Contents
Periarthritis of the knee joint is an inflammation of the periarticular tissues in the region of the internal condyle of the femur. It is in this place that the tendons of the quadriceps femoris (“crow’s foot”) are attached. Periarthritis develops against the background of chronic inflammatory processes affecting the knee joint, or may be the result of injury or overstrain of tendons and muscles.
The disease is most often diagnosed in women who have crossed the line of 40 years. However, even children are not immune from it. Pediatricians sometimes make such a diagnosis for babies aged 3 years and older, during their active growth period. In this case, the disease is not dangerous and goes away on its own as the child grows up. While at a more mature age, periarthritis can even become the cause of a person’s disability, as it sharply limits his ability to move.
In the international classification of diseases, periarthritis of the knee joint is indicated by the code M77.8 and belongs to the group “Other soft tissue lesions”.
Periarthritis of the knee joint is characterized by pain that occurs when a person makes passive or active movements of the lower limb. There is no pain at rest.
Causes of periarthritis of the knee joint
Periarthritis of the knee joint can be caused by the following reasons:
Injuries of the soft tissues of the knee, which occur cyclically or simultaneously. It can be blows to the knee, a fall on it or a dislocation. When the tendon fibers are torn, internal hemorrhages occur, edema is formed, which entails a violation of the blood supply to the damaged area. As a result, periarthritis develops.
A sedentary lifestyle, as well as prolonged static loads on the lower limbs.
General hypothermia of the body.
Violation of the innervation of the lower extremities.
Disruptions in the endocrine system. In this regard, periarthritis is more often diagnosed in people with obesity or diabetes.
Hormonal imbalance in the body. Women who have entered the postmenopausal period are especially susceptible to periarthritis.
The presence of a chronic degenerative process in the knee joints: arthritis, arthrosis.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system in general.
Postponed operations on the knee joints. In this case, periarthritis acts as a complication.
Congenital connective tissue dysplasia, arthropathy.
Symptoms of periarthritis of the knee joint
Symptoms of periarthritis of the knee joint are directly related to the location of inflammation:
Pain in the knee joint.
Swelling of the inner surface of the knee, hyperemia of the skin.
The appearance of pain during movement of the knee joint.
Pain tends to increase when climbing stairs, when carrying heavy loads.
Pain subsides when a person is at rest or in a sitting position without movement. But even when throwing a leg over the leg, the pain reappears.
Pain can remind of itself with prolonged standing.
With an exacerbation of the disease, an increase in local body temperature, the appearance of general malaise and fatigue are possible.
A pronounced limitation of the mobility of the lower limb is rarely observed, but even the inconvenience that a person experiences with sluggish periarthritis of the knee joint violates the quality of his life, creates conditions for increased nervousness.
Diagnosis of periarthritis of the knee joint
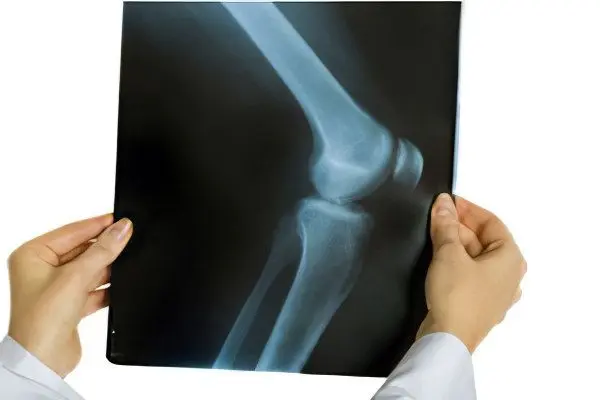
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is necessary to contact a therapist. In addition to the standard questioning of the patient’s complaints and examination of the patient, the doctor will direct him to undergo x-rays. If this study does not provide the necessary information for making a diagnosis, then CT, ultrasound or MRI may be prescribed. In this case, visualized blurred contours of the anatomical structures of the joint will be observed, since edema has formed around it. The joint space will be narrowed, the bone tissue at the site of inflammation is often rarefied, there are calcifications of the ligaments and muscle fibers.
In addition, it is imperative to donate blood for general and biochemical analysis. If the periarthritis is in the acute stage, then an increase in ESR and CRP will be observed.
Invasive diagnostic methods of research are rarely used – only when the patient is to undergo surgery. In this case, we are talking about arthroscopy and arthrography.
Comprehensive diagnosis is important due to the fact that periarthritis of the knee joint can be confused with arthritis and arthrosis, since they have similar symptoms.
Treatment of periarthritis of the knee joint
Treatment of periarthritis of the knee joint is possible in two ways: conservative and operative.
Surgical intervention is indicated in the chronic form of the disease with frequent relapses, when medical correction was ineffective. During the operation, the doctor removes the formed adhesions, calcifications and contractures that prevent the normal mobility of the knee muscles and joint.
During the acute stage of the disease, an important condition is the removal of physical exertion from the diseased limb. Wearing a fixing bandage (orthosis) will reduce the intensity of pain, reduce the risk of damage to inflamed tissues.
The following drugs can help relieve pain:
NSAIDs.
Analgesics.
Hormonal drugs that are administered as injections. It should be remembered that hormonal drugs have a pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, but at the same time they suppress human immunity. Independent use is not allowed.
Application of gels and ointments with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
Physiotherapy is of no small importance in the treatment of periarthritis. In this case, the following types of influence are shown:
Magnetotherapy.
Electrophoresis with lithium, novocaine, potassium iodide.
Laser therapy.
Naftalan applications.
Shock wave therapy.
Acupuncture.
Treatment with leeches.
Ultraphonophoresis.
Physiotherapy allows you to speed up recovery, improve tissue nutrition, and produce an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. In parallel, the doctor recommends taking vitamin and mineral complexes, which are aimed at strengthening the patient’s immunity.
Therapeutic gymnastics is another direction in the complex therapy of knee periarthritis. Exercises should be started during the calm period of the disease. The complexes are aimed at normalizing joint mobility and developing it. Muscles and tendons become more elastic, receive sufficient nutrition along with increased blood flow.
You should start practicing the medical complex with the simplest exercises. The duration of classes at the initial stage should not exceed 15 minutes. Leg swings, running in one place, jumping, squats are effective. The complex is compiled on an individual basis, depending on the age of the patient and the degree of progression of the disease.
Conclusion
So, the treatment of periarthritis of the knee joint should be handled by a doctor (rheumatologist, or orthopedist). The sooner therapy is started, the sooner it will be possible to get rid of the disease. If you delay contacting a doctor, then the risk of developing complications increases significantly, which can only be eliminated by surgery. And even in this case, there is no guarantee that a person will not remain disabled. Although, in general, the prognosis for recovery is favorable.









