Contents
- What is photodynamic therapy?
- Stages of photodynamic therapy
- The use of photodynamic therapy for the treatment of cancer patients
- Advantages of photodynamic treatment
- Cons of photodynamic therapy
- Indications for therapy
- Contraindications to PDT treatment
- What drugs are used in the treatment?
- Names of drugs used for PDT
- Application of Photofrin in practice
- Undesirable effects after photodynamic treatment
- How to facilitate rehabilitation after treatment
- Feedback on photodynamic treatment
- On the prospects for the use of PDT
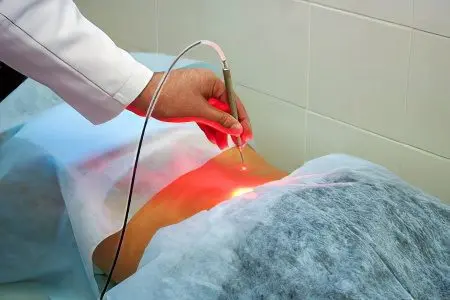
Photodynamic therapy is one of the newest methods of cancer treatment. Its essence is reduced to the selective accumulation of a photosensitizer by the tumor after intravenous or local administration. Subsequently, the cancerous tumor is irradiated with a light source (laser or non-laser). As a result, in the affected tissues, a reaction occurs with the release of singlet oxygen. This leads to the death of cancer cells.
Advantageous differences of photodynamic treatment from standard procedures for getting rid of cancerous tumors come down to the following factors:
During the treatment, the patient’s immunity does not suffer.
The patient does not experience toxic reactions.
There are no local or systemic complications.
The treatment can be repeated several times.
Hospitalization of the patient is not always required.
What is photodynamic therapy?
The method has an abbreviated name PDT and is reduced to the effect on a cancerous tumor of photosensitizers (a group of drugs) and a light source. The drug can be applied directly to the skin, or injected into the body through the veins. After a short time, it is absorbed in the tissues, and then a light beam is directed to the affected area.
The tumor, after exposure to photodynamic therapy, must be deprived of nutrition. For this purpose, it will be necessary to remove the blood vessels.
Stages of photodynamic therapy
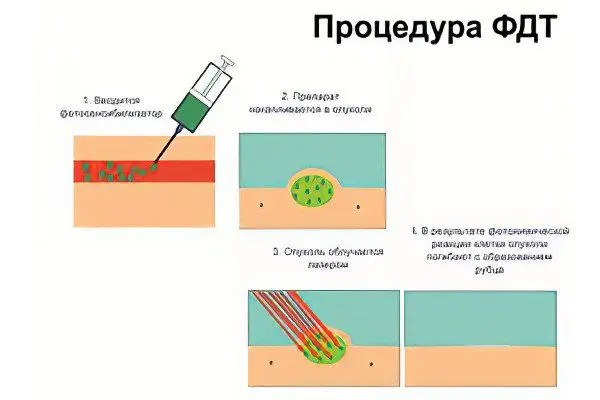
Photodynamic therapy is implemented through several successive stages:
The sensitizing solution is injected through a vein.
The drug accumulates in the affected tissues. This process may take several days.
A laser beam is applied to the tumor, destroying it. If the neoplasm lies in deep tissues, then special LED tubes are used for irradiation. This leads to a toxicological reaction and the tumor dies. At the same time, healthy tissues surrounding the unhealthy area are not adversely affected.
Pathological cells disintegrate, and mutated tissues are restored. This stage takes about 30 days.
The use of photodynamic therapy for the treatment of cancer patients
This type of treatment improves the quality of life of cancer patients. Although photodynamic exposure does not cause significant harm to health, it has not yet found wide distribution in many countries.
In the capital of Russia, this type of treatment began to be used back in 1998. At the moment, the procedure can be completed in five offices in Moscow. Approximately 2000 cancer patients received treatment.
The method of contact photodynamic therapy was created and successfully used in the Oncological Dispensary number one. In this case, the penetration depth of the laser beam is 2 cm.
Advantages of photodynamic treatment

Photodynamic treatment is a method of combating cancer and precancerous conditions.
Doctors are trying to actively use PDT when detecting oncology in the early stages of development, as this provides many advantages:
Only cancer cells are destroyed.
All patients tolerate this type of therapy well, regardless of their age.
Surrounding tumor tissues are minimally affected.
In the treatment of oncology of the skin, a positive result can be achieved, which is equivalent to 100%.
The impact of PDT on the cervix does not negatively affect the subsequent ability of a woman to give birth to children.
For treatment, it is not necessary to place the patient in a hospital.
If such a need arises, then photodynamic therapy can be carried out several times.
The method does not have a systemic effect on the body.
During the procedure, anesthesia is not required, as it is absolutely painless.
In the complex treatment of oncological diseases, photodynamic therapy can be implemented as an independent technique.
It has been established that photodynamic therapy has a devastating effect not only on cancer cells, but also on the human papillomavirus. In parallel, there is an antibacterial and antifungal effect, the immune defense of the body increases. Such a large number of advantages of PDT makes this method of treatment quite popular.
Cons of photodynamic therapy
In addition to the positive aspects, photodynamic therapy has a number of disadvantages, including:
The method has a limited scope. With its help, it is possible to influence only those cancer cells to which it is possible to access the light beam.
After the introduction of drugs-photosensitizers for a certain time period, increased sensitivity to light persists.
However, PDT allows you to get rid of cancerous tumors, so the disadvantages of the method can be considered insignificant.
Indications for therapy
The method of photodynamic therapy is effective for the treatment of the following diseases:
Various cancerous tumors and precancer.
Vitiligo, psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus and other dermatological diseases.
Diseases of the organs of vision.
Treatment of trophic ulcers and other wounds that do not regenerate for a long time.
Contraindications to PDT treatment

The list of contraindications for photodynamic therapy is quite small:
Diseases of the liver.
Kidney disease.
Decompensated diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Hypersensitivity reaction to the components of administered drugs.
Hematological diseases.
Pregnancy.
Lactation.
The method is used for the treatment of oncological diseases only according to strict medical indications.
What drugs are used in the treatment?
To implement the PDT method, preparations from two groups are applicable:
Sensitizers belonging to the first generation. They are made on the basis of porphyrins (Photohem, Photofrin-1 and Photofrin-2, as well as others). These drugs have a number of disadvantages, including: poor selectivity of accumulation in tumor tissues, the inability to penetrate to a depth of more than 1 cm. The use of first-generation drugs provokes the development of a photosensitivity reaction that lasts for several weeks.
Second-generation photosensitizers (Photolon, Photosens-aluminum-sulfophthalocyanine). They were designed to bypass those negative effects that occur with the use of first-generation drugs. These include phthalocyanines – these are synthetic porphyrins that absorb light in the range of 670-700 nm. However, the period of skin phototoxicity of these drugs remains quite long (from six months to 9 months). Chlorins and chlorin-like sensitizers are also second-generation drugs. They are able to absorb the light wave in the tissues at a greater depth.
Sensitizers of the third generation. One of the few representatives of this group is Bacteriochlorophyllide-serine. During experiments on animals, this drug showed excellent results in the treatment of melanoma and other oncological tumors.
The main characteristics of drugs used in PDT:
Drugs should accumulate exclusively in cancerous tumors, but not affect intact cells.
Drugs should have low toxicity.
Drugs must be quickly excreted from the body.
Drugs should not accumulate in the dermis.
Preparations must have luminescent properties.
Preparations must be stable during storage and administration to the body.
Preparations should have an intense absorption maximum of 660-900 nm.
Other characteristics of photosensitizers:
Fluorescence;
High light absorption coefficient;
Photoresistance to radiation used for cancer therapy.
Names of drugs used for PDT

Photofrin is one of the popular drugs used in photodynamic therapy. Its activation occurs after tissue exposure to red light.
With the help of Photofrin, the following diseases are treated:
Lungs’ cancer.
Cancer of the larynx. Photodynamic therapy is prescribed in cases where the neoplasm reaches an impressive size and its removal with a laser is impossible.
Barrett’s esophagus. Photofrin is prescribed for prophylactic purposes in order to prevent the development of oncology.
The drug that is used to treat senile keratosis is called aminolevulinic acid. Acid becomes active after being exposed to blue. It is allowed to apply the drug exclusively on the head and face.
In Russia, a domestic drug for photodynamic therapy called Photogem was developed, which has passed all the necessary clinical trials and has been approved for use since 1996.
Modern medicine also has other drugs for photodynamic therapy, however, they are used much less frequently.
Application of Photofrin in practice

The drug is injected into the body through a vein. After ingestion, it is distributed throughout the body, not penetrating exclusively into cancerous tumors. However, healthy tissues will get rid of Photofrin on their own after a few days. In cancer cells, the substance, on the contrary, will linger.
However, without exposure of the tumor to a beam of light having a certain wavelength, nothing will happen to it. The destruction process is activated only after the treatment procedure is completed.
When it is necessary to get rid of lung cancer, they are irradiated with a bronchoscope. Since the laser has a low power, it does not cause any damage to the lung tissue.
In general, the procedure can take 5-45 minutes. Its duration directly depends on where exactly the tumor is located and what size it is. After a few days, the body will get rid of the destroyed tissues on its own. When the need arises, the treatment procedure is repeated.
Contraindications to treatment with Photofrin:
Too narrow a channel separating the esophagus from the bronchi.
The presence of a neoplasm that affects large blood vessels.
Stomach ulcer.
Dilated veins of the stomach.
Individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Undesirable effects after photodynamic treatment

More often than other side effects from ongoing therapy, patients experience increased sensitivity to sunlight, swelling at the site of exposure and the appearance of minor pain.
Increased photosensitivity is explained by the fact that the drug is not excreted from the body immediately, but over time. Depending on the individual patient, this side effect may persist for several months. When sunlight and bright light hit unprotected areas of the dermis, blisters will appear on it. And this reaction happens almost instantly.
As for the duration of the increased photosensitivity reaction, this fact depends on which drug was used for treatment. When using sensitizers of the 1st generation, it lasts about 30 days, for sensitizers of the 2nd generation – up to six months, and for chlorins – no more than a few days.
To avoid negative reactions, it is necessary to reliably protect the skin and eyes. However, this does not mean that a person should remain locked in a dark room for several months. After all, daylight helps to remove the medicine from the body. Gradually, the photosensitivity reaction will decrease, but this will not happen earlier than 30 days after the treatment.
When the procedure was performed in the larynx, its swelling can lead to swallowing disorders. If the impact was made on the tissue of the lungs, then breathing difficulties are often observed. These symptoms should not be ignored, they must be reported to the attending doctor.
Other side effects are:
Headaches, vomiting or nausea, hiccups. They appear after photodynamic treatment on the esophagus.
Bronchitis, pneumonia and shortness of breath are side effects of lung cancer treatment.
If a person has any unusual symptoms, then the doctor must be the first to know about them.
How to facilitate rehabilitation after treatment

To reduce or completely avoid side effects from photodynamic therapy, the following recommendations allow:
All incandescent lamps in the house should be protected by lampshades or dark shades.
Curtains, after returning from the hospital, must be kept closed.
To protect yourself while returning home from a medical facility, you must take a hat with a wide brim, dark glasses. Clothing should have long sleeves, legs should not be bare.
For a month after the treatment, you need to stop going outside during the daytime. If this is not possible, then even with a cloudy sky, you need to carefully protect the skin.
Direct light should be avoided in the eyes.
Do not use a hair dryer. The fact is that even getting a jet of hot air on the skin can provoke unwanted side effects.
Compliance with these rules will minimize the risks of developing adverse events after the treatment.
Feedback on photodynamic treatment

In general, patients respond positively to this therapeutic method. PDT does not injure the skin, does not leave scars and scars, and the effectiveness of the treatment is very high.
All patients indicate that they did not experience pain during the treatment. However, a hypersensitivity reaction to light is observed in every patient. This causes corresponding difficulties in maintaining a habitual way of life.
As for the negative reviews, almost all of them come from people who were negligent about medical recommendations and did not follow them. It should be tuned in advance to the fact that in the treatment of a tumor of the larynx, difficulties may arise with swallowing food and breathing. However, after a while they self-destruct.
Professor S. D. Nikonov, who practices in Novosibirsk, has developed a new method of treatment using PDT. He practices it in diseases of the brain, as well as in carcinomatous pleurisy. The doctor has released a lot of scientific papers on the effectiveness of the technique he uses.
You can also undergo the PDT procedure at the Krasnodar Oncological Dispensary at number one. The medical institution has the most modern equipment, which guarantees high-quality therapy.
Thanks to the development of modern medicine, oncology is no longer a sentence for a person. If the disease is detected at an early stage, then it can be successfully eliminated.
On the prospects for the use of PDT

Currently, photodynamic therapy is widely used in the treatment of cancer. There is evidence of successful treatment of Barrett’s disease with the help of PDT. The method is applicable in the treatment of obstructive processes of the esophagus and biliary tract (in combination with laser therapy).
Research is being conducted on the use of photodynamic therapy for the treatment of malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract, breast, skin and soft tissues, and the abdominal cavity.
PDT gives excellent results in combination with other methods of therapeutic effects on the body, such as biotherapy, chemotherapy, hyperthermia, hyperglycemia.
PDT can be used as a method that improves the quality of life of palliative patients, patients with inoperable tumors, with multiple lesions of the body with metastases.
Scientists are constantly creating new photosensitizers and means of delivering light rays to the deep structures of the body.









