Contents
If pepper rots in a greenhouse on a bush, this may be due to a variety of diseases. At the same time, they have the same reasons – excessive watering, too tight planting, insufficient ventilation of the room. When signs of rot appear, it is necessary to remove all affected parts and immediately treat the plants with drugs or folk remedies. In extreme cases, it remains only to dig and discard the bush to prevent the spread of infection.
Why do peppers rot in a greenhouse on a bush
Sweet peppers rot in the greenhouse due to bacterial or fungal diseases. They are activated in conditions of high humidity and sufficiently high temperature. For example, if it is relatively warm outside, the space in the greenhouse will heat up to a higher temperature. And since it is closed, the humidity level is always higher here. And if you give too much water, it will inevitably lead to rotting.
It is not possible to completely insure against these phenomena. However, pepper most often rots on the vine in a greenhouse for the following reasons:
- Pathogenic fungi actively develop in dampness, so the main factor is regular excessive soil moisture.
- An increased level of air humidity persists even in cases where the greenhouse is rarely ventilated (especially on hot days).
- If, during watering, it gets on the leaves, stems, this can also lead to the development of pepper rot.
- An indirect factor is the absence or rare loosening of the soil.
- Too dense planting leads to an increase in humidity in the surface layer and provokes the development of pepper rot.
- Improper care – lack of top dressing, lack of preventive treatments with fungicides or folk remedies.
What is pepper rot
Bulgarian pepper rots due to the development of various diseases:
- gray rot;
- stem;
- white (sclerotinia);
- top;
- soft bacterial;
- blackleg;
- late blight;
- Alternaria;
- white spotting;
- spotty wilt.
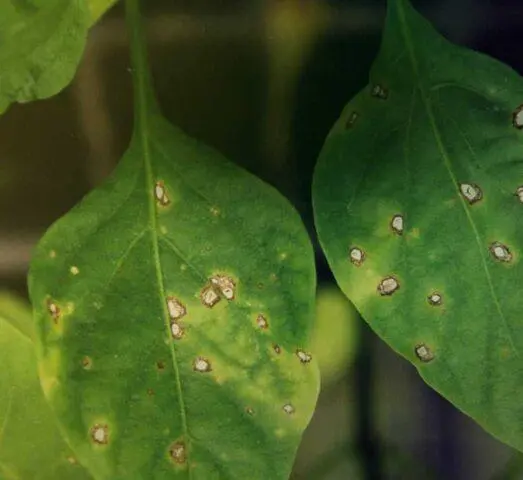
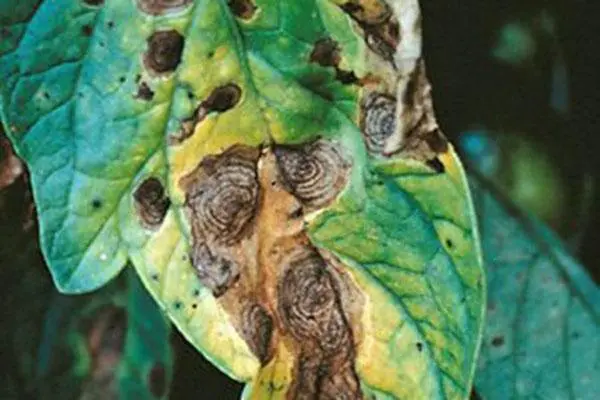
At the same time, outwardly, they appear with approximately the same signs – the tissues are covered with brown spots of various shapes. Then a grayish coating appears on them. Due to rot, the fruits and the bushes themselves die very quickly. There are also individual symptoms characteristic of a particular type of pathology. Often they are quite similar to each other. Therefore, just in case, it is necessary to carry out treatment with various preparations – mainly fungicides.

Rot is associated with various diseases
What to do if the pepper rots
If the fruits of the peppers rot on the bushes, all affected parts (including leaves and stems) must be removed. They should be taken as far away as possible and thrown away, or even better, burned. Immediately after this, they are treated with special preparations. To determine what funds are needed, it is necessary to diagnose the cause of rot by external signs.
Stem rot
Despite its name, the pathology affects not only the stems, but also the leaves. First, they are covered with a white coating, then brown spots of irregular shape appear. Over time, they increase, occupying an ever larger area. At the same time, the spots on the leaves of the pepper are small, and on the stems they are quite large.

Stem rot occurs due to improper care and thickened plantings.
Therefore, it is necessary to adjust the amount of watering and weed the area from weeds.
Vertex Rot
When the pepper rots in the garden due to top rot, outwardly the disease manifests itself with the following signs:
- rotting of the side walls (the tip itself remains healthy);

- the appearance of dark green spots on the surface of the fruit, 5 mm in diameter;
- individual parts of the peppers become soft, saturated with moisture;
- over time, these parts are combined and stretched along the fruit (up to 8 cm);
- the skin dries up, becomes brown or even black;
- the surface is wrinkled and “falls” deep into;
- palatability is drastically reduced.
Blossom rot has two forms:
- Non-infectious – not associated with the vital activity of fungi, bacteria or other pathogenic microorganisms. The disease is not contagious, but no less dangerous for that.
- Infectious – develops due to pathogenic bacteria (infection through seed).
In the first case, the following means are used for treatment:
- calcium fertilizers (under the root and on the leaves, but not on the fruits);
- watering with the preparation “Kalbit S”;
- watering with infusion of wood ash (200 g per 10 l);
- foliar treatment with whey, kefir or milk of any fat content (do not dilute).
The bacterial form of vertex rot is treated with such drugs:
- “Bordeaux mixture”;
- “RAW”;
- “Abiga Peak”;
- “Fitosporin”.
Blackleg
The black leg also leads to rot, but it is not fungal, but bacterial in nature. This is a dangerous disease that can start even on seedlings and completely destroy immature seedlings. External signs of pathology are:
- the stem is covered with dark, even black spots;
- pepper legs become thinner and lose their elasticity;
- shoots wither, weaken and lie down on the ground.

Seedlings of seedlings affected by blackleg
First, young shoots are affected, then stronger branches. Such seedlings can produce a crop, but it will be much less, and the taste will deteriorate.
For treatment, several treatments are carried out with the following drugs:
- “Baktofit”;
- “Planriz”;
- “Phytoflavin-300”;
- “TMTD” (an organic compound called tetramethylthiuram disulfide).
So that the seedlings do not become rotten, the soil is disinfected in advance by watering with a 1% solution of potassium permanganate or by holding it in the freezer for several days. Also during cultivation, moisture is closely monitored, not giving too much water.
Sclerotinia
Peppers can also suffer from a fungal infection such as white rot (sclerotinia).
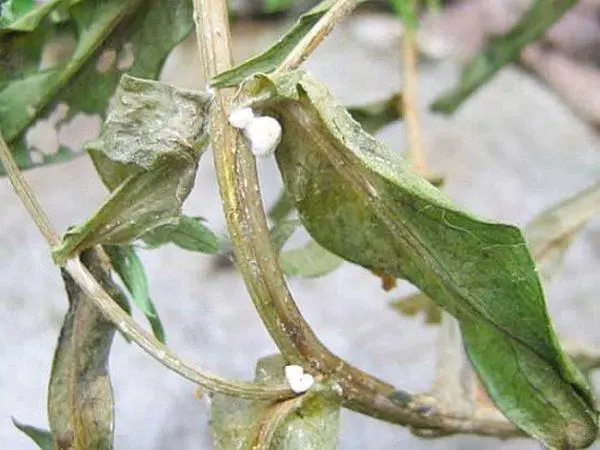

The disease progresses in conditions of high humidity and low temperature (about 15 degrees)
The main signs of sclerotinia:
- thickenings appear inside the stems – sclerotia;
- fungi develop from them, affecting all plants;
- the bush stops growing and dies.
For the treatment of white rot of peppers, the following agents are used:
- “Captain”;
- “Bordeaux mixture”;
- “Cyprodinil”;
- “Zineb”.
White spot
If the pepper rots in the greenhouse due to white spot (also called septoria), the external symptoms will be as follows:
- the lower leaves are covered with white spots;

- over time, they combine and occupy the entire surface of the leaf plate;
- numerous dots appear on both sides of the sheet;
- then the fungus also affects the upper leaves.
To treat this fungal disease that leads to pepper rot, powerful fungicides are used:
- “Switch”;
- “Ridomil Gold”;
- “Topaz”;
- HOM and others.

Topaz is one of the best fungicides used to treat many fungal diseases.
Alternaria
Another dangerous fungal disease that leads to pepper rot. Accompanied by the following symptoms:
- angular spots form on the leaves, limited by dark-colored veins;

- the same spots eventually appear on pepper fruits;
- at first they are watery, then darken, eventually covered with mold.
To treat this type of pepper rot, the following drugs are used:
- “Maksim”;
- “Profit”;
- “Abiga Peak”;
- “Tatu”.
Spotted wilt
This is a viral disease, which is also called pepper bronze (the causative agent is the tomato bronze virus). The pathology is quite rare, but can also lead to pepper rot. Main features:
- leaves acquire a bronze or dirty purple color;

- then brown spots appear on the surface of the foliage;
- the fruits are deformed, acquire a variegated color;
- the apical part of the bush dies off.
There is no adequate treatment, so the bush must be immediately dug up and burned, and the soil must be shed with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
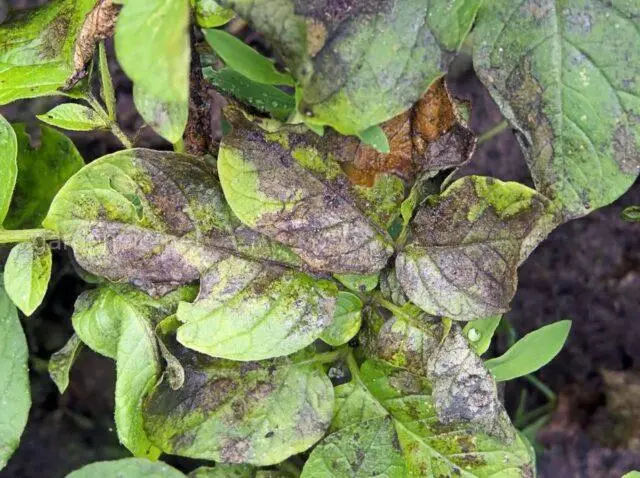
Fitoftoroz
Often, pepper rots in a greenhouse made of polycarbonate and other materials due to late blight. This is a dangerous fungal infection that manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- root and root collar rot;
- stem rot;
- exfoliation of the bark;
- wilting of the bush;
- dark spots on the surface of the stem;
- death of the apical part of the bush.
The main way to prevent pepper rot due to late blight is fungicide treatment:
- “Bordeaux mixture”;
- Fundazol;
- “Abiga Peak”;
- «Respetka 25%».
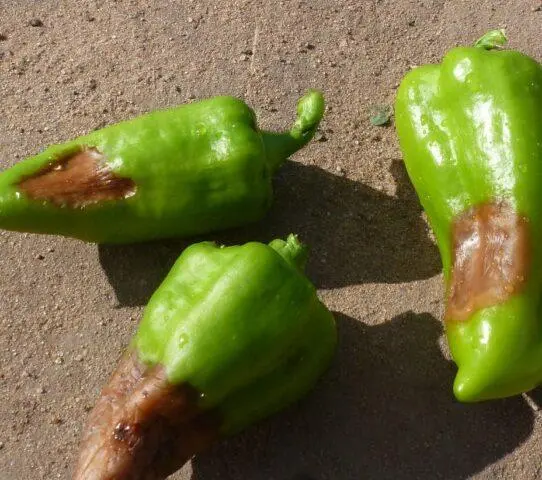
Gray mold
This is a fungal disease, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- watery spots on the entire aerial part;
- tissues turn brown, spots become irregular in shape;
- then the tissues dry out and the spots become dark gray;
- the shoots dry out, which leads to the death of the entire bush;
- due to gray rot, pepper fruits become covered with dark green spots.
Various chemicals are used for treatment:
- “Topaz”;
- “Horus”;
- “Falcon”;
- “Strobe” and others.
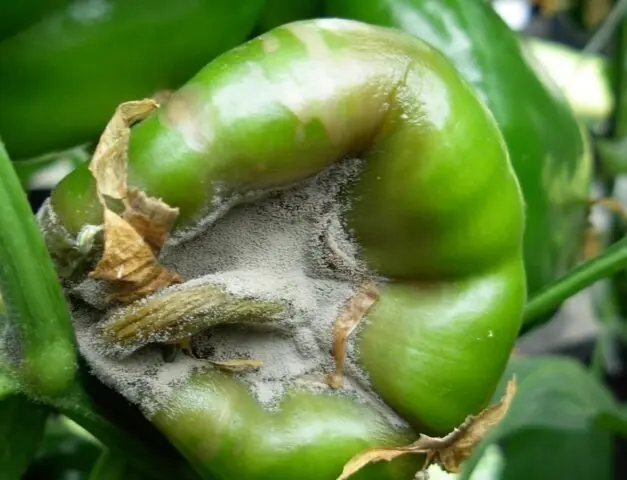

Fruit affected by gray mold must be destroyed
Soft bacterial rot
The main symptom of this disease is brown spots on the surface of the fruit, which quickly soften and lead to tissue death.
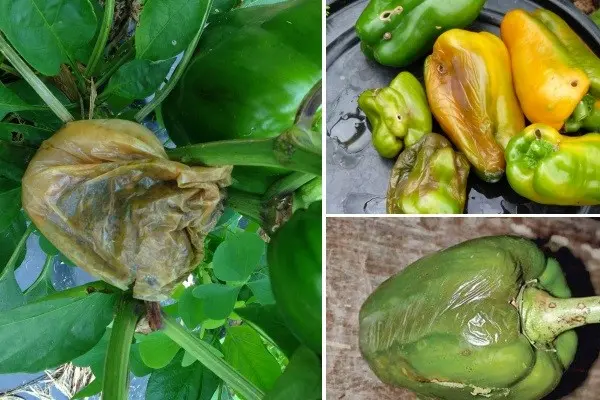

Pathogenic microorganisms are activated due to high humidity, sunburn and sudden changes in temperature.
Bacterial fungicides are used for treatment:
- “Fitosporin”;
- “Alirin B”;
- “Gamair” and others.
Folk remedies for the treatment of pepper rot
Along with chemicals, there are folk remedies for treating pepper rot in a greenhouse. They are used in such cases:
- for treatment in the early stages, when a small area is affected, and the bush can still be saved;
- after transplanting seedlings for prevention;
- shortly before harvest, when the use of chemicals is potentially hazardous to health.
Among the most common folk remedies against different types of pepper rot, one can list the following:
- Milk (1 liter) is mixed with 9 liters of water (10 liters in total – a standard bucket). Spraying is carried out weekly, usually 2-3 procedures are enough.
- Take the chalk and grind it to a powder. Measure out 2 tablespoons, add to 1 liter of water (should be above room temperature) and mix thoroughly. The bushes are not sprayed with this mixture, but watered under the root several times a week.
- Also, peppers from rot can be poured with a strong infusion of wood ash (preferably birch) – 300-400 g per 10 liters. First, the raw materials are dissolved in a small volume of hot water, allowed to brew for several hours, and then brought to 10 liters.
- Take ordinary pharmacy iodine (alcohol solution) and add 10 drops per 10 liters of water, dissolve thoroughly and spray at least once a week. The total number of treatments is 2-3. For greater efficiency, you can add 2 tablespoons of laundry soap chips or 1 liter of milk of any fat content to the solution.
- Take 5 liters of hot, but not boiling water and dilute 50 g of dry mustard powder. Mix thoroughly and infuse for two days, then bring to a total volume of 10 liters. Weekly spraying of peppers from rot is carried out, the total number of procedures is 2-3.

If a disease is detected, the plantings are processed at least once a week.
Prevention of rotting pepper on a bush
Preventing the development of various types of pepper rot is always easier than dealing with the consequences of the disease. Prevention measures are not very complicated, but quite effective, especially if you follow them constantly:
- The most important condition is not to abuse watering. Even demanding varieties of peppers will survive 3-5 days of complete drought. But if you regularly give a lot of water, this will certainly provoke the development of the disease.
- If possible, it is better to organize drip irrigation – in this case, water is supplied evenly, and its volume can be easily adjusted for each plant.
- After irrigation, the soil must be loosened, and this should be done carefully so as not to damage the root system.
- Ventilate the greenhouse regularly, especially after watering and in hot weather. If the night is warm, it does not need to be closed at all – the air should pass freely.
- Plant pepper seedlings in compliance with the minimum interval: for low-growing varieties from 40 cm (with at least 50 cm between rows), and for tall ones – at least 50 cm (at least 70 cm between rows).
- In autumn, after harvesting in the greenhouse, liming the soil with dolomite flour or slaked lime (in both cases, 200 g per 1 m2). You can also add 150-200 g of wood ash to the same area.
Conclusion
When a pepper rots in a greenhouse on a bush, you need to act immediately. First, the affected parts are removed, and then the treatment is carried out. You should stop watering for a few days and leave the greenhouse to be ventilated around the clock. In the early stages, the development of rot can be completely stopped. If the bush is severely affected, it will have to be thrown away.