What is phlegmon?
Phlegmon is a purulent inflammation of fatty tissue, which is characterized by an acute course. The pathological process in a short period of time covers the tissues surrounding the area of inflammation, and extends both to cellular spaces and to tendons and muscles.
Causes of phlegmon
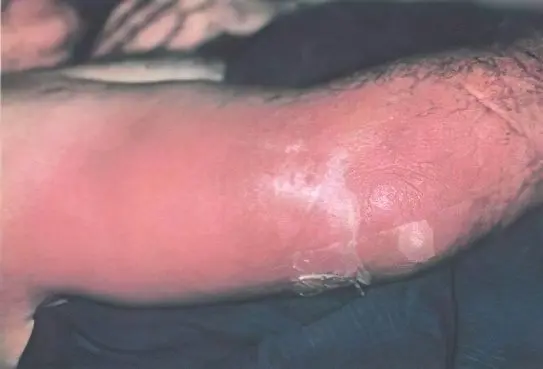
The place of localization of phlegmon can be subcutaneous, submucosal, as well as axillary tissue, thigh area, buttocks, lower back, perineum, anterior wall of the peritoneum. The disease can occur when a staphylococcal, streptococcal infection, pus-like microorganisms enter the human body. Pathogens can enter various ways: through damaged mucous membranes, skin or blood.
Phlegmon can also develop at the site of contact with the skin of irritating liquids: turpentine, kerosene, gasoline, etc.
If phlegmon arose as a result of secondary infection, then some diseases of the skin can be attributed to the causes of the appearance of phlegmon: furuncle, carbuncle, osteomyelitis.
Symptoms and diagnosis of phlegmon
Among the main symptoms of the disease, painful swelling, the rapid spread of the inflammatory process, and redness of a large area of the skin are noted. Body temperature can rise above 40 °C Celsius. The patient is in severe pain; the part of the body on which phlegmon is formed may cease to perform its functions, the disease is accompanied by intense thirst and general weakness.
Over time, the swelling of the inflamed area of the skin increases, the skin turns red and shiny. On palpation, you can determine the clear boundaries of the seal, which is motionless and very hot. Probing the affected area is painful for the patient.
At the beginning of the development of phlegmon, tissue infiltration is observed at the site of inflammation, after a couple of days, a serous-purulent discharge appears if the causative agent of the pathological process is streptococcus, purulent with staphylococcal infection, ichorous with putrefactive infection.
The appearance of all the above symptoms in a patient requires urgent hospitalization to clarify the diagnosis.
Timely diagnosis of abscesses and phlegmon is important for determining the nature of the occurrence of the pathological process.
Phlegmon can be non-odontogenic in nature, that is, it can occur as a result of the development of an inflammatory process in the lymph nodes. This also includes the appearance of phlegmon due to decay of the hematoma, phlegmon of some parts of the body: face, feet, etc.
Odontogenic phlegmon may appear in the area of a diseased tooth: maxillofacial, submandibular phlegmon.
Phlegmons are isolated, which are based on nonspecific and specific inflammation or erysipelas of tissues.
In advanced cases, phlegmon can cause a number of complications: lymphadenitis, lymphangitis, erysipelas, thrombophlebitis, septic inflammation, etc. When the pathological process spreads to neighboring tissues, purulent arthritis, tendovaginitis and other inflammatory processes of internal organs can begin.
Facial phlegmon threatens with the development of thrombophlebitis of the facial veins and meningitis. Phlegmon of the foot in advanced cases can lead to disruption of the functioning of blood vessels, which can lead to amputation of the limb.
Phlegmon of the face and neck can lead to the involvement of the most important venous and arterial vessels in the pathological process, which in turn leads to an abscess of the brain and impaired oxygen supply to the lungs and death. Another dangerous complication of phlegmon of the face and neck is the development of Ludwig’s angina.
Treatment of phlegmon
Phlegmon is treated in a hospital, where an accurate diagnosis is made and an effective treatment is selected depending on the type of phlegmon and the severity of the pathological process. Treatment of phlegmon is carried out in a complex.









