Contents
Polycystic ovary is a serious gynecological disease that is diagnosed in 65% of women suffering from infertility. It will not be possible to get pregnant in the presence of such a pathology, since the patient does not ovulate in the body. This means that the egg does not mature and does not leave the ovaries, that is, this process remains incomplete, which means that it cannot meet with the sperm. Polycystic disease leads to the fact that the eggs stop in their development, and multiple cysts form on the ovaries.
Forms of polycystic ovaries
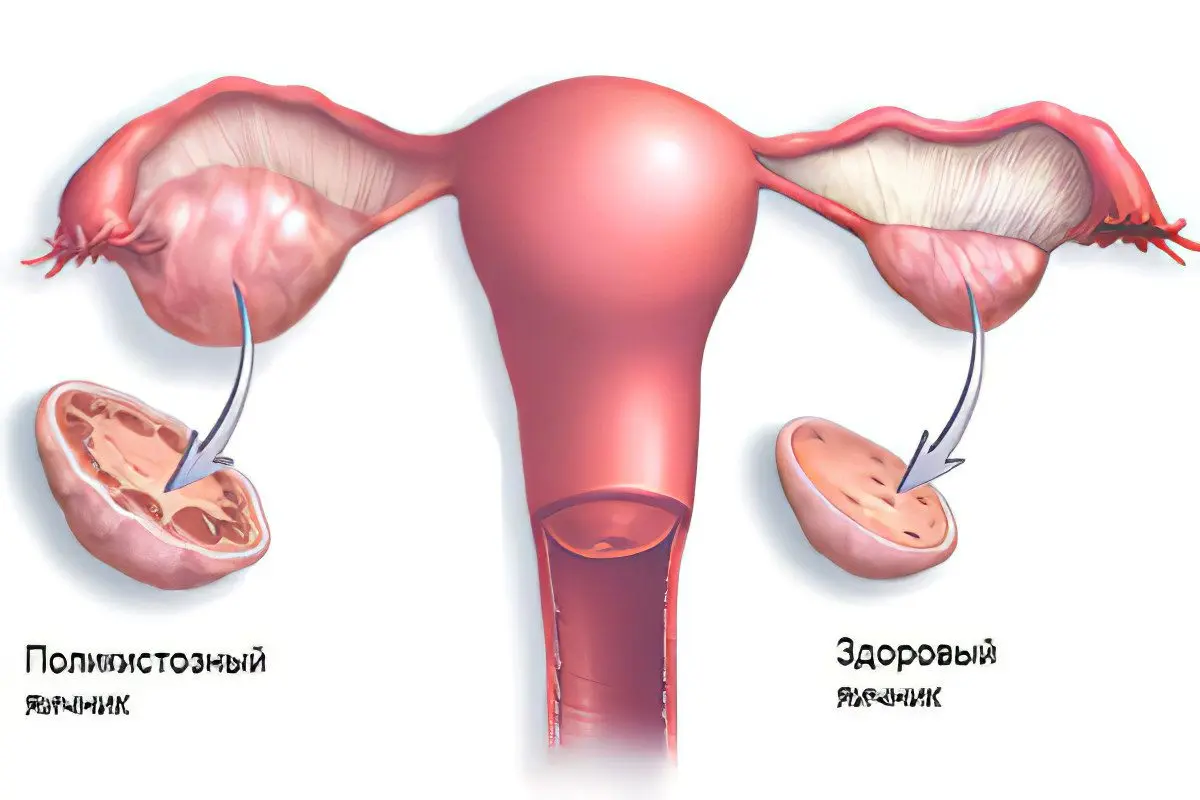
Polycystic can be primary or secondary:
With primary polycystic disease, symptoms appear as early as adolescence. This happens when the girl turns 12-13 years old. Therapy will be difficult, the course of the disease is severe.
The secondary form of the disease develops in adult women who have undergone childbirth or entered the menopause. The disease is accompanied by metabolic disruptions in the body, weight gain, insulin surges, which is due to disorders in the pancreas.
No matter what form of the disease a woman has, she will not be able to give birth until she is cured. Therapy is reduced to the appointment of hormonal drugs. Sometimes surgery is required.
Causes of polycystic ovaries
Polycystic can develop for the following reasons:
Hormonal disbalance. At the same time, follicular cysts form in a woman. They are a consequence of a violation in the work of the endocrine glands. Moreover, the pancreas, thyroid gland or adrenal glands, pituitary gland, or hypothalamus can fail. Often, polycystic disease develops against the background of an increased level of insulin in the blood with pathologies of the pancreas. When there is a lot of insulin in the body, it affects the work of the adrenal glands, which begin to produce androgen in excess quantities (male sex hormone). In the body, there is a shift in the balance between androgens and estrogens, which becomes the basis for the development of polycystic disease.
Infectious diseases. Frequent colds suffered in childhood, as well as a severe course of infection in an adult woman, can become the basis for the development of polycystic disease. At a doctor’s appointment, it is often possible to establish a connection between polycystic disease and tonsillitis, since the tonsils and ovaries have a certain dependence on each other.
Hereditary factor. It has been established that the disease can be transmitted at the genetic level.
Emotional turmoil. A number of experts are of the opinion that polycystic disease can be the result of stress.
Symptoms of polycystic

The main symptoms of polycystic ovaries:
Violation of the menstrual cycle. Menstrual disorders are observed in all women with polycystic ovaries. Sometimes they are absent altogether, and sometimes they come with a delay. The regularity of the cycle is not observed. If a woman’s periods occur 9 times a year or less, then this is a reason for examination. When menstruation does not come on time, this is the first sign that the egg in the body does not mature. Although sometimes menstruation may be absent for other reasons. Among them: inflammation of the genital organs, polycystic uterus. Therefore, the patient needs a comprehensive examination to make a correct diagnosis.
Absence of pregnancy. A woman with PCOS cannot get pregnant. For conception to occur, long-term treatment is required.
Excess male sex hormones. Often with polycystic women in the body there is an increased level of androgens. This causes the patient to begin to appear male sexual characteristics, for example, excessive hair growth, acne on the face, back and chest, male pattern alopecia.
Overweight. In women, against the background of polycystic, body weight begins to increase. And the increase is quite tangible. It is 10-15 kg. Therefore, the treatment of polycystic disease is always aimed, among other things, at weight loss, since it is problematic for women with obesity to become pregnant.
Pain in the ovaries. Polycystic can be manifested by pulling pains in the lower abdomen. However, most patients do not pay attention to this symptom.
Polycystic and pregnancy

Women with PCOS cannot get pregnant because they have too many male sex hormones in their bodies. Therefore, in order for conception to occur, efforts must be made to reduce them.
If hormone therapy does not achieve the desired results, the woman is referred for surgery. It is performed using laparoscopic equipment.
Provided that none of the listed methods allowed to achieve conception, the patient is shown IVF.
Diagnosis of polycystic ovaries
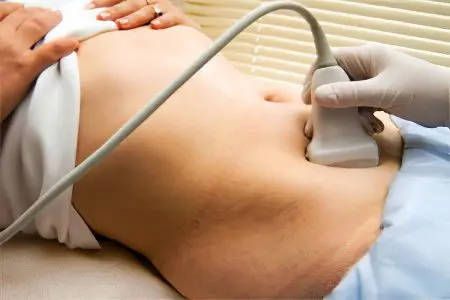
During the appointment, the doctor pays attention to such signs as:
Physique of the patient, the presence of excess weight.
Hair type.
Skin pigmentation.
The condition of the hair and dermis, their fat content.
Condition of the mammary glands.
The doctor performs palpation of the thyroid gland and abdomen, conducts a standard gynecological examination. The ovaries in women with polycystic are enlarged by 2-3 times compared to the norm, they give pain when pressed.
Diagnosis can be made on the basis of ultrasound. According to its results, it is possible to establish that the ovaries in diameter exceed 9 cubic centimeters. In addition, several small cysts are always found. There may be more than 10 pieces.
The ovaries are dense, surrounded by a white capsule. This can be visualized during a laparoscopic examination.
Be sure a woman with suspected polycystic disease will need to take a blood and urine test for hormones:
The ratio of luteinizing hormone to follicle-stimulating hormone in polycystic disease looks like 3:1.
Testosterone levels will be raised.
The level of progesterone in the second phase of the cycle decreases.
A high concentration of 17-KS is found in the urine.
Be sure to perform a study aimed at determining the level of insulin and glucose in the blood. Results may vary. In addition, with polycystic, a high level of fats in the blood is found.
Hyperplasia of the endometrium of the uterus is determined during diagnostic curettage, which is carried out with uterine bleeding.
Treatment of polycystic ovary
It will not be possible to quickly get rid of polycystic ovaries. A woman should tune in to long-term therapy. First, we need to focus on the fight against obesity.
Nutrition and physical activity

Adipose tissue produces both male and female sex hormones, which negatively affects the course of the disease.
Sweets are completely excluded from the diet. It is not enough just to follow a diet, it is necessary to increase physical activity. Loads should not exhaust a woman, you need to stop at a sport that will bring pleasure. It can be swimming, yoga, jogging, body flex.
Getting rid of insulin resistance
If a woman has insulin resistance, then she is prescribed Metformin. This drug allows the body to process glucose, stabilize its level in the blood. At the same time, appetite decreases. Treatment lasts from 3 months to six months. Sometimes such therapy allows you to stabilize the menstrual cycle.
Normalization of the menstrual cycle
After the weight returns to normal, you need to focus on the restoration of menstruation. For this, the patient is prescribed contraceptives, drugs aimed at reducing the level of androgens in the body (Yarina, Zhanin, Diana-35, etc.). The course of treatment can last from six months or more.
To cope with hirsutism, use Veroshpiron or Flutamide.
Stimulation of ovulation
When the menstrual cycle is restored, you need to focus on stimulating ovulation. This is important for those women who want to conceive a child. To do this, prescribe the drug Clomiphene, which has antiestrogenic properties. When it is canceled, the woman begins to actively produce FSH and LH, which stimulate the maturation of the follicle and ovulation.
Clomiphene is prescribed from the 5th to the 9th day of the cycle. Its dosage is 0,05 g per day. The course of treatment should not last more than 3 months. If there is no effect, then the dose can be increased to 200 mg.
The danger of taking Clomiphene is reduced to the risk of the formation of ovarian cysts, which can reach an impressive size. When there is no effect from the treatment, surgery is required.
Operation
In recent years, the operation has been performed using laparoscopic equipment. It is possible to perform a wedge resection of the ovaries or electrical coagulation of ovarian cysts. The second option is a sparing intervention, since large areas of ovarian tissue are affected during resection.
It must be taken into account that the more time has passed after the operation, the less likely it is to become pregnant. The maximum ability to conceive remains in the first 3 months after the intervention. In a year it will be unlikely. The operation is indicated for women who suffer not only from polycystic ovaries, but also from endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus.











