Contents
Pneumothorax – a disease whose name comes from two Greek words – pneuma and thorax (air and chest). An acute condition that occurs quite often these days is a concentration of air in the pleural cavity. The victim needs immediate medical attention.
What is pulmonary pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax of the lung – this is a life-threatening pathology in which air enters where it should not normally be – into the pleural cavity.
Air, once in the pleural cavity, can provoke a collapse of the lung, which has a full or partial shape. The development of the disease can be spontaneous or occur in connection with lung diseases already present in a person, injuries, medical manipulations. The ventilation function of the lungs is disturbed, they are compressed, there is a lack of oxygen, respiratory failure. The organs of the mediastinum (large vessels, heart) are displaced, there are failures in the processes of blood circulation.
What are the types of pneumothorax?
The presence / absence of communication with the environment divides the disease into the following varieties:
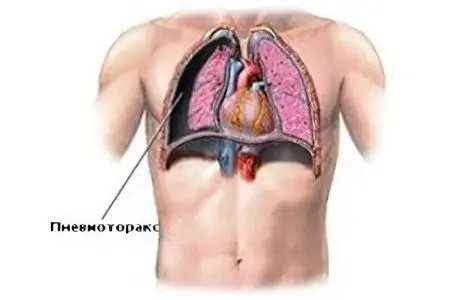
Open. There is a depressurization of the respiratory system. Through the hole in the chest, air seeps into the pleural cavity when inhaling, leaves it when exhaling, its accumulation does not happen. The pressure, which has ceased to be negative, leads to the fact that the lung collapses, ceases to participate in the respiratory process, gas exchange in it stops, and the supply of oxygen to the blood stops.
Closed. A certain amount of gas appears in the pleural cavity, its volume remains stable, since the acquired defect quickly closes. If the air leaves the cavity on its own (which is very likely with a closed wound), the compressed lung levels out, the respiratory processes normalize. This variety is among the lightest.
Valve. Displacement of the mediastinal organs, malfunctions of their functioning, pleuropulmonary shock – all these are the dangers that threaten the patient with this form of the disease, called the most severe. The appearance of the valve structure leads to the fact that the air is concentrated in the pleural cavity, without leaving it, pressure builds up. Air enters through the wound.
Depending on whether complications are attached, the following types of disease are called.
Uncomplicated. Complications do not develop as a result of the disease.
Complicated. Complications join: emphysema, bleeding, pleurisy, and so on.
Depending on the type of spread, pneumothorax can be unilateral or bilateral:
Unilateral. The patient has a collapse of one lung – left or right.
Bilateral. The patient has compression of both lungs. This pathological condition poses a serious threat to life, the patient needs emergency help.
In addition, pneumothorax in terms of air volume can be complete, parietal, encysted.
Full. In this case, the lung collapses completely. If the patient has a complete bilateral pneumothorax, he needs emergency care. Otherwise, a critical failure of the respiratory function can cause death.
Parietal. A small amount of air fills the pleural cavity, the lung is not completely expanded. (Mostly it is a closed form).
Bagged. Adhesions between the parietal and visceral pleura limit the zone of pneumothorax. Sometimes there are no symptoms, the species does not pose a particular danger, but theoretically it can cause lung tissue ruptures in the area of adhesions.
Pneumothorax in all its manifestations is not a purely “adult” problem; even babies who have just been born face the disease. In young children, the disease can form for many reasons, causes a number of unique symptoms, but doctors fight it in the same way as they treat adults.
Causes of pneumothorax
Iatrogenic, traumatic, spontaneous – these are the main groups of reasons why a patient can develop this pathology.
Spontaneous pneumothorax
A pathology in which a sudden violation of the integrity of the pleura occurs, filling its cavity with air. In this case, the patient does not receive external injuries. Depending on the cause, it may be primary or secondary.
The occurrence of primary pneumothorax has no clear cause. High growth, belonging to the male sex, 20-30 years old, the presence of bad habits (cigarettes) – these are the main risk factors. It is extremely rare for the disease to occur after the age of 40, and women are also less likely to suffer from it.
The following diseases and pathologies can give rise to spontaneous pneumothorax:
genetically determined weakness of the pleura, in which laughter, a fit of coughing, physical stress are enough to break it;
congenital lack of the enzyme alpha-1-antitrypsin, causing pathological processes in the lungs;
air travel (pressure drops), diving, snorkeling.
Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax develops due to pulmonary pathology. It can be:
lung diseases that injure the connective tissue (sarcoidosis, lymphangioleiomyomatosis, idiopathic pneumosclerosis, tuberous sclerosis);
malignant neoplasms (lung cancer, sarcoma);
respiratory diseases (cystic fibrosis, severe bronchial asthma, COPD);
infectious diseases of the lungs (lung abscess, tuberculosis, pneumonia on the background of HIV);
systemic connective tissue diseases, including lung damage (dermatomyositis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic scleroderma, polymyositis, Marfan’s syndrome).
In most cases, this disease is encountered in old age – 60-65 years.
Iatrogenic pneumothorax
The main source of this form is various medical manipulations. The disease can be activated by:
installation of a venous (central) catheter;
lung ventilation;
biopsy of the pleura;
puncture of the pleural cavity;
cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Traumatic pneumothorax
Wounds, chest injuries – this is the main source of this form of the disease:
closed chest injury resulting from a fall from a height, a fight, and so on (traumatic rupture of the lung, damage to pieces of broken ribs without violating the integrity of the skin);
penetrating wound of the chest (gunshot, stab wounds causing rupture of the lungs).
Pneumothorax in newborns
Pneumothorax is an anomaly that often appears in young children, newborn babies.
Causes of pneumothorax in childhood may be as follows.
Increased crying leads to rupture of the pleural commissure.
Rupture of an acquired or congenital cyst.
Pulmonary forced ventilation.
Genetic lung pathology causes rupture of dilated emphysematous alveoli.
Lung abscess rupture.
Most often, the occurrence of this disease in a child is associated with genetic deformities of the lungs and pleura (wrong structure), injuries and inflammatory processes. Sometimes birth asphyxia becomes an activating factor, a rupture of the lung tissue of an infant occurs with forced artificial respiration. Pneumothorax can also occur as a result of clogging of the airways with amniotic fluid or mucus.
Symptoms of pneumothorax

Pneumothorax can manifest itself with the following symptoms, their appearance depends on the specific type of disease, the severity of its course, the presence / absence of complications, and other factors.
Sudden appearance of shortness of breath – the patient has superficial rapid breathing, it is difficult for him to breathe.
Sharp pain in the chest area – activated during inhalation, acute; recoil to the shoulder from the injured side is also possible.
Attacks of dry cough.
The patient takes a forced posture (half-sitting, sitting).
Feeling of weakness, fear, increased heart rate, lowering blood pressure.
Appearance of sticky cold sweat on the skin.
Subcutaneous emphysema – when exhaling, air enters the subcutaneous fat, when you press the swelling, a noise similar to the crunch of snow appears.
Cyanosis of the skin – a symptom occurs with severe failures in the processes of blood circulation, respiration.
Isolation of “foamed” blood from the wound (with open pneumothorax).
Symptoms of spontaneous pneumothorax
Almost all patients who are diagnosed with spontaneous primary pneumothorax tell doctors about chest pain, manifested by the defect, about shortness of breath that has suddenly appeared. The intensity of pain sensations varies from very strong to minimal. Most patients describe it first as acute and then as dull or aching. The clinical picture lasts no more than a day, regardless of whether the disease is treated.
If a patient has a spontaneous secondary pneumothorax, he will certainly experience shortness of breath, regardless of how much air is in the pleural cavity. Most often, there is also pain localized on the affected side. Probably, the addition of hypoxemia, hypotension.
Symptoms of valvular pneumothorax
The patient is in an excited state, complains of a sharp pain in the chest. Pain sensations can be stabbing or dagger in nature, give to the shoulder blade, shoulder, abdominal cavity. Weakness, cyanosis, shortness of breath develop instantly, fainting is quite likely.
Symptoms of pneumothorax in infants
Symptoms of pneumothorax in babies under one year old may look like this:
the appearance of puffiness of the face;
tachycardia;
cyanosis of the skin;
anxiety, agitated state;
shortness of breath, shortness of breath;
occurrence on the trunk, neck of subcutaneous crepitus.
Consequences of pneumothorax
Complications of pneumothorax, according to statistics, are observed in approximately 50% of patients.
Inflammation of the pleura (pleurisy). May be accompanied by the appearance of adhesions that violate the expansion of the lung.
Ingress of air into the tissue of the mediastinum, compression of large vessels, heart.
Intrapleural bleeding.
Subcutaneous emphysema is a condition in which air is trapped in the subcutaneous fat.
Fatal outcome. It is possible in severe cases – a penetrating wound of the chest, a large amount of damage.
Emergency care for pneumothorax
Pneumothorax in valvular or open form is one of the urgent conditions, upon the occurrence of which an ambulance should be called immediately. Then be sure to do the following:
stop the process of filling the pleural cavity of the victim with air;
stop bleeding.
You will need to apply a tight, airtight bandage. In an emergency, in the absence of sterile means, you need to use improvised things – a shirt, a T-shirt. The cleanest area is applied to the wound. To seal the wound, a plastic bag (oilcloth, film) is applied over the makeshift dressing.
You should also simplify the patient’s breathing process, for which he must be placed in an elevated position. All actions are performed very carefully, as they cause additional pain to the victim. If a person faints, be sure to bring him to his senses. If ammonia is not at hand, any product with a pungent odor will do, for example, gasoline, perfume, nail polish remover. The tool is brought to the nose.
The last task is to prevent the development of pain shock, this will help banal aspirin or analgin. After providing first aid, you should wait for the arrival of an ambulance.
Treatment of pneumothorax
Pneumothorax is life-threatening, so the treatment process begins even before arriving at the hospital.
On the way to the hospital
Anesthesia. If the patient is worried about excruciating pain, he is given narcotic analgesics – omnopon, morphine. If there are no pronounced pains, it is possible to get by with analgin.
oxygen therapy.
Removal of the cough reflex. To rid the patient of coughing fits, antitussive drugs are used – libexin, codeine, tusuprex.
Pleural puncture. This procedure becomes necessary if the patient’s condition deteriorates sharply (rapid drop in blood pressure, increased shortness of breath), which is caused by valvular pneumothorax. A puncture can be done not only by a doctor, but also by a paramedic.
Treatment in hospital
Patients with pneumothorax are subject to mandatory hospitalization. Medical care consists in puncturing the pleural cavity, removing air, and forming negative pressure in the pleural cavity. Treatment depends on the form of the disease.
Conservative expectant therapy is relevant when it comes to closed limited small pneumothorax. The patient is given rest, painkillers are administered. If necessary, air is aspirated using a puncture system. Pleural puncture is done on the side of the injury along the midclavicular line in the second intercostal space.
In the case of a total form, to prevent a shock reaction and quickly straighten the lung, drainage is placed in the pleural cavity, followed by active (using an electrovacuum device) or passive (according to Bulau) air aspiration.
The first task with an open pneumothorax is to transfer it to a closed one. To do this, the wound is sutured, the penetration of air into the pleural cavity stops. This is followed by manipulations similar to those carried out with a closed form.
If the victim has valvular pneumothorax, a decrease in pressure inside the pleura is required. It is first made open with a puncture, followed by surgical treatment.
Spontaneous recurrent pneumothorax provoked by bullous emphysema is treated surgically.
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is an important point in the fight against pneumothorax, painkillers are required for the patient both at the stage of lung collapse and when it is expanded. In order to prevent recurrence of the disease, pleurodesis is carried out with silver nitrate, talc, glucose solution and other sclerosing drugs. So in the cavity of the pleura, the adhesive process is deliberately stimulated.
Rehabilitation and prevention
After leaving the hospital, a patient who has had a pneumothorax should refrain from any physical activity for 3-4 weeks. Air travel is prohibited for 2 weeks after treatment. You should not engage in parachuting, diving – all this causes pressure drops. It is strictly forbidden to smoke, you should definitely quit this dangerous habit. Doctors also advise to be tested for tuberculosis, COPD.
Unfortunately, there are no methods of prevention that can turn into reliable protection against pneumothorax, but some actions are still worth taking:
To give up smoking.
Examination for lung diseases, their timely treatment.
Spending enough time outdoors.
Breathing exercises.
Pneumothorax is not a sentence at all, most patients successfully cope with it. Uncomplicated forms of the disease with their timely treatment guarantee a successful outcome, but not the absence of the risk of relapse.
The sooner a patient who has signs of pneumothorax is taken to the hospital, the more chances he has for a successful recovery.









