Contents
It is recommended to form a melon in a greenhouse according to a certain pattern. Melon is a heat-loving plant of southern latitudes that does not tolerate a drop in temperature. To obtain a crop in a polycarbonate greenhouse structure, it is necessary to create conditions for it that are as close as possible to the natural growth environment.
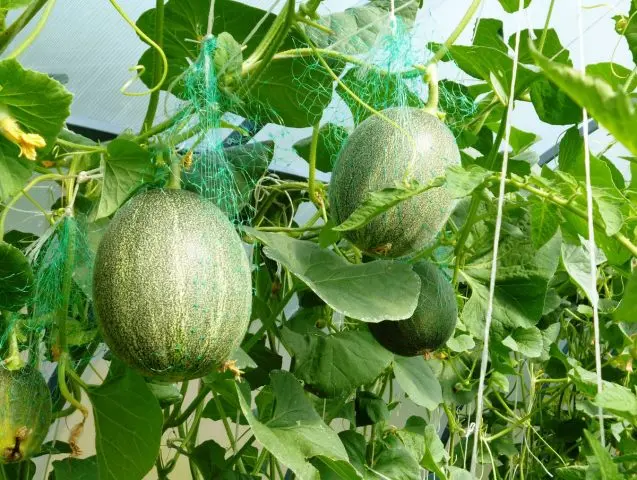

Is it possible to grow melons in a greenhouse
Melon crops in the open field are grown only in a warm climate zone. Transportation to regions with a cold climate requires a certain amount of time and material costs. On the shelves, the fruits come at a high price and not always of good quality.
In temperate climates, it is advisable to grow the crop indoors. Polycarbonate structures are available to everyone: they are inexpensive, easy to assemble. Therefore, the cultivation of melons in the Urals and in the Moscow region is practiced in a greenhouse. In order for the pumpkins to ripen and the plant not to die, they follow the appropriate agricultural practices for the culture.
For the cultivation of melons in greenhouses (pictured) located in large farm areas or in household plots, the following conditions are created:
- Air circulation. A heat-resistant plant does not respond well to high humidity, so air ventilation is necessary. If the weather is warm, during the day the greenhouses are opened for airing. If it’s cold outside, ventilate only with the help of vents.
- During the period of fruit formation, the plant accumulates starch, by the time of ripening, sugars are obtained from it by splitting. In order for the fruits to be sweet, this process must take place at a high temperature.
- Melon photosynthesis requires a large amount of ultraviolet light, the culture needs a light period of up to 16 hours, so care should be taken to install special lamps.
- The root system of the melon is deep, a large amount of nutrients is needed to form a bush, so the soil in the greenhouse must be nutritious.
Growing gourds in a temperate climate is possible, but requires certain physical and material costs. The plant cannot be called unpretentious in care. A big plus of such cultivation can be called the fact that the fruits can be obtained throughout the year, the fruiting is not affected by weather conditions.
How to plant a melon in a greenhouse
Melon is grown in two ways: early varieties by sowing seeds in the ground, later varieties by seedlings. The second method is productive, but more laborious. In spacious, well-heated farm greenhouses, seed planting is used. On a personal plot, for example, in the Moscow region, it is better to grow melons in a greenhouse in seedlings. Germinate planting material in two ways:
- seed distribution on porous paper;
- in peat tablets.
Pre-seeds are disinfected in a solution of manganese, then dried. The work is carried out in early April, after 30 days the material is ready for placement in the greenhouse.

The sequence of work for the germination of material on paper:
- Unwind 1 m of toilet paper.
- They retreat from the edge of 2 cm, lay out the seeds, taking into account that they have enough space for the formation of sprouts.
- A roll is made of paper, tied with a thread.
- It is lowered into the container with the side of the indent (without seeds), water is poured so that it covers 1/3 of the bundle.
- Placed for germination at a constant temperature of +260 C.
On the 4th day, sprouts appear, the material is carefully transplanted into peat cups. Planting in tablets is carried out according to the same principle, only the peat base is laid out on a pallet and filled with water, after the appearance of sprouts it is placed in peat glasses. Pots for planting material are taken with a diameter of at least 15 cm. Melon does not tolerate transshipment well, planting material is placed in the greenhouse together with the planting container.
Recommended dates
The time for planting melons in a greenhouse for growing in the Moscow region is chosen according to weather conditions. A layer of soil 15 cm deep should warm up at least +180 C. Seeds are not sown in cold soil, they will not germinate, planting material may completely lose its germination capacity. For the transfer of seedlings, the same conditions. The temperature regime in the greenhouse must correspond to the norm required for the melon vegetation. Daily rate not lower than +220 C, night +190 C. For temperate climates, this is any date in May.
Soil Preparation
The melon culture is demanding on the composition of the soil; growing melons in a greenhouse without preparing the soil for planting will not give the desired result. The plant will not be able to fully form the root system, slow down the growing season and will not bear fruit. The best composition for a melon in a greenhouse is loam with a neutral reaction. Acidic soils are “corrected” by adding alkali.
The site has been prepared since autumn, dug up, and fragments of plants are removed. 1 m2 beds are necessary:
- organic – 5 kg;
- urea – 20 g;
- potassium sulfate – 15 g;
- superphosphate – 30 g;
- nitrogen-containing agent – 35 g;
- dolomite flour – 200 g.
Organics can be replaced with peat mixed with coarse sand in a ratio of 3 * 1.
In the spring, in a greenhouse on a prepared bed, they dig a trench 25 cm deep, fold the top fertile layer next to:
- Drainage from pebbles, expanded clay or crushed stone is placed at the bottom of the recess.
- Topped with straw.
- Pour a layer of humus, above sawdust or dry leaves.
- Fill the ditch with soil.
- Pour over with hot water, cover with a black film.
By the time of planting, the bed will warm up, the seeds will sprout faster.
How to plant melons in a greenhouse
During the growing season in the greenhouse, the melon needs to form a bush. Properly distributing the culture, provide free access to plants and save space. On the one hand, the greenhouses make a wider garden bed, it occupies 2/3 of the territory. Melons are planted in a checkerboard pattern, with an interval of 40 cm. On the opposite side, 20 cm recede, a trench is laid, the melon is planted in one row with the same interval. Landing pattern:
- Mark the planting points for melons.
- They make indentations, pour ashes on the bottom. For seed breeding, a recess of 5 cm is sufficient, for seedlings – to the depth of a peat cup.
- The wells fall asleep, compacted, watered.
If there is a threat of a drop in temperature, the seedlings are covered with spunbond.
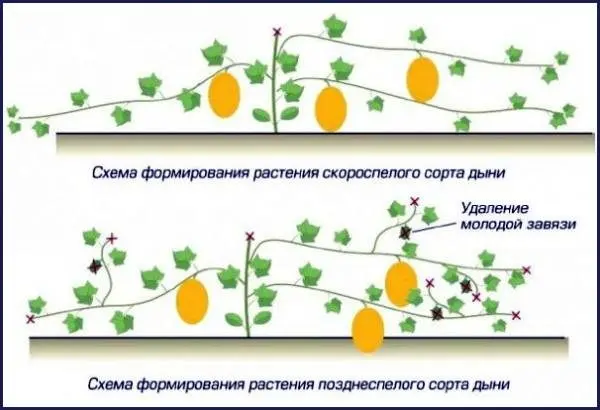
Rules for growing melons in a polycarbonate greenhouse
Schemes of the formation of melons in the greenhouse and videos will help to get a general idea of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbgrowing techniques. The culture requires constant care and monitoring of the growing season.
Watering Schedule
Melon is a drought-resistant plant that can go without watering for a long time. In the greenhouse, the melon is watered under the root, avoiding waterlogging of the soil and getting moisture on the root neck. The culture quickly and negatively reacts to high humidity, the root system rots, fungal and bacterial infections develop.
Watering is carried out with water, the temperature of which is not lower than +35 0C, cold application is not recommended. In industrial greenhouses for watering melons, titans with a thermostat are installed. Watering is carried out if the top layer is dried up to 5 cm. During fruit ripening, watering is reduced to a minimum, two procedures per month are enough.
When caring for melons in a greenhouse, top irrigation (sprinkling) is not used, because the plant does not tolerate high humidity. It is periodically observed that condensation does not accumulate on the walls, which falls on the plant and contributes to the development of fungal diseases.
Pollination of melons in a polycarbonate greenhouse
Most varieties of melons of different ripening periods are not self-fertile. For the formation of ovaries, they necessarily need pollinators. In greenhouses, you will have to pollinate the plant yourself manually. In large farms, mobile apiaries solve this problem. In a greenhouse on a personal plot, manual pollination is carried out as follows:
- find male flowers;
- pollen is collected from them with a cotton swab;
- shake off in the middle of the women’s.
The procedure is carried out 3 times with an interval of 24 hours.
How to pinch melons in a greenhouse
The formation of a melon in a polycarbonate greenhouse begins after the appearance of four leaves. Pinch off the top of the central stem. The melon gives two lateral shoots, they are left, they go to form a bush. During the growing season stepchildren grow, which are cut or broken. The number of ovaries is normalized in accordance with the variety, if the fruits are medium in size, 4 pieces are left on each shoot. After the extreme ovary, three leaves are left at the top, and the stem is pinched. The plant will not spend nutrients on the crown, they will go to the growth of the fruit.
Do I need to tie a melon in a greenhouse
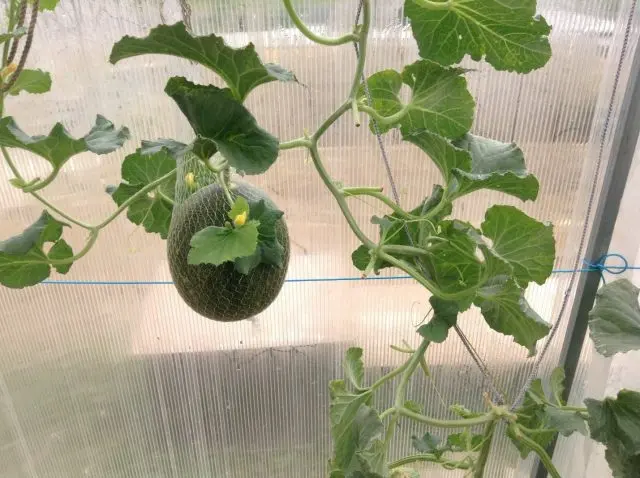

The fixation of melon stems in the greenhouse begins immediately after planting. The twine is pulled and fixed to the greenhouse structure. As the shoots grow, they are twisted along the support in the form of a spiral. In the process of ripening, the mass of fruits increases. In the greenhouse, a nylon mesh with large cells is put on each melon and tied to a trellis. If the first fruits lie on the ground, special material or boards are placed under them, the melons should not be allowed to come into contact with the ground.
When and what to feed
In the greenhouse, the melon is fed at the time of fruit formation with Kemira complex fertilizer with an interval of 14 days within one month. At the same time, potassium or wood ash is added. Top dressing is increased at the time of pumpkin ripening, the complex includes huminates and the Zircon growth stimulator. To enrich the soil with microelements, a fermented herbal infusion is added under the root with each irrigation. Melon will not bear fruit in acidic soils, so the root circle must be constantly covered with ash.
You can feed with a mixture of NPK (potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen) for 20 liters of water, 25 g of the product is consumed. The solution is applied under the root once a week throughout the growth period.
Conclusion
Forming a melon in a greenhouse begins after the formation of the fourth leaf with two side shoots. For the entire growing season, conditions are created, including: moderate watering, fertilizing, removing stepchildren, tying fruits and stems to a support. By installing lamps, increase the time of daylight hours, monitor the humidity of the air.









