Contents
Potato haulm diseases damage crops and can cause plant death. These lesions are of various origins. Diseases are caused by fungi, viruses and bacteria. Depending on the symptoms, choose a method of treatment.
Causes of potato diseases
Potato diseases can be diagnosed by changing the state of the tops. Usually their pathogens are mixed from the stems to the root system.
There are various reasons why potato diseases appear:
- low resistance of varieties to pathogens;
- the presence of a fungus in the soil that affects potatoes, tomatoes and other nightshade crops;
- high humidity and hot weather, provoking the spread of the fungus;
- lack of nutrients;
- improper fertilization and watering.
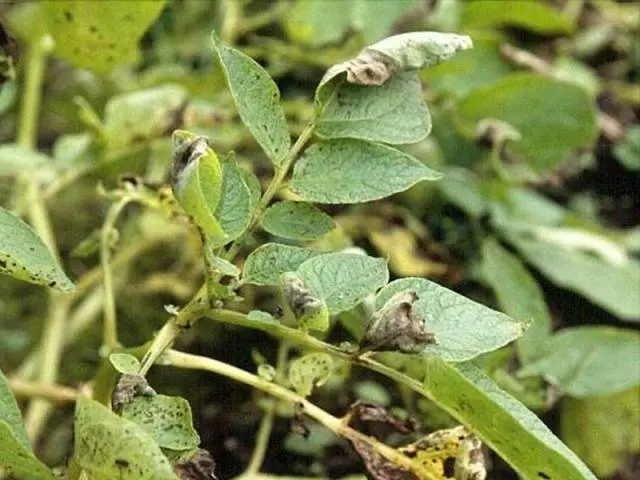

Fungal diseases
Fungal-type diseases spread harmful spores. They can be stored on inventory, in planting material, old tops. The development of fungal diseases occurs at high humidity and high ambient temperature. The main diseases of potato tops, photos, descriptions and treatment are given below.
Fitoftoroz
Late blight is one of the most common and dangerous potato diseases. The disease spreads to stems, tops and root crops. Symptoms of late blight appear in the second half of the growing season, when the flowering of plants begins.
Late blight has the following symptoms:
- weeping spots appear on the lower leaves, which eventually turn brown;
- a white coating forms on the reverse side of the sheet;
- the appearance of hard gray spots on potato tubers.
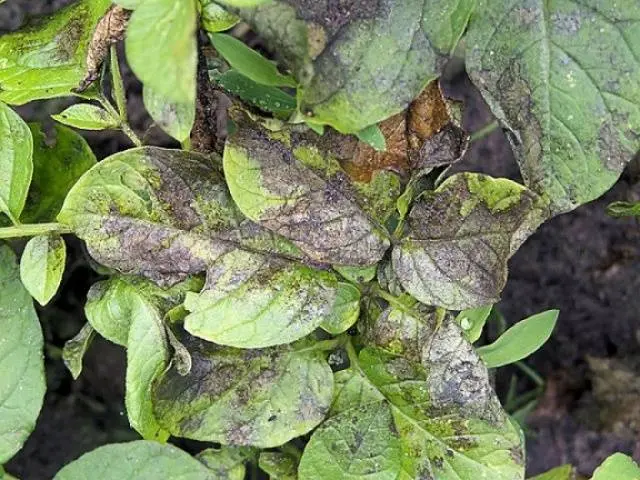

A set of measures will help prevent late blight. All of them are aimed at strengthening plant immunity and destroying the source of the disease:
- use of potash fertilizers;
- feeding potatoes with solutions based on boron, manganese and copper;
- spraying seedlings with a 0,2% solution of copper sulfate.
When the first signs of the disease appear, chemical protective agents are used:
- Spraying with Bordeaux liquid 1% concentration. For its preparation, two solutions are prepared: based on copper sulfate and quicklime. Potato processing is carried out every week.
- The use of chemicals. Against phytophthora, Oxyx is an effective remedy. A bucket of water requires 20 g of the substance. The resulting solution is sprayed with potatoes.

black scab
The disease manifests itself in the form of a black coating on the tubers, which is easily removed. Black scab is dangerous in that it damages potatoes intended for planting next year.
The disease actively develops with early planting of potatoes, when high humidity and low temperatures are observed. As a result, the germination of tubers slows down. When exposed to black scab, the seedlings become brown, ulcers appear on them.
To protect potatoes from this disease, planting sites are constantly changing. Potatoes should be planted only after the soil has warmed up well. The crop is harvested only in dry weather to avoid the spread of the fungus.

If a disease is detected, the tubers will have to be removed. The remaining root crops are treated with the following preparations:
- “Ditan M-45”. 0,2 kg of the substance is added to a bucket of water, after which the tubers are placed in the solution.
- Boric acid. A 1% solution is prepared for processing.
potato cancer
Cancer is one of the most dangerous potato diseases. The lesion covers tubers on which growths appear. Today, about 18 varieties of the fungus are known to be capable of provoking potato cancer.
The causative agents of the disease affect different types of plants that belong to the nightshade family. A favorable environment for the spread of the disease is a temperature of about 20 degrees and high humidity. The causative agent remains viable for 30 years.
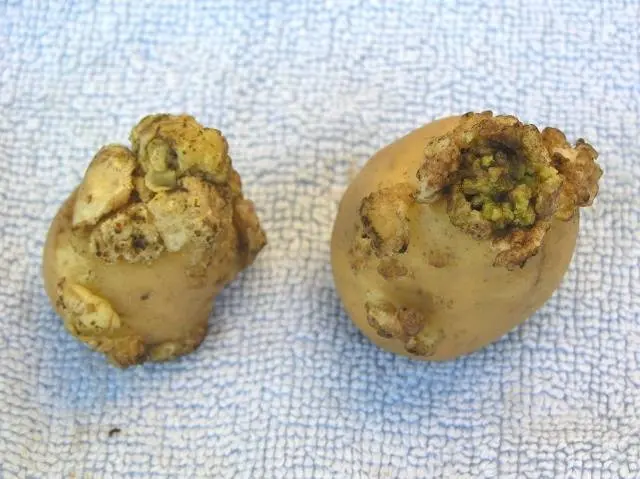
Cancer has the appearance of growths that gradually grow and turn brown. As a result, the tuber is destroyed. The causative agent of the disease spreads during the growing season of potatoes due to the formation of zoospores. The fungus is transferred to the soil with root crops, seedlings, stored on garden tools and equipment.
Quarantine measures help prevent the development of the disease. Planting material is sorted out, after which the affected specimens are eliminated.
The soil is disinfected with a 2% Nitrafen solution. For each square meter, 20 liters of solution are required. Processing is carried out according to the instructions in early spring using protective equipment.
Dry rot
The disease is common in the southern and eastern regions. Dry rot can lead to the death of 40% of the crop.
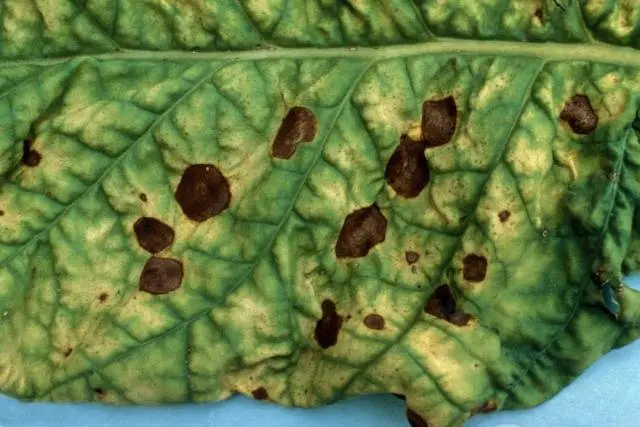
Its causative agent is a fungus that infects potato tubers. The spread of the fungus occurs through infected roots, soil and plant debris.
The signs of the disease are:
- the top of the bush brightens and gradually fades;
- the lower part of the stem becomes brown;
- at high humidity, an orange or pinkish coating is found on the stem;
- when cutting the stem, the vessels of the plant are visible;
- over time, the potato bush wilts.
On the affected tubers, grayish depressed spots spread, under which the pulp dries. In the root crop, voids appear in which the mycelium is located. Such tubers germinate with difficulty and form weak bushes.

There is no universal remedy for dry rot. To prevent the disease, planting material is treated with Fitosporin. So that the disease does not spread during the storage of potatoes, the tubers are placed for some time in a solution of the drug “Maxim KS”.
Alternaria
The spread of alternariosis is observed on the stems, tops and tubers of potatoes. The disease leads to a decrease in yield by 30%. Usually the disease is diagnosed on varieties of medium and late maturation.
Alternariosis has a number of symptoms:
- two weeks before flowering, large brown or brown spots appear on the leaves;
- with the development of the disease, the spots merge, the tops of the potato turn yellow and die;
- stems have elongated spots.
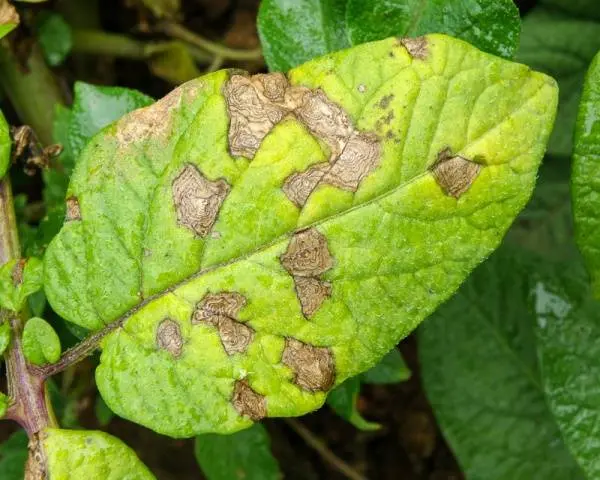

The disease is spread by insects and raindrops. When the temperature rises to 26 degrees and high humidity, the active development of the fungus on the potato begins. Weakened plants with low immunity are especially susceptible to Alternaria.
To combat the lesion, solutions of chemical preparations are used: Kuproksat, Profit, Novozri, Metaxil, Ridomil. For the purpose of prevention, planting material is processed.
macrosporiosis
Macrosporiosis is a fungal disease that affects nightshade crops. It is determined by the following signs that appear before flowering begins:
- small spots of gray, brown or brown on the tops of potatoes;
- the spread of a weak black plaque;
- with a lack of moisture, the tops gradually dry out.

The disease can also appear in the later stages of potato development. In this case, the lesions are located along the edges of the sheet and differ in a rounded shape. With a high degree of development of the disease, the leaves are rolled up.
The following methods help to get rid of the disease:
- Bordeaux liquid (during the growing season, a 1% solution is prepared, after harvesting, a 3% mixture is processed);
- polycarbocin (working solution is prepared from 0,4 kg of the drug per liter of water and is used during budding, then the procedure is repeated after two weeks);
- potassium permanganate (10 g of the substance is taken per liter of water, after which the potato tops are sprayed).

Viral diseases
Diseases of a viral nature cause irreversible changes in plant organisms. Their impact leads to a change in color and deformation of the tops. As a result, the potato has an oppressed appearance and slowly develops.
The infection persists in the tubers and has no external manifestations. After planting the infected material, the development of potatoes is disrupted. The spreaders of the virus are bugs, aphids, leafhoppers and other insects.
Diseases can be avoided by taking preventive measures. This includes the choice of high-quality material for planting, preventive treatment of tubers and soil.
Listed below are viral diseases of potato tops with photos and descriptions.

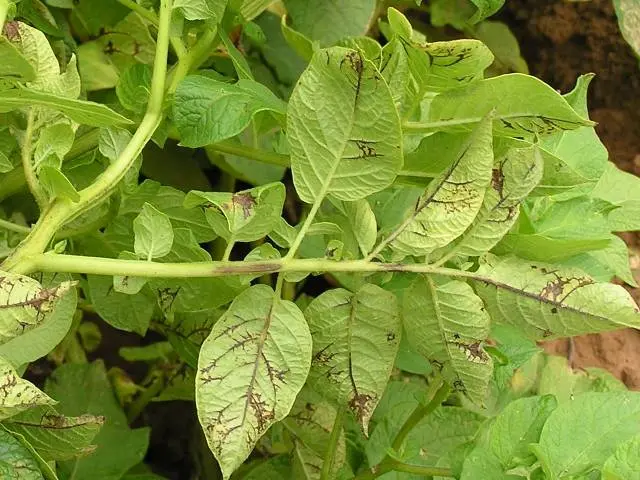
striped mosaic
The disease affects the ground part of the potato and is diagnosed by the presence of mosaic spots or stripes. Dark brown stripes appear on the veins on the underside of the leaf. As a result, the stems become more fragile.
In the last stages of the growing season, the lower leaves of the potato dry up and fall off. When the tubers are affected, bulges and rings appear on them.
The banded mosaic is spread by aphids. The disease passes to healthy tubers through mechanical damage.

wrinkled mosaic
A wrinkled-type mosaic appears as a swelling of the leaf between the veins. As a result, the leaves become corrugated.
The disease is difficult to diagnose in the first year, since its manifestations are hardly visible externally. After three years, the wrinkled mosaic results in slow plant development. This is determined by the height of the plants, which does not reach the norm.
When a mosaic is damaged, potatoes have small wrinkled leaves that break easily. Such potatoes do not bloom, and the process of its vegetation is reduced by 4 weeks compared to healthy plants.

Leaf curl
Potato leaves curl under the influence of a virus that spreads in the seed material. During the growing season, infection occurs through insects: aphids and bedbugs.
Viral damage leads to a decrease in yield. Losses can be up to 70%. At high soil and air temperatures, the spread of the disease accelerates. Lack of watering also causes twisted leaves on potatoes.
The disease is determined by the following features:
- the plant acquires a pale green color;
- the tops turn yellow, and on the back of the leaf – pink;
- first, the lower leaves of the potato curl, after which the disease spreads to the top of the bush;
- twisting occurs along the central vein in the form of a boat;
- the sheet plate becomes rigid and breaks at any external contact.
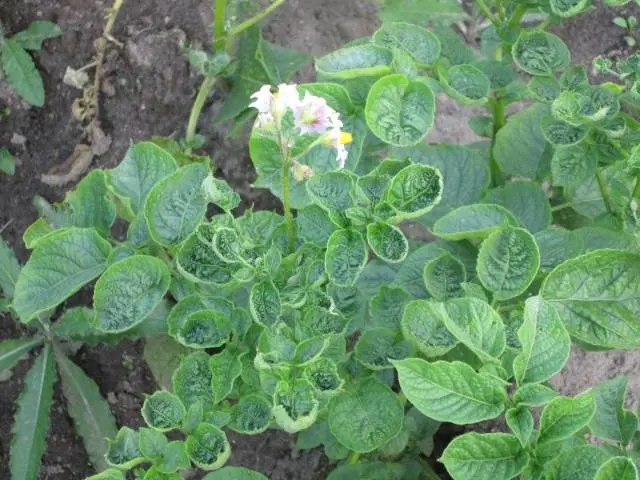

The process of infection of potatoes can take up to two years. If twisted leaves are found, the plant is eliminated. Torsion is not treatable, therefore, increased attention is paid to the choice of planting material, periodic checks of plantings, and pest control.
Before planting, the tubers are disinfected with the help of special preparations. This will destroy the virus before it spreads to the potatoes.
Mottling
In the presence of this disease, spots in the form of a mosaic appear on young leaves. They are light green in color and irregular in shape. With the development of the disease, dark brown spots are diagnosed on the leaves.
The causative agent of mottling is a virus that is transmitted by the interaction of healthy potato bushes with affected leaves. This occurs as a result of direct contact, through damage caused by garden tools or insects.

For the prevention of mottling, the soil is treated with phytopreparations. The first procedure is carried out after the appearance of the first shoots of potatoes. Then the treatment is repeated twice during the season.
On the site you need to eliminate weeds, which also attract the virus. Increased attention is paid to the fight against aphids, which serve as a carrier of infection.
Tuber gothic
This disease is of viral origin and leads to stretching of potato tubers. As a result, they acquire a cylindrical shape resembling a spindle.
The virus infects potatoes at any stage of development. Upon contact with the affected tops, the disease spreads to the leaves and stems of the plant. The pathogen can live in the ground, it is carried by bedbugs, Colorado potato beetles and grasshoppers.

Gothic can be identified by a number of signs:
- small leaves located at an acute angle with respect to the stem;
- potato shoots do not branch;
- tops turn yellow after flowering;
- in the second year, the affected plants do not produce inflorescences;
- potatoes contain an increased number of eyes;
- in drought, the tubers crack and become stained.
Gothic appears on any variety of potato. To prevent the disease, after harvesting, oats and rye are planted on the site. The root system of these plants has the ability to disinfect the soil.
The virus can be stored for up to two years on garden tools. In the soil, the viability of the pathogen persists for two months.

Bacterial diseases
Bacterial diseases may not appear for a long time. Harmful bacteria are usually contained in planting material that looks perfectly healthy on the outside. The disease is detected after planting potatoes, when violations occur in the process of its development.
Blackleg
The disease develops on seedlings of potatoes, the tops of which begin to fade. As a result, the leaves turn yellow and gradually bog down. The potato stalk turns black and is easily pulled out of the ground.
At high humidity, the blackleg extends to adult plants. When the stem rots, its tissue acquires a dark green color, cavities appear on it, and the vessels blacken. The spreader of the disease passes to the formed potato tubers.
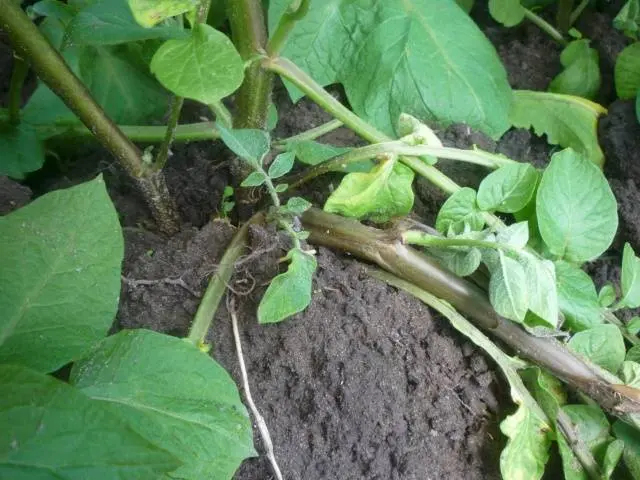

With the defeat of the black leg, up to 80% of the crop is lost. Infected root crops are not subject to storage, as they quickly rot. If the disease has spread to healthy tubers, weakened plants are formed as a result.
The infection spreads at low temperatures and high humidity. If adverse symptoms are detected, the plants are removed from the site. Healthy plants are treated with a solution of potassium permanganate at a concentration of 3%. Potato stalks can be sprinkled with ashes.
Ring rot
Disease Ring rot proceeds rather slowly. In this case, the following symptoms are observed:
- tops turn yellow;
- stems gradually wither and fall to the ground.

Ring rot continues until the potato harvest period. The development of the disease provokes drought and hot weather. When the tuber is damaged, the vascular ring turns yellow, softens and rots.
When a disease is detected, the affected bushes are dug up and burned. Warming up the seed will help prevent ring rot. The disease manifests itself when the temperature rises to 18 degrees. Soft potato tubers, on which black depressions have appeared, are not used for planting.
Ring rot can be avoided by choosing the right planting site and using quality planting material. Nitrogen and potassium-based fertilizers are required to help strengthen the immunity of potatoes.
Preventive measures
With timely preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of the spread of diseases.
Potato disease prevention measures are as follows:
- Selection of varieties resistant to pathogens. It is best to choose varieties obtained specifically for your region. They take into account the composition of the soil and the climatic conditions of the area.
- If signs of disease are found, curly leaves and other affected parts must be destroyed by burning.
- Compliance with the rules of crop rotation. Potatoes are recommended to be planted in places where cabbage, pumpkin, cucumbers, and legumes used to grow. It is forbidden to plant on beds where sunflowers and nightshade crops used to grow.

- Treatment of tubers before planting. The use of special preparations allows you to destroy the sources of the disease that live on the planting material. For these purposes fit “Fitosporin”, “Prestige” or “Maxim”. First, a working solution is prepared according to the proportions indicated on the package. Potato tubers are dipped into it for 15 minutes.
- Timely planting care. This includes hilling plants, watering and fertilizing.
Conclusion
You can identify the development of diseases by the external state of the potato: the leaves begin to curl and turn yellow, spots appear on them. As a result, plant development slows down and crops are lost. Compliance with agricultural practices and the selection of high-quality tubers for planting will help protect potato plantations from diseases. Potatoes need to be processed periodically to prevent diseases.










