Contents
Plum Kabardinka is one of the most popular varieties of crops grown in the warm regions of the country. It is valued for good yields of fruits of excellent sweet taste. In addition, it is considered one of the proven self-fertile varieties of plums, producing large purple fruits.

History of variety breeding
The plum variety Kabardinskaya early was obtained at the North Caucasian Research Institute of Horticulture in the city of Nalchik by accidental pollination of the Anna Shpet plum. Kabardinka has been included in the State Register since 1959 and is recommended for cultivation in the North Caucasus region.
Description of the plum variety Kabardian early
Variety Kabardinka by type refers to the domestic plum. The tree is characterized by rapid growth and reaches a height of 6 m. The crown is compressed, pyramidal in shape, its diameter is no more than 3 m with densely arranged branches. Leaf plates are oval in shape with pointed, elongated.
The fruits grow large, the weight of one is 40-50 g. The main color of the skin is purple, there is a barely noticeable wax coating and almost indistinguishable white specks. The shape of the plum is rounded, the seam is weakly expressed. Under the dark dense skin hides bright orange flesh, which quickly becomes brown when cut. The pulp is characterized by juiciness, medium density and unusually sweet taste with a pleasant sourness. The tasting score of Kabardinka is 4,5-4,9 points out of 5, other early ripe varieties of plums cannot boast of such fruit taste.
Early Kabardian is grown in the warm regions of the country, which include the Stavropol Territory, Adygea, Kabardino-Balkaria, Krasnodar Territory and others.
Characteristics of a variety
The characteristics of the Kabardinskaya early plum variety are presented below as an assessment of the most important varietal indicators.
Drought resistance, frost resistance
Drought resistance of Kabardinka can be assessed as low. During the period of drought, the fruits become very small, lose their taste. The frost resistance of the variety also leaves much to be desired. Kabardian early suitable for cultivation in the southern regions of the country. Withstands mild frosts down to -100C. Stronger frosts have a detrimental effect on the fruiting of this plum.
Plum pollinators

Plum Kabardian early does not need a pollinator, it is completely self-fertile. Blooming begins at the end of April. The mobility of flowering, characteristic of this variety, does not guarantee that a fruit will be tied in each flower. Kabardinka is a plum with an early fruiting period, its fruits are harvested as early as July.
Yield and fruiting
The yield of the variety may seem quite high (from 50 to 120 kg of plums from one tree), but in comparison with the dimensions of the plant itself, this indicator is considered average. In addition, the yield of plums directly depends on the degree of care and climatic conditions. Fruiting begins early – already at 4-5 years of plant life.
Scope of berries
One of the advantages of the Kabardian early variety is the versatility of using the harvested crop. Plums are suitable not only for fresh consumption, but also for conservation, drying and freezing. Fresh fruits are not stored for long, therefore, with a high yield, they are sent for processing and all kinds of compotes, jams, juices, etc. are prepared.
Disease and pest resistance
Plum Kabardinka has good resistance to various common stone fruit diseases, such as moniliosis (gray fruit rot), red spot. Also noted is the average susceptibility to the plum codling moth, one of the most malicious pests of the crop.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The undeniable advantages of the Kabardian early plum variety are:
- self-pollination;
- high taste characteristics of berries;
- the versatility of the use of fruits;
- precociousness;
- easy separation of the stone from the pulp of the fetus;
- high transportability of plums.
Obvious disadvantages of the variety:
- loss of taste under adverse weather conditions during the ripening period;
- low winter hardiness;
- rapid fall of ripe plums;
- the need for annual crown formation.
After weighing all the pros and cons of the characteristics of the Kabardinka plum variety, you can decide whether it is worth planting it on your site or not.
Features of landing
Planting and growing Kabardian early have their own specific features, without which it is impossible to achieve a good yield of the variety.
Recommended dates
Kabardinka seedlings are planted in spring and autumn. Early planting is carried out in late March – early April, when the buds on the plants are still closed, and the earth warms up enough. The time for autumn planting is at the end of September – mid-October.
Choosing the right place
An ideal place for growing Kabardinka plums is a windless and well-lit area from all sides. The soil should be well-drained, loose – any moisture stagnation will lead to diseases of the tree.
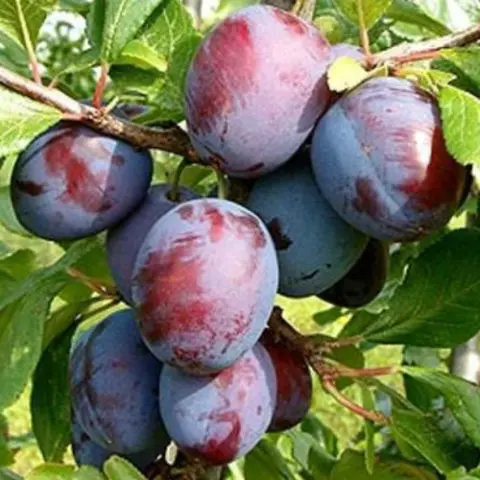
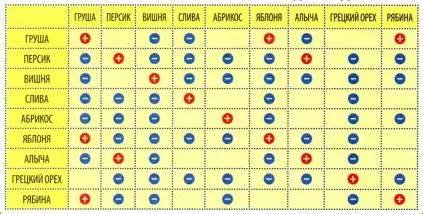
What crops can and cannot be planted nearby
Plum Kabardian early should be located away from pears, poplars, birches, and other stone fruit crops. Pome fruit trees are also not good neighbors, with the exception of apple trees. Fruit bushes are considered neutral neighbors: raspberries, gooseberries, black currants.
Selection and preparation of planting material
Plum seedlings, whose age does not exceed 2 years, take root quickly and successfully. Such trees have a height of no more than 1,5 m and the corresponding size of the root system. The plant should not have any mechanical damage, spots, cobwebs and other traces of pest activity.
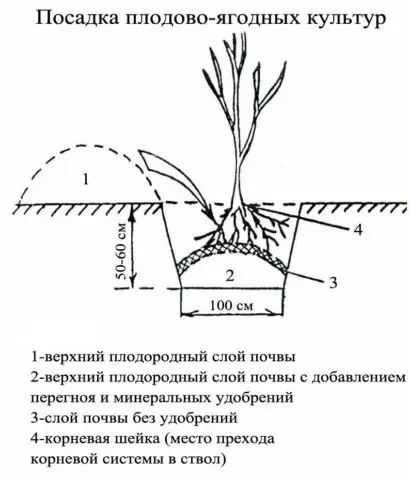
Landing algorithm
The planting sequence for Kabardinka is not much different from the planting technology for other home plum varieties.
- 2 weeks before planting, you need to dig a landing hole measuring 70 × 60 cm, the top layer of discarded earth is mixed with humus, ash, peat and a mixture of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
- A plum seedling is placed in a hole so that the root neck is 7 cm above ground level, and the roots are straightened.
- The soil near the roots of the Kabardian early is carefully compacted, covered with a nutrient mixture to the end.
- A small hole is made around the plum, after which it is plentifully watered and mulched with peat.
Plum Aftercare
Early Kabardian is one of the most capricious plum varieties, but in the first year of planting, caring for it comes down to standard events.
- Pruning. When planting a seedling in the spring, its top is shortened to stimulate growth. In the future, the formation of the Kabardinka crown will be an indispensable part of caring for it, since productivity suffers when the crown is thickened.
- Watering. After planting, it is important to monitor the soil moisture in the near-stem circle: it should not dry out and crack, but it should not be swamped either. In subsequent years, the early Kabardian is watered abundantly throughout the season, until the plums ripen. With drought, they will lose their size and taste.
- Top dressing. In the first two years, Kabardinka does not need to be fed, since all the elements were laid in the pit during planting.
- Preparation for winter and protection from rodents. Annual plum seedlings of this variety can be covered with hay, branches, spruce branches and tied at the top with a rope. To protect the root system from frost, the trunk circle is mulched. The trunk of Kabardinka can be protected from frost by wrapping it in several layers with paper.
There are two ways to protect a tree from voracious rodents: either wrap the trunk with breathable materials (nylon, mesh, burlap, etc.), or treat it with a repellent solution with a sharp unpleasant odor.
Careful care for the Kabardian early after planting will help her quickly adapt and endure her first winter on the site.
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
Diseases and pests of the early Kabardian plum are summarized in the tables.
Table 1 – Possible plum diseases
Name of the disease | Methods of struggle | preventive measures |
A witch’s broom | Cutting down to healthy tissue and burning barren thickening branches. After that, the place of the cut on the tree is disinfected and painted over. | Before planting a plant, it must be warmed up at a temperature of +460C. Young plums are immersed in water heated to the indicated temperature for 15 minutes. |
Sooty fungus | Black soot deposits are thoroughly washed off, after which the tree is treated with a solution of any fungicide. | Compliance with the scheme of planting trees, timely thinning of the crown. When grown in a humid climate, preventive treatments with fungicides are required. |
Milky luster | The disease is incurable, there are no drugs and folk methods to eliminate it. Infected plums are dug up. | Acquisition of planting material only from reliable sources, timely treatment of damage to the tree, planting plums away from poplars. |
Table 2 – Pests of the Kabardinka variety
Name of the pest | Methods of struggle | Prevention |
Red fruit mite | Spraying with Fufanon, Fitoverm, Danadim before flowering (when larvae appear) or treatment with Apollo, Neoron, Sunmite for severe plum damage. | Timely application of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, preventive treatment in spring and autumn with insecticides. |
Plum Storkock | Of the folk methods, they use wormwood, coniferous infusions or a solution of gasoline. Chemical treatment is carried out with Chlorophos, Karbofos or Fufanon. | Digging in the fall of the trunk circle, collecting and destroying carrion. Timely collection of affected fruits from the tree will help prevent the pest from settling. |
Conclusion
Plum Kabardinka is a capricious representative of the culture, but in order to get a high yield of very sweet and large fruits, many gardeners who have summer cottages in the southern regions of the country grow this particular variety.









