Contents
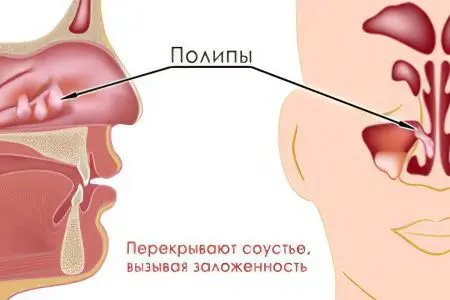
Polyposis sinusitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in one or more paranasal sinuses and contributes to the appearance and growth of polyps.
Nasal polyps are quite common. According to various sources, up to 4% of all people on earth suffer from this pathology. Men are more susceptible to the disease than women. Often, polyposis growths in the nose are diagnosed with relapses of chronic sinusitis.
The nasal polyp is represented by abnormal epithelium, which is located on the stroma. Polyps do not have nerve endings, may contain a small amount of glands and blood vessels.
Causes of polyposis sinusitis
The causes of polyposis sinusitis are diverse, otolaryngologists identify the following factors that affect the development of the disease:
Polyposis sinusitis, which occurs due to violations of air microcirculation in the nasal passages against the background of structural features of the nasal cavity (congenital and acquired). If the nasal septum is curved, then the mucous membrane of the nose and sinuses is irritated as a result of the constant incorrect exposure of it to the air stream that occurs during inhalation. It is known that in just a day a person inhales at least 20 times, which, with certain anatomical anomalies, leads to edema, impaired drainage and aeration, and then to the formation of polyps;
Polypous sinusitis against the background of bacterial or mycotic inflammation of the sinuses. In this case, the cause of the formation of polyps is prolonged irritation of the nasal mucosa with purulent discharge from the sinuses. Bacterial sinusitis is most often provoked by streptococci and staphylococci, Haemophilus influenzae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Moraxella. Fungal sinusitis is less common than bacterial sinusitis, but it can also provoke the growth of polyps;
Polypous sinusitis, included in the aspirin triad, in combination with aspirin intolerance and existing bronchial asthma. In this case, polyposis sinusitis occurs against the background of a disease of the whole organism, which is associated with abnormal production of arachidonic acid and allergic reactions.
Modern otolaryngology classifies polyposis sinusitis as a polyetiological disease that requires a selective approach to treatment.
Symptoms of polyposis sinusitis
Symptoms of polyposis sinusitis cannot go unnoticed by a person, since they are inextricably linked with impaired respiratory function.
The clinical picture of the disease is characterized by the following features:
Nasal congestion and difficulty breathing;
Violation of the olfactory function, up to its complete loss;
Feeling of discomfort in the nasal passages, there may be a feeling that there is always a foreign object in the nose;
If polyposis sinusitis occurs against the background of a purulent process in the nasal sinuses, then liquid mucous contents of yellow or green color with an unpleasant odor are separated from the nose;
In the area of the inflamed sinus, painful sensations arise that can radiate to various parts of the head and to the ears;
There may be a feeling of fullness in the ear;
Human sleep is disturbed, which provokes the development of chronic fatigue. In general, the body experiences a lack of oxygen, which negatively affects the functioning of all organs;
If the disease is acute, then the body temperature can rise to high values. In the chronic course of polypous sinusitis, body temperature may remain normal or reach subfebrile levels.
Treatment of polyposis sinusitis
Treatment of polyposis sinusitis will directly depend on what caused the development of the disease. However, in addition to medical correction, surgical intervention is always required, since an already existing formation in the nasal cavity cannot be eliminated on its own.
Treatment of polypous sinusitis in anatomical disorders of the nasal septum. If polyposis sinusitis develops as a result of the curvature of the nasal septum, then surgical intervention is required, which is reduced to performing septoplasty or submucosal cristotomy. In parallel, a polypectomy is performed. As a rule, drug treatment for prophylactic purposes is not required for this group of patients.
Treatment of polypous sinusitis of a bacterial or fungal nature. If polyposis sinusitis develops against the background of a bacterial infection, then antibiotic therapy is necessary. Most often, drugs from the group of penicillins and respiratory fluoroquinolones are used for this purpose. Topical corticosteroids in combination with antibiotics can improve the course of the disease and speed up recovery. This allows you to normalize the drainage of anastomoses, quickly remove swelling, reduce inflammation.
As for surgery, endoscopic surgery using a shaver is indicated to remove polyps. If the mucous membrane of the nasal sinuses has undergone irreversible changes, then endonasal intervention is necessary with the opening of the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth and complete resection of the mucous membrane.
Treatment of polypous sinusitis of an allergic nature. If polypous sinusitis develops against the background of the aspirin triad, it is necessary to wait for the period of exacerbation of bronchial asthma and an attack of hay fever to subside. After the symptoms subside, an operation is performed, which involves a polypetmoidectomy, in which the ethmoid labyrinth is completely opened.
In general, the prognosis for recovery is favorable with adequate therapy aimed at eliminating the cause of the development of polyposis sinusitis. Although no otolaryngologist can give a 100% guarantee of a recurrence of the disease.









