Contents
Deterioration of erectile function, discomfort and deformation of the penis, accompanied by the appearance of a plaque, may indicate a rare disease – Peyronie’s disease. The appearance of such symptoms requires immediate medical attention.
Peyronie’s Disease
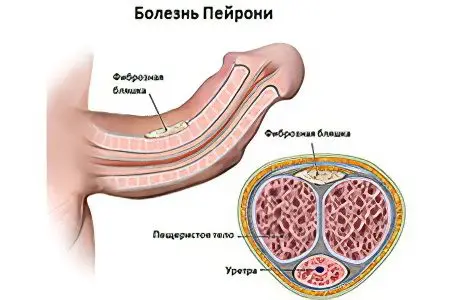
Peyronie’s disease is also called fibroplastic induration of the penis. With this pathology, the penis is deformed during an erection. Scar tissue forms under the skin of the organ. Most often, it grows in the lower part of the organ, although sometimes it begins to form at the top of the penis. During an erection, a man experiences pain, since the cicatricial joints do not have sufficient elasticity. Being in an excited state, the man’s sexual organ begins to deform. This leads to the fact that intimacy becomes impossible. Against the background of the disease, the man begins to suffer from neuropsychiatric disorders.
Thus, Peyronie’s disease is a curvature of the penis against the background of the growth of fibrous compounds. Plaques or benign neoplasms form on the genitals.
Main Risk Factors
The disease is not often diagnosed. On average, it is detected in 0,5-1% of men aged 35-60 years. The older the man, the less elastic the tissues of his penis. This leads to the fact that during an erection, the likelihood of microtrauma and ruptures increases. In young people, this pathology is rarely found. After the age of 60, the risk of developing Peyronie’s disease is also low, since intimacy during this period happens infrequently. According to WHO, 1/3 of men over 60 years of age are not at all able to have sexual intercourse.
Peyronie’s disease symptoms

The main symptom of pathology is pain, which can have a different intensity.
In addition, Peyronie’s disease is manifested by symptoms such as:
Curvature of the penis to one side.
Deterioration of erectile function. During arousal, the penis does not harden to the desired state.
A seal appears under the skin.
The penis decreases in size as it loses its normal shape.
The early stage of the development of the disease may not manifest itself. Its duration is 6-18 months. The sooner a man pays attention to a developing problem and goes to see a doctor, the more favorable the prognosis.
However, in practice, it happens that the first signs of the disease do not become a reason to visit a doctor. Most men try to cope with the problem on their own, using traditional medicine methods. This leads to the fact that the disease progresses and it will be difficult to cure it.
Causes of Peyronie’s Disease
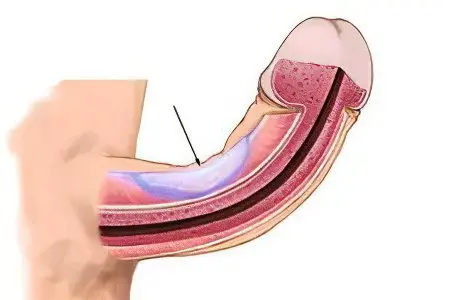
The symptoms of Peyronie’s disease were first described in 1561. A little later, it was discovered by a surgeon from France, Francois Gigot-de-la Peyronie. Despite this, the causes of the disease are not yet fully understood. Only risk factors are known that can provoke its occurrence.
These include:
Injuries to the penis, for example, during blows or falls.
Closed fractures of the penis, in which the skin remains intact, but internal hemorrhage occurs.
Microscopic damage that a man can receive during intimacy.
Violations in the work of immunity.
Diabetes.
Narrowing of blood vessels, which occurs with atherosclerosis.
Hormonal disorders.
Diseases of the connective tissue.
Gout, in which there is a high level of uric acid in the blood.
Deficiency of vitamin E and calcium.
Hereditary predisposition.
Treatment of impotence with certain drugs.
High levels of serotonin in the blood.
Peyronie’s disease can be either congenital or acquired. The first type of violation is rare. It manifests itself in the case when the child’s urethral canal does not develop fully, or there is hypoplasia of the albuginea.
With the acquired form of the disease, plaques form on the penis, and benign neoplasms on the urethra. Pathology requires treatment, as it will progress.
Stage of the disease
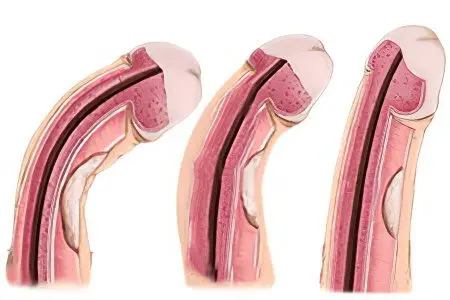
There are 4 stages of Peyronie’s disease:
hidden stage. At this time, the man experiences discomfort during arousal. The plaque at this stage is invisible, it cannot be palpated. The deformation of the penis is just beginning, but it is difficult to detect it. During the examination, the doctor can detect a violation of the blood supply to the organ.
Initial stage. Slight pain begins to disturb a man not only during an erection, but also at the usual time. The plaque becomes noticeable, but it does not have a clear border. It can be palpated. During sexual arousal, you can notice the deformation of the penis. The seal is detected during an ultrasound, but an x-ray will not give any information.
stage of stabilization. The pains are weak, the plaque becomes clearly defined, resembles cartilage in appearance. The organ is severely deformed. The plaque can be visualized both during an ultrasound scan and on an x-ray.
Final stage. There is no pain, the plaque hardens and resembles bone. The penis is severely deformed.
Classification of the disease
By degree of flow

Specialists distinguish between the painful and functional period of the development of Peyronie’s disease.
During the painful period, a man experiences discomfort both during an erection and at rest. Pain indicates tissue stretching and plaque formation in the albuginea. The sexual organ begins to deform, this curvature is noticed by the man himself.
The pain period lasts 6-18 months. If at this stage a man seeks medical help, then he will be able to cope with the pathology without surgical intervention.
The symptoms of the functional period are as follows:
The erect penis is severely deformed.
During arousal, a man experiences severe pain.
The plaque becomes clearly defined.
The nutrition of the organ is disturbed, erection suffers. In 30% of men, potency worsens.
By type of deformation
Depending on the type of deformation, there are:
Dorsal curvature – the penis is deformed in an upward direction.
Ventral curvature – the organ is directed downward.
Lateral – the penis is curved to the side.
Diagnosis of Peyronie’s disease

During the initial appointment, the doctor interviews the patient, listens to his main complaints, and clarifies the severity of the symptoms. Then the doctor performs an examination of the penis using a vacuum erector. This will allow you to assess the degree of curvature, the shape of the organ and the location of the plaque.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor will refer the patient to undergo the following diagnostic procedures:
MRI of the penis. This technique makes it possible to clarify the location of the plaque, to detect existing problems in the blood supply to the penis.
Cavernosography. This procedure is reduced to taking pictures on an x-ray machine. During the study, a contrast agent is used. The method allows you to assess the condition of the internal tissues of the penis, to clarify whether there are any changes in its spongy and cavernous body.
Ultrasound. The method is aimed at assessing the blood flow of the penis. This procedure is prescribed for exacerbation of the disease.
Complications
If a man does not seek medical help in time, this will lead to the development of the following complications:
Impotence.
Infertility.
Depression.
Intense pain during intimacy and sexual arousal
Complications can be the result of the progression of the disease, as well as the use of folk remedies. With an advanced stage of the disease, it will not be possible to do without surgery. Its negative consequence is the shortening of the penis.
Peyronie’s disease treatment
Treatment of Peyronie’s disease has two directions:
Conservative treatment, in which a man will need to take medicines. Such therapy is available at stages 1, 2 and 3 of the disease.
Surgical intervention. It is resorted to at 4 stages of the development of the disease.
There are no uniform standards of treatment, the doctor proceeds from the individual characteristics of the course of Peyronie’s disease in a particular patient.
Non-surgical treatment
Algorithm for the treatment of patients with Peyronie’s disease, which is at an early stage of development:
Pain reduction.
Removal of inflammation.
Plaque resorption.
Stop the progression of the disease.
Treatment should last at least six months.
At this time, drugs such as:
Interferon.
Vitamin E.
Drugs from the group of NSAIDs.
Colchicine.
Tamoxifen, etc.
Experts do not recommend injecting any drugs directly into the plaque itself. The fact is that even minor damage to the integrity of the penis can increase fibrosis. However, sometimes it is not possible to do without injections.
For this purpose, drugs such as:
Steroids. They are used only if a person has been ill for no more than 1,5 years and the plaque has not completely formed. Hormones are rarely used, as they do not achieve the desired effect.
Enzymes (collagenase). This tool allows you to soften scar tissue, as it breaks the peptide bonds of collagen. The drug is injected into the plaque perpendicular to the penis. In 65% of cases, it is possible to reduce the curvature. Treatment continues for 6 weeks. Injections are given 2 times in 7 days. The procedure should be carried out by a professional, since an overdose of the enzyme is dangerous with hemorrhages and the appearance of new areas of fibrosis.
Interferon. To date, there is no accurate data on the effectiveness of the use of this drug.
Verapamil. This drug is injected into calcified plaques and into areas of fibrosis in an acute inflammatory process. It promotes the dissolution of such areas.
For oral administration, such medicines are recommended as:
Vitamin E. It slightly reduces the deformation of the organ and helps to reduce the intensity of pain.
Colchicine. The drug prevents the production of collagen and activates its own collagenase, and also helps to reduce pain and inflammation. However, during the reception, many patients begin to suffer from liquefaction of the stool.
Tamoxifen. This drug has antiestrogenic and antitumor effects. Thanks to its intake, T-lymphocytes and macrophages die.
Potaba. This drug is aimed at slowing down the production of fibrin.
Pentoxifylline. In a patient receiving this drug, the blood supply to the organ improves, the content of nitric oxide in the blood increases. This stops the progression of the disease and even contributes to its reverse development.
PropionylL-carotene. This drug allows you to reduce the degree of deformation and reduces the intensity of pain.
In addition to the use of drugs, a man may be recommended a physiotherapeutic effect on a diseased organ:
Magnetotherapy.
Use of diadynamic currents.
Laser treatment.
Mud treatment.
Electrophoresis.
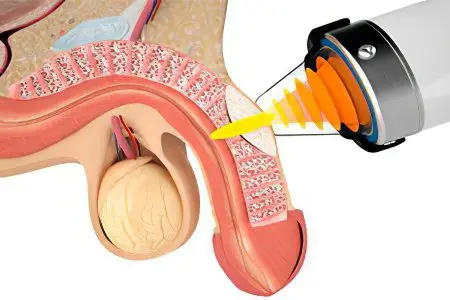
UVT. In this case, a special device is used, which is a source of impulses. The doctor directs them directly to the site of fibrosis. This allows you to soften the plaque and straighten the penis. To be able to implement UHT, the curvature should not be more than 45 degrees.
It is important to remember that it is forbidden to use any drug on your own! This can lead to the development of serious complications and health problems.
Surgery
Surgery is resorted to in the case when conservative therapy has not achieved the desired results.
Indications for surgery:
Curvature of the penis more than 45 degrees.
Problems with erection.
Plaque calcification.
The operation can be of 3 types:
Shortening of the penis. In this case, the doctor removes a portion of the tunica from the side opposite to the curvature. The penis flattens out but becomes shorter. Apply this method if the curvature does not exceed 60 degrees.
Plaque excision. All fibrous structures are removed, and the resulting voids are filled with biological or synthetic material. This procedure is carried out when the curvature exceeds 60 degrees. The technique is associated with the risk of complications, so they resort to it infrequently.
Falloprosthetics. This method is used in the case when an erection in a man is impossible. The doctor does not touch the plaque itself, but instead of the cavernous body, an implant is implanted.
Prevention

Measures to prevent Peyronie’s disease:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Refusing to have sex while under the influence of alcohol or drugs, as this increases the likelihood of injury.
Proper nutrition, daily routine. Food should saturate the body with vitamins and minerals.
Blood pressure control.
Doing sports.
Weight control.
Regular visits to the doctor by patients with diabetes, as well as men aged 30-60 years.
If a person notes discomfort in the penis area, you need to contact a urologist and not try to cope with the problem using traditional medicine methods.
Which doctor to contact
Peyronie’s disease is treated by an andrologist and a urologist. Also, a man may need the help of a surgeon, rheumatologist, physiotherapist.
An andrologist is a doctor who specializes exclusively in “male problems”. He treats diseases of the male reproductive system.
The urologist is engaged in the identification and elimination of pathologies of the genitourinary system and male genital organs.
Video: Surgeon, urologist-andrologist Kerimov Anar Kurbanovich about Peyronie’s disease:









