Contents
Pork is the type of meat that is best digested by humans. It is ideal even for people suffering from liver diseases. But only under one condition: the meat must be lean. Pork and lean meat seem to be incompatible concepts, but there is a Pietrain pig breed that can satisfy this need. Lean pork is drier and less tasty than pork with some fat. But it is known that useful tasty does not happen.
The promotion of a healthy lifestyle has done its job, and Pietrain pigs are very popular in European countries and Latin America. In Our Country, due to climatic conditions, Pietrain has not received wide recognition and the breed is mainly used for crossing with meat and tallow breeds to improve the productive characteristics of offspring.
History of origin

The Pietrain breed has a very short and clear history of origin. There are no mysterious ancient ancestors of these pigs. Pietrain was bred in Belgium at the beginning of the XNUMXth century by crossing Berkshire, Great White and Yorkshire pigs. Not without the addition of local Belgian breeds of pigs, too. In breeding, inbreeding was often used to improve the meat qualities of the breed. Meat quality has improved, and the overall survival and acclimatization of Pietrain pigs has deteriorated.
In a difficult period in the pig market in the early 50s of the last century, the Pietrain breed gained popularity and was brought to Germany in the early 60s. There Pietrain is still used today to improve the productive characteristics of other pigs.
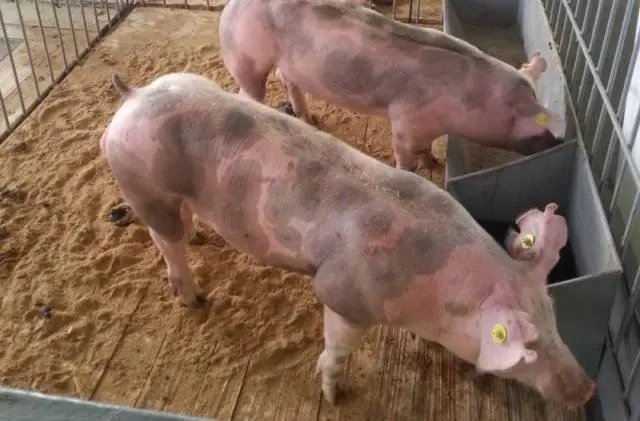

Pietrain were brought to the USSR back in 1964, but just those qualities that were worsened in the process of breeding the breed prevented the wide distribution of these pigs in the country. The Union needed unpretentious animals capable of adapting to different climatic zones. The breed characteristics of Pietrain pigs did not meet the requirements set by Soviet livestock specialists for productive farm animals. But a certain number of livestock remained, as representatives of the breed were able to improve the productivity of meat-fat pigs familiar to Our Country.
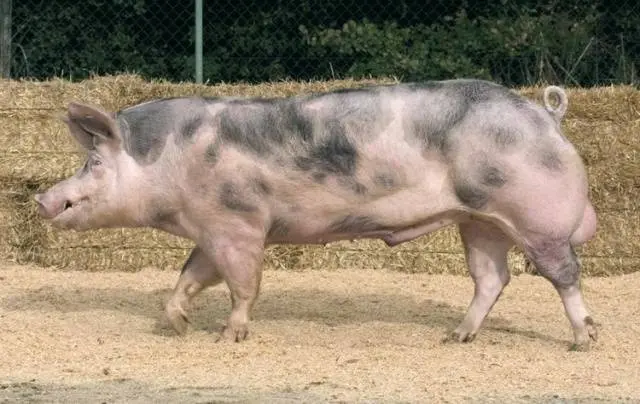
Description

When looking at the photo of a representative of the Pietrain pig breed, there is no doubt in the direction of productivity. The Pietrain boar has a pronounced structure of the animal meat direction:
- long cylindrical body with a shallow chest;
- powerful hams;
- fleshy forearms no.
- small head with large but thin auricles.
In the description of the Pietrain pig breed, a characteristic groove along the ridge, a straight head profile and a wide sacrum are also indicated as characteristic features. But you can’t see it in the top photo. A straight profile is not visible on the bottom.

A more characteristic sign of the breed is the black and piebald color – the only possible Pietrain pig.
Productivity
The productive characteristics of the Pietrain pig breed are not impressive, although the slaughter yield from the carcass is 80%. But the weight of the carcass itself is not great. The live weight of a wild boar is up to 240 kg, pigs – up to 150-170 kg. At the same time, representatives of the breed have a very high feed consumption during fattening. Pietrain piglets daily give an increase of 500 g, but at the same time they need 2,5-3 kg of feed per day. By 7 months, Pietrain piglets grow up to 90 kg. Other breeds of pigs can gain up to 6 kg by the age of 100 months.
This is the main reason why this meat breed has conquered the European market. In addition, Pietrain feels good in the mild European climate.
Pros of the breed
The main advantage of the breed is resistance to circovirus. The virus often leads to the death of animals. Young animals of all breeds of pigs suffer from the disease, except for Pietrain.
The pluses also include:
- no tendency to obesity;
- yield of pure meat from the carcass up to 65%;
- improvement of meat characteristics of other breeds.
Cons
Pietrain has much more disadvantages and this prevents the spread of the breed in private backyards:
- sensitivity to temperature changes;
- poor ability to acclimatize;
- sensitivity to stress;
- exactingness to feed;
- low weight gain;
- low milk production of sows;
- poor quality meat.
Pietrain meat quickly oxidizes in air and loses moisture.
Content
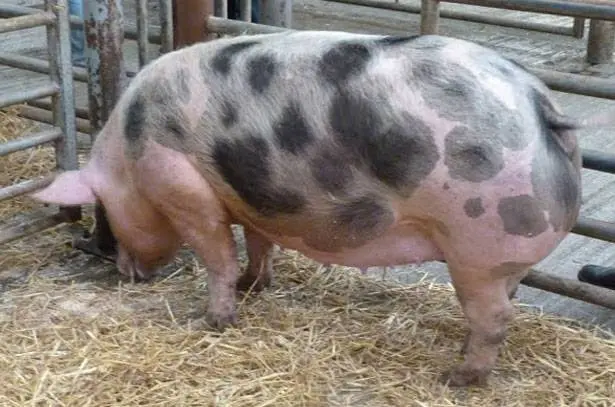
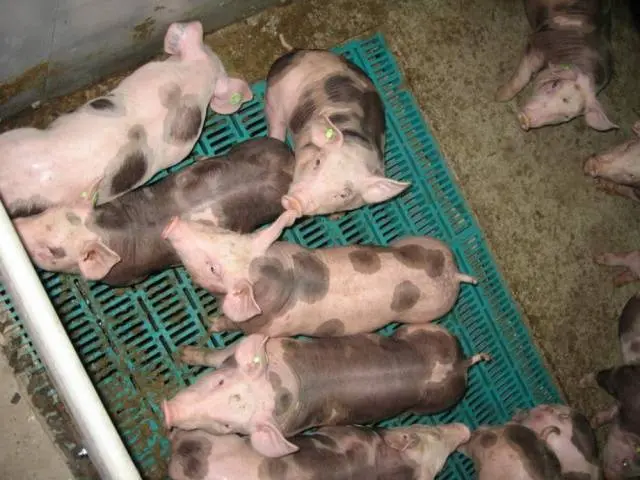
Due to the very thin layer of fat, Pietrain pigs are equally resistant to both cold and heat. Already at +15°C they feel uncomfortable. And at + 30 ° C, they can get a heat stroke. Breeding this breed of pigs requires a specially equipped climate-controlled pigsty. In Our Country, heating systems are traditionally installed in animal rooms; cooling is usually not required in summer. But not in this case. In order for the livestock of these pigs to feel good, an air conditioner will have to be installed in the pigsty. In particular, the photo shows a Pietrain pig in such a specially equipped pigsty.

Due to the thin skin, these pigs cannot be kept on a metal grate, as they do with Big whites. Frequent cleaning of the bedding is also required so that the urine does not corrode the skin. All this complicates and increases the cost of keeping Pietrain piglets. In general, only large complexes or breeding stations can breed this breed.
Feeding

Muscle fibers always require more food to maintain mass than fat of the same volume. But during a hunger strike, the muscles “deflate” first. This feature of living organisms plays a bad role in the cultivation and fattening of Belgian meat pigs. Due to the rapid burning of nutrients to ensure the life of the “muscular jocks”, Pietrain requires more feed per kilogram of weight than meat-fat pigs.
When breeding, it will be necessary to take into account that sows have low milk production. Milk alone from a sow is not enough for piglets. Feeding piglets will have to be introduced very early. And this despite the fact that usually on farms, piglets begin to be fed already on the 5th day of life. Accordingly, Pietrain will have to give additional food almost from the first day.

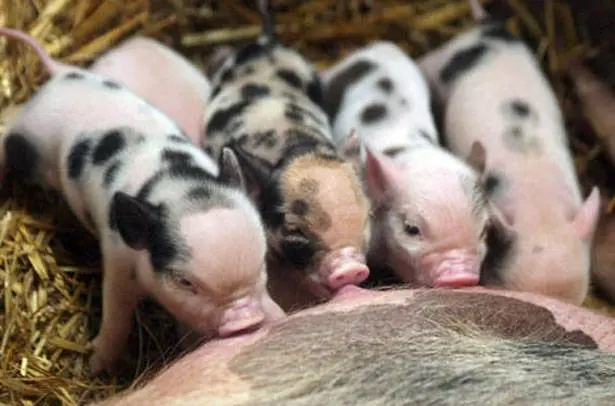
At the same time, the sow usually brings no more than 8 piglets per farrow.
Young animals for fattening are given food rich in carbohydrates and proteins:
- meat production waste and meat and bone meal;
- fish and fishmeal;
- return;
- dairy production waste;
- kitchen waste;
- boiled potatoes;
- roots;
- beans.
Pigs are actually very poor at digesting grain feed, especially whole grains. Therefore, it is not necessary to be especially zealous with corn, barley or oats.
The natural food of pigs is various types of nuts, acorns, roots, berries, sometimes animal food. Wild boars rarely graze on cereals.
Breeding

Before breeding a breed in your own backyard, you need to carefully analyze your ability to create suitable conditions for these pigs. Experienced pig farmers do not advise trying to recruit a herd exclusively from representatives of the Belgian breed. The best option would be to cross the Pietrain boar with the Landrace or Duroc sow. When crossed with Landrace, the young grow faster, and when crossed with Duroc, the meat characteristics of the offspring improve. Often used and three-breed crossing: Big White, Landrace and Pietrain. But such crossing is available only for pig-breeding complexes. A private trader does not have the opportunity to keep such a set of pigs.

Nuances of breeding
Puberty in boars occurs at 8 months. Pigs mature earlier, as in any other breed. But in order to obtain full-fledged offspring, the Pietrain sow is not recommended to happen before 10 months.
Sows have a significant drawback: they are not only infertile and give little milk, but they also have enough milk for only 6 cubs. If the number of piglets in the litter is more than 6, they must be fed from the very first day. Otherwise, the weakest will die of starvation.

When feeding is introduced, it should be given to all piglets. The best feeding would be a whole milk substitute for piglets.
Such substitutes often cause severe diarrhea in piglets and it is better to buy a more expensive, but better quality.
The second option for feeding: reverse and whey after making cottage cheese. It is better if the milk is curdled with calcium chloride. The whey from such cottage cheese is not sour and contains an additional dose of calcium.
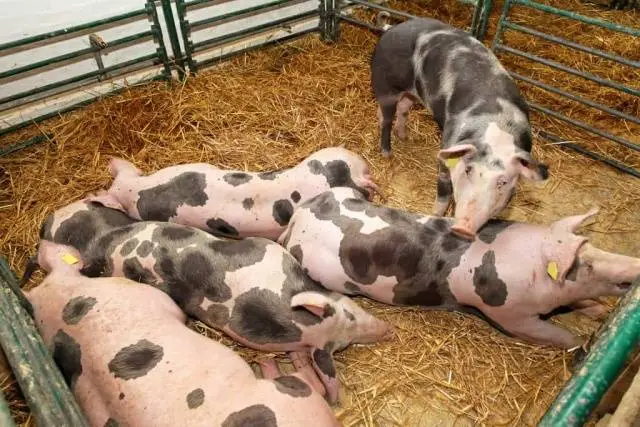
To increase milk yield, a sow should be fed 4 times a day, giving high-calorie and juicy feed. With properly organized feeding, you can save even a dozen Pietrain piglets, as in the photo below.

Reviews
Conclusion
Reviews about the Pietrain pig breed from private owners are usually not laudatory. This is due to the characteristics of Belgian pigs. It is difficult for private owners to provide the necessary conditions. The best option: buy fattening hybrids at the breeding station.









