Contents
- Symptoms of polyps in the stomach
- Causes of polyps in the stomach
- Polyps in the stomach – is it dangerous?
- Types of polyps in the stomach
- Diagnosis of polyps in the stomach
- Answers to popular questions
- Treatment of polyps in the stomach
- Removal of polyps in the stomach
- Diet after removal of a polyp in the stomach
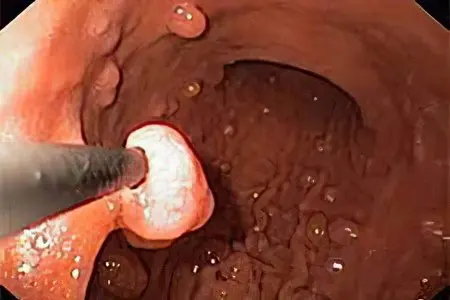
Polyps in the stomach are tumor-like formations of a benign nature, formed from the glandular structure of the mucous membrane of the organ. These tumors appear on the inner wall of the stomach and grow into its lumen. They can have a wide base – sessile tumors and an oblong stalk – lancet tumors. The latter are found at the tops of the mucous membrane, becoming a continuation of its fold. The shape of the tumor is most often round or oval, although mushroom-shaped and papillary polyps are sometimes found. Their color varies from gray to deep red. The more glandular cells in the composition of the tumor, the softer its consistency will be. The average size of the formation is 15 mm, although sometimes there are large tumors reaching 60 mm.
According to statistics, men are more likely to suffer from this pathology, they have formations found 2 times more often than women. The average age at which gastric polyposis is diagnosed is between 40 and 50 years of age. Single formations are detected less frequently than multiple 47% and 52%, respectively. Diffuse polyposis is extremely rare – no more than 2% of cases. As for the departments of the organ, formations most often appear in the region of the pylorus of the stomach (up to 70% of cases), and, somewhat less often, in its body.
Up to 5% of tumor-like formations can lead to cancer. Adenomatous polyps are susceptible to rebirth, which are detected in 20% of cases. The larger the polyp, the higher the risk of its malignancy.
Symptoms of polyps in the stomach
Pathology is manifested by a number of symptoms, which, first of all, depend on its size and histological structure. The smaller the formation, the poorer the clinical signs will be, up to their complete absence.
Dyspeptic symptoms. It is this combination of signs that most often indicates the presence of a tumor in the organ. The patient suffers from increased gas formation, from heartburn, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, which is often replaced by constipation. The intensity of these signs depends on how long ago the polyp appeared. As the tumor grows, there is an increase in negative manifestations from the digestive tract. All dyspeptic symptoms are manifestations of the pathology against which the polyp was formed. Most often, it is they who force the patient to go to see a doctor, after which a tumor is detected.
Pain. Painful sensations in the presence of a tumor are periodic. Mostly they occur after eating, since it is it that irritates the formation located on the gastric mucosa. The feeling of fullness in the stomach appears due to the fact that due to the polyp, its natural volume decreases. The larger it is, the stronger the food that has entered the cavity of the organ, stretches it. Such stretching causes pain that occurs against the background of irritation of the nerve endings present in the serous membrane of the stomach. Depending on the area in which the tumor is located, the time of onset of pain after the next meal will depend. Immediately after eating, it occurs if the polyp is located high, in the cardial part of the organ. The deeper the tumor is localized, the later pain will appear – an hour or an hour and a half after eating.
Bleeding. The cause of bleeding is most often formations that have a long stem, shaped like a mushroom. When it is twisted or injured, blood begins to be released. However, polyps with a wide base can also cause bleeding, which occurs due to their necrosis. The fact that the patient has begun gastric bleeding can be suspected by darkened feces, bloody vomiting, a drop in pressure and an increase in pulse. Additional signs are unnatural pallor and perspiration. Ignoring the symptoms of bleeding can lead to the development of hemorrhagic shock, which leads to disruption of the work of all organs.
Difficulties with evacuation of food. This symptom is observed when the tumor is localized in the pyloric part of the stomach. At the same time, the food that has entered the cavity of the organ does not pass into the duodenum, but stagnates in it. This leads to the development of decay processes. In this case, the patient complains of pain in the epigastric region, he has an unpleasant odor from the mouth, and often there is fetid vomiting of putrefactive contents. As the polyp grows, vomiting occurs more often.
Anemia. The fall in the level of hemoglobin and erythrocytes occurs against the background of prolonged occult bleeding. It is observed if the polyp is subjected to permanent injury. Since blood loss is rather insignificant, they do not cause a visit to the doctor.
The symptoms of polyposis are very non-specific and can be easily confused with signs of other diseases, so in this case, the competent help of a specialist is so important.
Causes of polyps in the stomach
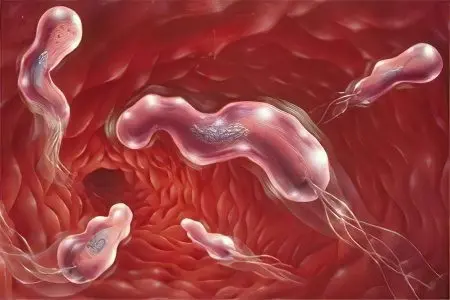
The appearance of formations in the cavity of the stomach may be due to the following factors:
Infection Helicobacter pillory – a bacterium that is able to populate various parts of the organ and the duodenum. Penetrating into the gastric mucosa, it leads to its erosion, causing the development of an ulcer, and later, the growth of a polyp. The longer the bacterium exists in the stomach cavity, the higher the risk of malignancy.
Genetic predisposition to the formation of a precancerous tumor of the stomach. This applies to adenomatous formations.
Radiation exposure, namely ionizing radiation. The mucous membrane lining the stomach is one of the first to react to radiation fluxes of photons and ions. This factor is confirmed by the fact that in areas where there is an increased level of radiation, the frequency of diagnosing polyps is extremely high.
Consumption of food with nitrites and nitrates. This applies to vegetables, for the cultivation and storage of which various chemicals are used. In addition, all smoked, dried, salty foods, as well as alcohol, have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa.
Taking medicines. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are considered the most dangerous, which can irritate the gastric mucosa, making it more vulnerable and vulnerable.
Nicotine, which comes with tobacco smoke, can irritate the epithelial cells of the organ. This, over time, leads to the fact that they begin to be reborn.
Age. Every person who has crossed the line of 40 years is at risk for the detection of polypous growths in the stomach.
Diseases of an inflammatory nature. They become the reason that formations with a fibrous structure are formed in the stomach. They are unable to transform into cancerous tumors, but can lead to the development of bleeding.
Digestive system diseases. The most dangerous in terms of the development of polyps are gastritis and stomach ulcers. In addition, in chronic polyadenomatous gastritis, a patient has multiple polyps and cystic growths on the surface of the stomach, which is not a consequence, but a manifestation of the disease.
Polyps in the stomach – is it dangerous?
Any formation in the stomach, even the smallest one, is dangerous for human health and life:
The risk of malignancy. If, after diagnostic measures, it is established that there is an adenomatous polyp in the patient’s body, then this significantly increases the risk of its subsequent degeneration into a malignant tumor. In addition, it has been found that such formations larger than 20 mm are malignant in 50% of cases. In this case, they affect not only the diseased organ, but are also capable of spreading throughout the body with the help of metastases. The prognosis is unfavorable, and mortality among the sick is high.
Pinching of the legs of education. The danger of infringement of the leg on which the tumor is located is that the risks of gastric bleeding increase, in the absence of emergency medical care. A patient with an injury or torsion of the knives experiences acute pain, which is localized in the epigastric region. If the formation is located near the exit to the stomach and it is infringed, it will prevent the normal movement of food into the duodenum. This will cause stagnation of food that has entered the body and vomiting of putrefactive masses.
Bleeding. Bleeding can be either massive or latent. Both of these are dangerous. Abundant blood loss is fraught with the death of the patient in the absence of medical assistance, and hidden bleeding leads to the development of anemia and chronic hypoxia of the tissues of the whole organism.
Digestive disorders. First of all, the danger lies in the impossibility of passing food into the intestines. The problem gets worse as education grows. The patient may experience an ongoing feeling of nausea, his appetite decreases, and body weight decreases.
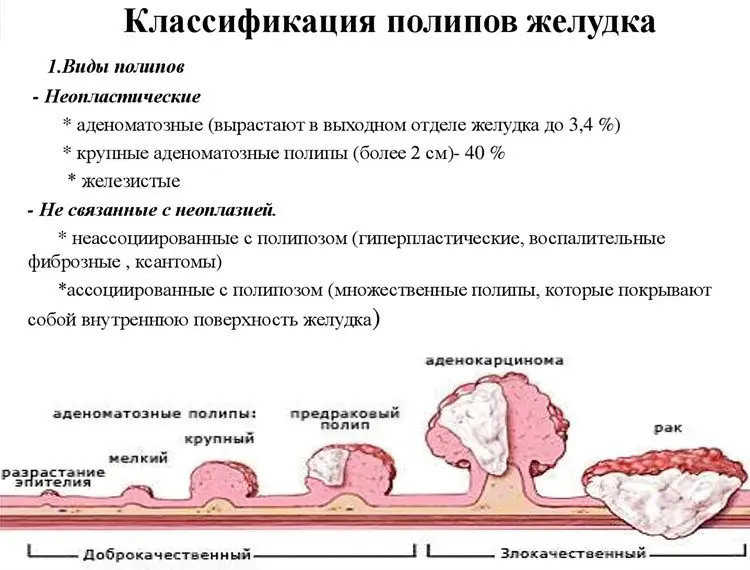
Types of polyps in the stomach
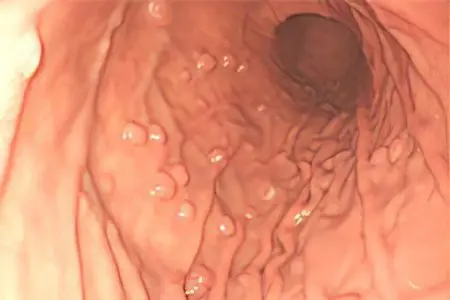
There are many approaches to the classification of polyps that form in the stomach.
If we take their morphological structure as a basis, then two types of tumors can be distinguished:
Adenomatous tumor, which can be tubular, papillotubular and papillary;
Hyperplastic tumor;
Xanthoma of the stomach.
In addition, multiple polyps that can be inherited are isolated separately: Peutz-Jeghers polyps, Gardner polyps and juvenile polyps. If a patient is diagnosed with one of these forms of polyposis, then the entire area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe stomach will be covered with growths.
Adenomatous polyp of the stomach
If a diagnosis of “adenomatous polyp of the stomach” was made, then the patient should understand that an early surgical intervention is necessary. This is due to the fact that this type of tumor is more likely than others to regenerate. The share of such formations in their total mass accounts for no more than 10%. The risk of their degeneration increases as the pathology progresses.
The tubular formation consists of glandular cells, which are externally limited by connective tissue. It is tubular tumors that more often and faster than others degenerate into malignant tumors.
Villous or papillary adenoma of the stomach consists of a layer of the mucous membrane of the organ, it has many finger-like outgrowths of various widths.
Papillotubular adenoma is a mixed tumor consisting of glandular cells and villous structures. It is an intermediate formation between the villous and tubular tumor.
Hyperplastic polyp of the stomach – what is it?
One of the varieties of formations is hyperplastic polyps. They are more common than others and account for up to 70% of all detected tumors. The term hyperplastic implies that the polypous proliferation occurred as a result of hyperplasia of the epithelial cells of the organ, that is, there is no mutagenic basis or elements of degenerated cells in its origin.
Very rarely, formations of this type are transformed into cancerous tumors. The percentage of rebirth does not exceed 0,5.
Inflammatory and infectious processes occurring in the body lead to the development of hyperplastic polyps. In particular, the vital activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
As for the prevalence of formations within an organ, they can be either single or multiple, they can be scattered over its area, or they can gather in nests or merge with each other. The maximum size of such a formation is 60 mm, although sometimes there are huge polyps that exceed this figure.
Although such tumors carry a minimal possibility of degeneration into a cancerous tumor, nevertheless, they are capable of leading to bleeding and stagnation of food.
Juvenile gastric polyps
Such tumors are quite rare and can be found at any age. Although they are mainly formed in the first 10 years of a child’s life, thanks to which they got their name. Juvenile-type polyps often affect the large intestine, and not just the stomach. Mostly, such formations are diagnosed in the antrum of the organ. The size of juvenile polyps varies from 5 mm to 20 mm.
The structure of the juvenile polyp is represented by elongated tortuous cysts that grow from the inflamed edematous mucous membrane of the organ. After opening the formation, mucus will be released from it. The same thing happens when pressing on the tumor. Such growths are prone to degeneration into cancer, as the pathology progresses. However, with a small amount of them, regression of the disease can occur.
Diagnosis of polyps in the stomach
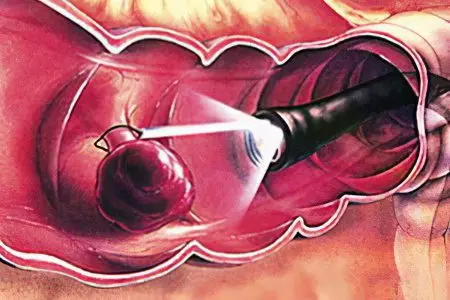
There are two basic methods for detecting polyposis growths in the stomach – these are endoscopy and x-ray examination. Additional methods are considered to be laboratory tests and the detection of infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Endoscopic examination. It boils down to the fact that a flexible tube called an endoscope is inserted into the cavity of the organ. At its end there is an eyepiece, it is he who transmits information to the monitor. The doctor gets the opportunity to examine in detail the entire surface of the stomach and determine the presence of polypous growths. Of all the existing options for endoscopic examination, gastroscopy is considered the best method for detecting polyps.
The survey takes place in several stages:
With the help of a local anesthetic, the patient’s oropharynx is treated.
A mouthpiece is inserted into the patient’s mouth, which he fixes with his own teeth. Through it, an endoscope is inserted into the esophagus, leading it to the stomach. To reduce the gag reflex, a person needs to breathe as deeply as possible.
Through the endoscope, air is supplied, which allows you to straighten the folds of the stomach.
If a tumor is found, a biopsy is performed.
The endoscope is removed from the stomach.
Sometimes gastroscopy can aim not only to diagnose, but also to remove the formation. When a small growth is detected, the doctor may decide to immediately remove it from the body. However, more often only a small area of the polyp is taken for further study.
X-ray examination. If for some reason the implementation of gastroscopy is impossible, then the patient is prescribed an X-ray examination using a contrast agent. In this case, the patient is invited to drink a barium suspension, after which several pictures are taken using an X-ray machine. They are performed in several projections. Barium is used in order to get better visualization, as the relief of the stomach walls becomes clearer on the pictures. The procedure is forbidden to be performed if the patient is carrying a child, if the patient is in serious condition, and also has problems with swallowing or there is a suspicion of gastric bleeding. Therefore, gastroscopic examination is the best method, which allows not only to identify polyps, but also to assess the condition of the gastric mucosa.
Non-instrumental examination methods.
Non-instrumental examination methods include:
A complete blood count will help identify the presence of occult bleeding, which can be suspected by low levels of hemoglobin and red blood cells.
The delivery of feces to identify occult blood in it also allows you to identify latent bleeding. It is impossible to see slight impurities of blood in the feces with the naked eye, since its color does not change. That is why such a study is being carried out.
Identification of Helicobacter pylori is possible using the PCR method (saliva, blood serum or feces can be used for it), using a breath test, or by cytological and histological examination of the material that was taken during the biopsy.
Answers to popular questions
Should a stomach polyp be removed? Surgery to remove the formation from the body is not always required. Sometimes it is possible to get rid of the polyp of the stomach with the help of conservative treatment. An unambiguous indication for the removal of an existing tumor is its size exceeding 15 mm. In addition, the polyp should not cause discomfort to the patient and cause the development of complications.
Can polyps in the stomach resolve themselves? There is a possibility of self-elimination of the polyp of the stomach, with the elimination of the cause that caused it.
Treatment of polyps in the stomach
Therapy of education can be both conservative and surgical. The decision on the method of treatment is made by the doctor based on the results obtained. If it was decided to treat the patient with drugs, then in parallel the patient must adhere to a certain diet, and the principle of fractional nutrition. In addition, periodic monitoring of the condition of the gastric mucosa is important, that is, the patient will need to undergo a gastroscopic examination at least once a year.
Due to the fact that polyps are formed against the background of various diseases, drug treatment is reduced to taking antacids (to reduce the secretion of gastric juice and protect the stomach from the action of hydrochloric acids.) And omeprazole (restores the gastric mucosa). If Helicobacter pylori is found, antibiotics are prescribed.
If conservative treatment does not achieve the desired result, then the patient is sent for surgical treatment.
Removal of polyps in the stomach
Endoscopic polypectomy
Surgical intervention is carried out with the help of an endoscope inserted into the cavity of the organ. This or that device is carried out along it, which destroys or cuts off the existing formation. Endoscopic polypectomy can be of three types:
Mechanical endoscopic polypectomywhen the tumor is cut off with a metal loop. The cut-off formation is removed using an endoscope. This method is dangerous because there is a risk of bleeding.
Electroexcision. Most often, this method is used to remove polyps from the stomach. It allows you to remove formations ranging in size from 5 mm to 30 mm, since the selection of a loop for excision occurs on an individual basis.
Electrocoagulation allows you to remove a polyp from the stomach using an electric current. For this purpose, biopsy forceps are used, which are applied to the tumor tissues, heat it and cause the pathological cells to evaporate.
Whichever method of endoscopic polypectomy is chosen, it does not guarantee that the growths will not reappear. In addition, there is always a risk of perforation of the organ wall. It is impossible to perform the procedure in patients with a pacemaker, as well as in violation of blood clotting processes and in a serious condition of the patient.
The patient during the operation is under the influence of anesthesia, only after its action, an endoscope is inserted into the stomach cavity and the polyposis tissues are destroyed.
Open surgery
The operation is performed with a scalpel. They make an incision, after which the polyp is removed from the stomach. This method of surgical intervention is used if the formation has a size exceeding 30 mm, several fused polypous growths are found, in close proximity to each other, the polyp has a wide stalk.
The course of the operation is as follows:
The patient is put into a state of anesthesia.
Tissues are excised in layers to gain access to the stomach.
With the help of a scalpel, growths are removed along with the mucous membrane.
The removed material is sent for histological examination.
The excised tissues are sutured in layers.
The patient is taken out of anesthesia.
This method of surgical intervention is considered the most dangerous in terms of the development of complications. The wound can be infected, in addition, there is a risk of collapse of the lung tissue, disruption of the heart, the development of pneumonia, thrombosis and intestinal obstruction.
Resection of the stomach
This method of surgical intervention is the most traumatic and leads to the development of many complications. Therefore, there are strict indications for its implementation:
The polyp is very large or multiple growths are found.
Polyps repeatedly recur.
The tumor is necrotic or has a pinched leg.
Education is the cause of intestinal obstruction.
There is a high risk of tumor degeneration.
The polyp has already degenerated into a cancerous tumor.
During the operation, not only the formation is removed, but also part of the damaged organ itself. After the procedure, the patient may experience quite serious complications, among which dumping syndrome comes first. In this case, the patient suffers from severe weakness, from nausea and vomiting, his heart rate increases. The most dangerous complication is the oncology of that part of the organ that remained intact after resection.
Diet after removal of a polyp in the stomach

After the procedure was performed to remove the tumor, the patient needs a diet aimed at restoring the organ. If an endoscopic procedure was performed, then, as a rule, rehabilitation does not take much time. Full recovery of the mucous membrane of the organ will occur after a period of 10 to 40 days.
Refusal to eat is necessary only on the first day after the intervention. Then the patient should adhere to a certain diet, the diet should not include products that have chemical, thermal and mechanical irritation. This will allow you to quickly establish the work of the digestive system.
During the recovery period, it is forbidden to include in the diet:
Of the cereals, only semolina falls under the restriction.
From flour products, it is worth abandoning any fresh pastries, from cakes and pastries, from muffins and fried pies.
Meat dishes in the diet should include lamb, pork and beef, as well as fatty poultry (duck and goose).
The first courses should not be spicy or salty, so you should not consume kharcho soup, hodgepodge and other soups made from fatty meat broth.
Some vegetables and fruits are also prohibited for consumption. Among them are peas and white cabbage, radish and radish. Figs, plums and grapes should not be eaten.
As for the eggs, they should not be fried.
Any sausages, canned food and marinades are prohibited. You should unload the diet as much as possible by the absence of hot sauces and any food additives in it.
You can not add margarine to dishes, and butter is under the restriction. As for milk, it can be drunk if there is no individual intolerance, the fat content of the product should not be high.
Foods that can be included in the diet after stomach surgery:
Boiled cereals, for which cereals are suitable: buckwheat, rice, oatmeal.
From flour products sugar-free crackers, unsweetened biscuit cookies, dried bread are allowed.
Soups should be prepared either without meat at all, or in a weak meat broth.
As for meat products, you can include chicken breast, veal, rabbit and turkey in the diet.
Bananas and apples are allowed, and zucchini, beets (once a week), carrots, pumpkin and cauliflower inflorescences are also not banned.
Sometimes you can include pasta and dietary rabbit or poultry ham in your diet.
Eggs are boiled or cooked like an omelette, but steamed.
You can eat non-acidic cottage cheese, sour cream (low-fat), yogurt and kefir.









