are quite suitable for use, but their nutritional value is lower than healthy ones. The starch content in the harvested crop in this case is reduced by almost half. But these are not all the “gifts” of the scab. Such potatoes are poorly stored, rot develops faster in it. A rich harvest can also turn into a rich amount of waste: potatoes, for which so much effort has been spent on growing, are simply thrown away. Successfully overwintered diseased tubers, planted again on the site, will not bring a healthy generation. The general damage to the peel extends to the eyes, they will hatch, but will give weak shoots, so you can forget about a good harvest.
Such a disease can be ignored for some time, but it tends to spread rapidly, covering more and more new tubers, and the spores of the disease are very viable, they can successfully stay in the ground for up to 3 years.
Forms of scab and signs of damage
Potato scab, like any serious disease, has several varieties. We will give a description of each here so that you can accurately learn to identify the affected tubers.
There are 3 forms of scab:
- common scab;
- Parsha dusty;
- silver scab.
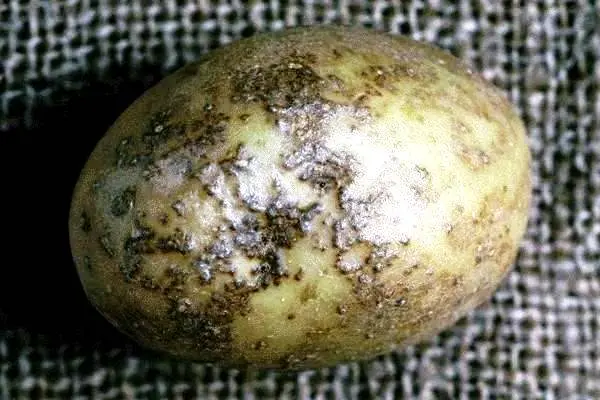

Common scab develops comfortably at high temperatures (+25-30 degrees) and in alkaline soil, depleted in moisture. If you carried out liming of the soil on the site, then this is also a favorable factor for the development of potato scab. The causative agent of the disease is formed on organic residues in the soil and, if favorable conditions are created, passes to the tubers through any mechanical damage to the peel. When storing potatoes, it is impossible to become infected with the disease, so it does not develop, this is possible only in the soil, but when infected, it is preserved until next year and does not disappear anywhere. Only tubers are affected, you can notice this if you dig up the root crop. Visually, these are ulcers that have an irregular shape, with the growth of potatoes, these areas also grow in size and harden. Sometimes the affected areas form cracks. You can even observe the picture when the potato is completely covered with such formations. Scab opens the way in tubers for rot pathogens, both dry and wet. The causative agents of the disease are very viable, they can successfully exist in the soil for years. To this type of scab, varieties with a thin skin or those that have a red color are most susceptible.

Another type of potato scab is powdery scab, generated by a special type of fungus that can move independently and is a small slimy lump. In this case, not only the tuber is affected, the roots and the underground part of the stem become ill. During storage, infected tubers shrink, and if there is a slight excess of moisture in the storage, the potatoes actively rot. A visually diseased tuber is covered with a colony of “warts”. Spots can have a different shape and pronounced relief. When the potato is already dug up, these formations dry up so much that the peel bursts, forming ulcers. These ulcers are filled with dusty brown substance, which includes spores of the fungus and the remains of potato tissues. Similar potato “craters” are shaped like stars with the edges turned inside out. On the roots, the disease manifests itself in the form of the formation of growths of an irregular shape of white color. The source of such a misfortune is disease-infected soil, manure and damaged planting material. Favorable conditions for powdery scab are waterlogged soil, while the temperature can be relatively low – 12-18 degrees. Most often it develops on heavy soils, where it retains its viability for 5 years.
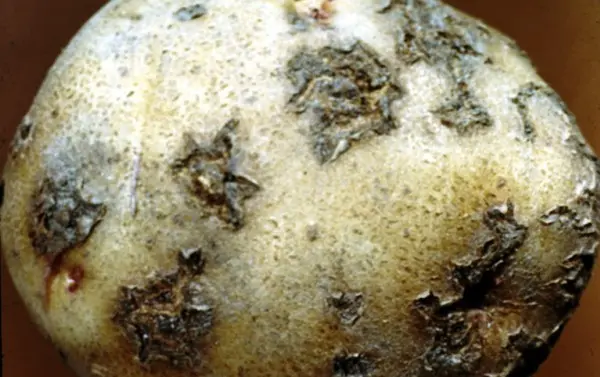
The silvery scab of potatoes differs from previous diseases in the main feature – the affected tuber does not rot during storage. Here the action is somewhat different. Affected tubers lose moisture, and, accordingly, mass. The peel is wrinkled, in places of defeat it has a silvery sheen, lesions are especially noticeable on red-skinned varieties. The causative agent of this type of scab is a type of fungus, it penetrates the tuber through the soil and spreads to other tubers. During harvesting or during storage, gray-brown spots of various sizes form in the potatoes, they can be slightly depressed, if you peel the peel, then black formations are observed under it. The lesions are clearly visible in early spring or on green potatoes. Diseased tubers do not germinate well. This disease is formed when growing vegetables on sandy and loamy soils, if there is an elevated temperature during the period of tuberization. The disease spreads at high humidity – more than 90%, and temperatures higher than 3 degrees.

Methods of prevention and treatment
Each of the forms of scab we have considered has different pathogens, but the result is the same – the potato deteriorates, and the yield of the site drops. Even if you did not find signs of illness on the dug out tubers, this does not mean that it will not come to your garden next year, so you should know not only methods of treatment, but also take preventive measures. And you can fight potato scab in any of its manifestations.
Planting material should be monitored – this is the most important rule. Try to take only healthy, viable tubers for planting. Use measures for pre-treatment of tubers, there are special preparations for this. If, nevertheless, slightly affected tubers are caught in the planting, then during the flowering period of the plants, the potatoes should be watered abundantly with water. Copper, manganese and boron applied during planting significantly reduce the percentage of the disease.

Try to change the place of planting potatoes and alternate it with the planting of legumes. If the place is permanent and there is no way to change it, never apply fresh manure as a fertilizer.
If your soil has alkaline signs, it should be acidified, for this we apply ammonium sulfate solution – 2 tbsp. tablespoons of the substance per 10 liters of water. Water during flowering at the rate of approximately half a liter per 1 bush.
10-14 days before harvesting potatoes, it is useful to mow all the tops so that the potato peel is well strengthened.
After harvesting, plant an empty area with green manure. They will contribute a large warehouse to the improvement of the soil and saturate it with useful substances. It can be cereals (rye, wheat), legumes (lupins, peas), cruciferous (rapeseed, mustard) or mixtures of these crops.
Monitor the state of the environment in the room where the potatoes are stored. Avoid severe waterlogging and heat.

Zircon is able to suppress the development of potato scab. Apply it during the budding period. It’s a growth regulator. Even its single application gives a high positive effect, and the yield increases at the same time.
The drug “Phyto Plus” is able to greatly reduce the damage to tubers. They should treat the planting potatoes and spray the plant during the growing season. Dose for use – 1 sachet per 3 liters of water.
Highly resistant varieties
If your crop improvement measures are ineffective, it is worth considering changing the planted variety. We note right away that varieties that are absolutely resistant to scab have not yet been bred, but there are the most resistant diseases.
Varieties bred by us: Aspia, Bezhitsky, Bryansk novelty, Ramensky, Varmas, Vestnik, Vilnya, Vyatka, Zhukovsky early, Lyubimets, Posvit, Prasna, Reserve, Rodnik, Skoroplodny and others.

There are also foreign analogues: Alpha, Element, Krostotr, Lady Rosetta, Mentor, Nicolas, Ostara, Patrones, Prevalent, Prokura, Saturn.
Don’t forget about preventive measures, even when using varieties that are highly resistant to potato scab, and then your harvest will only please.
Video “Potato scab and how to deal with it”
The video tells about such a potato disease as scab, and about methods of dealing with it.









