Contents
Potatoes are grown in every household and summer cottage. It is hard to imagine that there are no potatoes on the table. This vegetable has a lot of vitamins, trace elements that a person needs daily. And how many delicious dishes you can cook from it! Moreover, tubers are used for the treatment of diseases, for the preparation of cosmetic preparations.
Growing potatoes is not difficult. Any beginner can grow a garden. But diseases and pests can suddenly deprive the crop. Potato alternariosis should be noted among the common diseases. To get rid of the problem, you need to know about the features of this disease of nightshade crops. We will present you with a photo, description, tell you about the methods of treatment and prevention of Alternaria disease.

Overview
Mankind has been growing potatoes for a long time. The s owe the appearance of delicious tubers to Peter I. Subject to agrotechnical rules, you can get good harvests. But this plant has its own diseases.
Potato Alternaria disease is often found in the gardens of s. The culprits of the problem are imperfect fungi – Alternaria alternata Keissler and Alternaria solani. Alternariosis and late blight – diseases of potatoes and its relatives – peppers and tomatoes. It is also called brown spotting. Due to this disease, which affects nightshade crops, more than 5% of the crop can be missing. In recent years, alternariosis on potatoes has spread widely in the Baikal region and the Far East region. Here, due to Alternaria disease, farmers lose almost half of their crops.
Alternariosis of potatoes is first exposed to growing young shoots. If you do not take emergency control measures, then spores can germinate on root crops.
Most often, early-ripening potato varieties suffer from alternariosis, but a vegetable with an average and late ripening cycle suffers much less.
Why and how does Alternaria disease occur? The thing is that in recent years, mineral fertilizers are used less and less. There is a clear lack of calcium, nitrogen and an excess of phosphorus in the soil, plants are not able to resist the disease due to a decrease in immunity. Where nitrogen-containing and potassium mineral fertilizers are used, damage to the bushes by Alternariosis is minimal.

Description
The onset of Alternaria potato disease is the second half of June, when the first flowers appear on the plant. If the process is not stopped in time, it will hit the entire potato plantation by the end of summer and can easily switch to other nightshade crops.
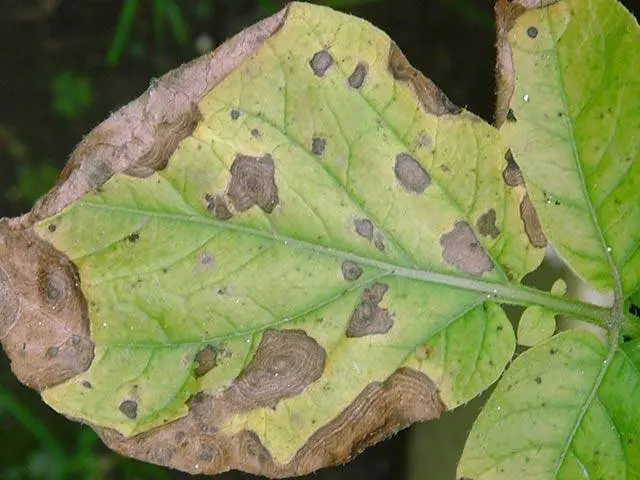
The onset of Alternaria disease is not always immediately visible, since at first the focus of the disease is on young green shoots with succulent leaves. On them, in a chaotic manner, closer to the center, you can find small spots of brown color. Their diameter is from 10 to 3,5 ml. With alternariosis, oval-angular spots form on potato leaves, concentric rings are visible in the figure, as in the photo below.

Gradually, these spots increase in size. Alternariosis disease passes to other leaves, shoots, can affect tubers. The tissue in the affected area gradually dies off, a depression forms in it, which after a while turns into a hole.
Potato Alternariosis spores, formed in the first focus of the disease, become the cause of the further development of the disease. Dried leaves with curled edges stop participating in photosynthesis. They are fragile and lifeless. As a result, potatoes slow down growth, which is the reason for the low yield. In addition, weakened plants can be attacked by other pests.
At temperatures from +25 to +27 degrees and low humidity, spores begin to multiply intensively.
How alternariosis migrates
Now let’s see how the disease ends up in our gardens. Appearing in one place, potato alternariosis can quickly turn from a focal disease into a mass one. The reason for the spread is simple. Spores are easily carried by wind, raindrops, insects.

Alternariosis fungus multiplies several times during the summer season, so stopping the disease is not so easy. In addition, mycelia and conidia overwinter well, tolerate low temperatures. For wintering use any plant remains. In addition, the potato disease Alternaria affects not only the leaves and stems of plants, but also penetrates into the tubers and calmly waits for spring there.
Tuber disease symptoms
The potato tuber (photo below) has clear signs of alternariosis.
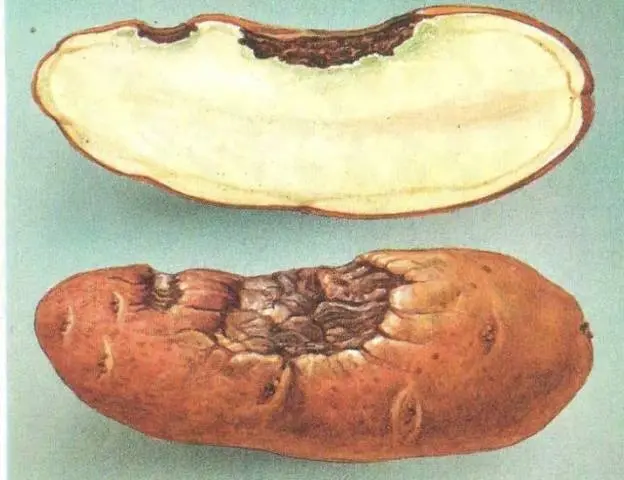
Depressed spots are visible on the surface of the potato. They are irregular in shape and differ in color from the tuber. On large spots, wrinkles are located in a circle. If you cut a potato, then tissue necrosis is visible to the naked eye. It looks more like dry rot. The spot is dense, hard and dry, dark brown in color. Hence the name – brown spotting.
If potato alternariosis has affected tubers in the soil, then signs of the disease can be noticed immediately. But healthy potatoes affected by the fungus, when harvested or in contact with the ground, will be no different. The spots will appear in 2-3 weeks.
Potato treatment for disease
It is necessary to treat plants with alternariosis at the first signs of the disease. Potatoes can be processed:
- 4% Bordeaux mixture. Spraying is carried out XNUMX times a day for a week.
Cooking Bordeaux liquid:
Copper oxychloride. Twice a day for a week.
- Chemical preparations. Today there are a number of fungicides that can cope with Alternaria.
The drugs recommended for the treatment of potato alternariosis are partially presented in the table.
| Preparation | Mode of application |
|---|---|
| Alirin b | Before planting tubers. For triple spraying from the moment of shoots. Repeat after 10 days. |
| Bactofit | Twice for spraying. |
| Acrobat MC | Spraying during the vegetative period up to three times. |
| Albite | Spray when bushes close. Twice a season. |
| Gamair | Treatment of tubers before planting and double spraying. |
| Vitaplan | Before planting for processing tubers and growth period. |
| Bravo | Triple spraying in 7-10 days. |
| Integral, Ridomil Gold, Skor | Presowing treatment of tubers. |

The list of fungicidal preparations for the treatment of potatoes from Alternaria can be continued. In specialized stores, sellers will tell you by what means you can still defeat the fungal pest, and, most importantly, what is available. The dosage and frequency of treatments is indicated in the instructions. Work is carried out in protective clothing in calm, calm weather.
Safety measures
- During spraying, you can not drink, eat, smoke.
- At the end of work, you need to change clothes and wash with soap.
- The solution is diluted strictly according to the instructions.
- To treat plants, use a sprayer with a long nozzle.
- The sprayer must be washed with any detergent so that no fungicide residues remain in it. They can harm plants if you foliar later.
The best way to fight disease is prevention
We have presented you with a photo description and treatment of potato alternariosis. But experienced gardeners are well aware that any plant disease is easier to prevent than to fight it. If there was an infection of potatoes, then you will have to spend money not only financially. Imagine how much time and effort it will take to spray a potato field. It is good if several buckets of potatoes are planted. And if several bags are planted on the plantation?
Over the years of growing potatoes, gardeners have developed preventive measures against alternariosis of potatoes. They are based on knowledge of agricultural technology. Let’s take a look at the recommendations:
- Only healthy tubers are prepared for planting. If you purchased potatoes from another farm, check each tuber. The slightest suspicion of Alternaria disease, planting material is discarded. Germination of tubers and their heating allows you to identify signs of the disease.
- If possible, treat the seed with fungicides. There are varieties of potatoes that are resistant to Alternaria. These are Alena, Snow White, Lasunok, Resource, Temp and some others. Although no one gives a 100% guarantee that these varieties will not get sick.
- The use of crop rotation is an important point in the prevention of any disease. The place for planting potatoes should be changed after 2-3 years.
- It is not recommended to leave weeds, tops and tubers on the field. They are to be destroyed. After all, it is in organic residues that a fungal disease can easily overwinter.
- Before digging potatoes, many gardeners mow the tops. Thus, they prevent the penetration of Alternaria spores into tubers. Moreover, the peel on the potato hardens better.
Conclusion
Fortunately, the disease is not common in all regions of Our Country and the former republics of the USSR. Most often, outbreaks of potato early blight, which reduce yields, are observed in Belarus, in the north of Ukraine, in the European regions of Our Country, in the Baikal region and in the Far East.
Farmers need to be careful about planting potatoes in order to prevent the spread of Alternaria disease. And the best thing to do is prevention.









