Contents
Prader-Willi syndrome – This is a genetic disease that is extremely rare. Its development is due to the fact that seven genes, or their parts, located on the 15th paternal chromosome are absent or cannot function normally. The syndrome was described in 1956 by scientists A. Prader, G. Willi, A. Labhart, E. Ziegler and G. Fanconi.
According to statistics, the syndrome is detected in 1 newborn out of 10-25 thousand. The manifestation of pathology is influenced by the paternal genetic material, since the disturbed part of the 15th chromosome is subject to the phenomenon of imprinting. That is, a copy of only one gene among the genes of a given region will work in full.
Symptoms of Prader-Willi Syndrome
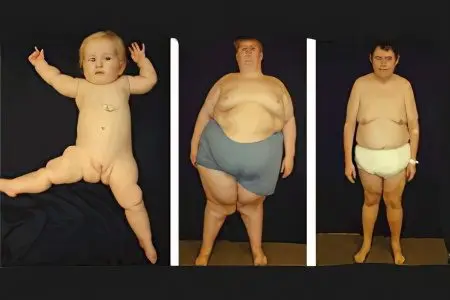
The following symptoms of Prader-Willi syndrome allow the patient to be correctly diagnosed, even if they do not appear in full:
During intrauterine development, the motor activity of the fetus is reduced, women often suffer from polyhydramnios, fetal presentation is detected.
During birth, the child is in the breech presentation, there is lethargy and hypotension. Weak muscle tone affects the sucking reflex, causing difficulties during breastfeeding. The child may experience breathing problems. Hypogonadism syndrome is characteristic of this genetic disease.
In early childhood, the lag in physical development comes to the fore, there are problems in the intellectual plan. The child quickly gets tired, prone to drowsiness. Often strabismus develops. It is for early childhood that scoliosis is characteristic, which is not diagnosed in infancy.
Older children are characterized by speech disorders, overweight is observed. At the age of 2 to 8 years, the child begins to show a tendency to overeat, physical coordination is disturbed, and sleep suffers. Scoliosis continues to progress.
In puberty, adolescents often experience delayed puberty, the growth of such children is lower than their peers. Flexibility is abnormally high, body weight exceeds the norm.
By the age of 18, people with Prader-Willi syndrome suffer from the inability to conceive a child, as they are infertile. The hair on the intimate area is liquid, hypogonadism continues to progress. Obesity, low blood pressure, intellectual problems, learning difficulties are all symptoms caused by existing genetic disorders. In addition, during the period of majority, a person may already be diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, provoked by an existing gene pathology.
Adults with the Prader-Willi symptom have the following external characteristics: their nose is wide and large, their forehead is high, the eyelids are lowered, the eyes are almond-shaped, the upper and lower limbs are small, the fingers are narrow, the body weight is excessive. Compared to other close relatives, the hair and skin of a sick family member is somewhat lighter. The sexual and motor development of a person is impaired, striae form on the skin, there is a tendency to dermatillomania (plucking out skin areas).
Neuro-cognitive impairment
In 1992 Kurf and Freem examined the level of intelligence in people with Prader-Willi syndrome. It was found that the majority of patients (39%) have a slight mental retardation, 27% of patients each had moderate mental retardation, or were on the border of intellectual activity, giving an intelligence level in the range from 70 to 85. With a low average level of intelligence, 5 % of people, and with severe mental retardation 1%. At the same time, profound mental retardation was observed in less than 1% of cases.
It has been established that in childhood, patients have the ability to read, they have an extensive vocabulary. However, speech impairments reduce their comprehension. With difficulty, such people are given mathematics and writing, concentration of attention, visual and short-term memory suffer. Therefore, even despite the level of development of the intellect, problems in these areas do not disappear with age.
Behavioral disorders
Increased appetite leads to the development of obesity.
Compulsive behavior is expressed in an increased level of anxiety and in dermatillomania.
Violations in mental development are manifested in depression, paranoia, hallucinations.
Often, it is behavioral disorders that lead to the fact that patients are hospitalized.
Endocrine disorders
In people with Prader-Willi syndrome, there is a lack of growth hormone in the body, which leads to the development of obesity, increased bone density.
Hypogonadism is the reason that the testicles do not descend into the scrotum in men, and in women there is early sexual hair growth (adrenarche). However, both of these conditions can be corrected surgically and conservatively.
Causes of Prader-Willi Syndrome
The causes of Prader-Willi syndrome lie in genetic disorders. As a result of certain mutations, there is a loss of a section of chromosome 15 of the paternal copy of the genes.
Another cause of chromosomal rearrangements, in addition to gene mutations, are:
Inheritance of two pairs of chromosomes only from the mother (maternal uni-paternal disomy);
Violations resulting from a break in the chromosome or due to unequal crossing over (deletion);
Violations as a result of chromosomal translocations with the transfer of a portion of the chromosome to a non-homologous chromosome.
At the same time, the risk that a second child in the family will be born with Prader-Willi syndrome depends on what caused the perestroika. Thus, uniotsomnia and deletion reduce the risk to only 1%, chromosomal translocations increase it to 25%, and mutations due to imprinting up to 50%. Parenatal testing allows you to calculate all these options.
Diagnosis of Prader-Willi syndrome
Timely diagnosis of Prader-Willi syndrome allows not only to identify existing disorders, but also to begin immediate treatment, which greatly improves the prognosis for the development of pathology.
If earlier the diagnosis was made only on the basis of clinical signs, then modern medicine uses the method of genetic testing. It is mandatory for all newborns with hypotension.
With regard to differential diagnosis, this genetic pathology must be distinguished from Down syndrome.
Treatment of Prader-Willi syndrome
There are no drugs that can completely get rid of genetic disorders. However, drugs for the treatment of Prader-Willi syndrome, or rather for the relief of its symptoms, are under development.
Therefore, doctors recommend that all children with Prader-Willi syndrome be diagnosed without fail to undergo physiotherapy, which is aimed at increasing muscle tone. The learning process must also be adapted to the intellectual capabilities of the child.
Obesity remains a big problem, so it is recommended that such children receive injections of recombinant growth hormone every day. This allows you to control your appetite and also gives you the opportunity to support the increase in muscle mass, rather than adipose tissue.
To rule out obstructive sleep apnea, patients are advised to use a ventilator on an ongoing basis.









