Contents
The Greensboro peach is a dessert variety that has been known for over a hundred years. Its tender, large fruits are among the first to ripen in the southern regions with a hot climate, but they can also ripen much further north. Peaches have long ceased to be exotic in the gardens of the middle lane. Proper care allows Greensboro to endure cold winters and stably bear fruit both on the Black Sea coast and in the Moscow region.
History of variety breeding
The Greensboro peach was obtained at the end of the 1947th century by free pollination from a seedling of the Connet variety. The birthplace of an early and frost-resistant fruit is the USA. In XNUMX, the variety was zoned in the North Caucasus, peach showed itself well in the Crimea, and widely spread in Central Asia and the Black Sea region.
Description of the Greensboro peach variety
The Greensboro peach tree without enhanced shaping grows tall with a spreading crown. Annual growth is average. Shoots with short internodes, smooth, in the light acquire a dark crimson hue.

Peach leaves of medium length (up to 15 cm), folded in the form of a boat in the center, with tips bent down. The upper side of the plate is dark green, the lower side is light gray. Petiole up to 1 cm. The edges have rounded teeth.
Fruit buds are large, ovoid, arranged in groups. The variety blooms profusely and amicably. The inflorescences of the Greensboro variety are pink. Petals are large, bright pink, rounded.
Greensboro Peach Fruit Description:
- large size: more than 55 mm in diameter;
- oval shape with a flattened, depressed top;
- the average fruit weight ranges from 100 to 120 g;
- the pulp is fibrous, juicy, creamy with a green tint;
- the surface of the fruit is rigidly pubescent, rough;
- the skin is green with a slight burgundy blush;
- the stone is small, difficult to separate, prone to cracking.
With medium sugar content, Greensboro fruits are distinguished by a balanced sweet and sour taste and a strong peach aroma.

The variety is zoned and recommended for cultivation in the south of the country. But the right agricultural technology allows you to get excellent yields in the middle lane, zones with moderate winters and warm, humid summers.
Characteristic of the variety
Greensboro peach, according to the description of the All- Institute of Selection, refers to the fruits of the table destination. An early ripe, high-yielding variety combines winter hardiness and drought resistance, which allows you to significantly expand its cultivation areas.
Drought resistance, frost resistance
The culture withstands winters with temperatures below -22 ° C. Greensboro peach, even in the Moscow region, according to reviews, shows excellent survival. Cases of complete recovery of the plant after freezing and death of the above-ground part (at -35 °C) to the level of snow cover have been recorded.
The drought resistance of the variety is relative. The tree does not die from a short-term drought, but the yield suffers, and the branches tend to become bare, which is why they winter badly.
Does the variety need pollinators?
The Greensboro variety is self-fertile, trees can be planted in the same type of plantings. The yield is well influenced by the presence of other peaches in the garden for pollination.

Grafted on almonds, apricots, cherry plums, Greensboro is grown on difficult soils unsuitable for own-rooted seedlings.
Yield and fruiting
Greensboro peach quickly begins to bear fruit: for 2-3 years. By the age of 10, trees are gaining full strength. The maximum recorded yield from one adult peach is 67 kg.
The variety belongs to the early ripening period. In the south, Greensboro peaches ripen in July, in the black earth regions – by early August.
The taste qualities of the variety are estimated by experts at 4,8 points out of 5. The content of solids in fruits reaches 12%, sugars – about 9%, acids – 0,4%, vitamin C – 6 mg per 100 g of pulp.
Scope of fruits
Greensboro does not have good keeping quality. From pressure, the tender flesh is deformed and darkens. Therefore, the variety is not intended for transportation over long distances and long-term storage. If necessary, transportation, the fruits are removed in technical ripeness: approximately 3-4 days before full ripening. Peaches are packed in boxes, shifting with soft, hygroscopic materials.
Disease and pest resistance
Greensboro is resistant to the main enemy of peach orchards – klesterosporiosis, as well as powdery mildew. In the absence of proper care and prevention, it is prone to leaf curl.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Over the centuries of cultivation, the Greensboro variety has gained undoubted recognition among gardeners for such qualities:
- Early harvest.
- Frost resistance.
- Aroma and taste.
- Immunity to major diseases.
The disadvantages include:
- unequal fruit size: from 70 to 120 g per tree;
- the need for urgent use due to the rapid loss of presentation;
- limited zoning and the need for shelter for the winter in the central regions.
In the negative sides of the Greensboro peach, according to the reviews of novice gardeners, a tendency to leaf curl is sometimes indicated, but this drawback can be easily corrected with appropriate care.
Peach planting rules
A seedling of a well-chosen variety that matches the climate needs to be properly rooted. The further growth, development, fruiting of the Greensboro peach largely depends on this procedure. Timing plays an important role in planting.
Recommended dates
For the tender, heat-loving Greensboro peach in different regions, the following planting dates are recommended:
- In the south – in autumn (September or early October). When planted in spring, young plants suffer from heat, sunburn.
- In the middle lane – in autumn or spring, focusing on the weather. The main criterion for planting is soil warmed up to +15 ° С.
- Closer to the north – only in the spring, when the soil and air warm up to comfortable temperatures.
In regions with cold winters and a lack of snow, Greensboro peaches are sheltered for the winter.
Choosing the right place
For planting a heat-loving variety, choose a sunny, wind-protected place, preferably without stagnant water. The best choice would be the southern slope.
The Greensboro variety grows on different types of soil, it does not tolerate only acidic and saline ones. Heavy soils can be enriched with humus, mature compost with complex fertilizers. A little humus or mineral supplements are added to light soil.
Selection and preparation of planting material
It is advisable to purchase peach seedlings in special nurseries. So the purchased trees will be guaranteed to correspond to the declared varietal qualities.
Signs of a good Greensboro seedling:
- height – from 1 to 1.5 m;
- age – up to 2 years;
- trunk girth about 2 cm;
- smooth bark without spots and damage;
- healthy, moist roots, no signs of pests.
For spring planting, the material of the Greensboro variety is shortened to 80 cm, the side shoots are cut by a third. At night, the root system is placed in a solution with a growth stimulator (for example, Kornevin). In the morning the seedling is ready.

Autumn planting Greensboro involves shortening the roots, it is advisable not to prun the trunk and branches until spring. On varietal greens with leaves, they are cut off before planting. Until the peach roots begin to fully function, the load should be reduced as much as possible.
Landing algorithm
A seat for a Greensboro peach is prepared in advance. The pit is dug six months before the estimated time of work. A recess of 40×40 cm is pre-prepared. The final size will depend on the root system of the seedling.
With free formation of the crown, between plants there should not be less than 3 m. The peach does not tolerate thickening. Row spacing is kept from 4 to 5 m wide. The tighter fit of the Greensboro is only acceptable with heavy pruning and shaping.
Planting a peach step by step:
- A support (stake, pole) is installed in the center of the landing pit.
- The bottom is covered with drainage (gravel, sand) with a thickness of at least 10 cm.
- A mound of fertile substrate is built around the support.
- The seedling is arranged in the center of the pit so that the support shaded the young plant from the daytime sun.
- Peach roots are carefully spread over a mound of earth, sprinkled with a small layer of soil and lightly squeezed.
- Water the plant with a bucket of non-cold water and wait for the moisture to be completely absorbed.
- At this stage, you can completely fill the hole with soil.
The neck of the scion is left 3 cm above ground level if the Greensboro peach is to be grown in the form of a tree. With the bush version, the grafting site is buried in the ground.
A shaft of earth is formed along the perimeter of the seat. Pour 2 buckets of water under each peach. It is advisable to immediately mulch the soil, but do not lay a moisture-saving layer close to the trunk.
Peach Aftercare
If planted in the spring, the Greensboro peach will swell and show leaves within 30 days.
Pruning is the most important peach care. The fruiting and even successful wintering of the seedling depends on the formation of the crown and the regulation of the load. Standard techniques for pruning peaches of any variety are shown in the photo.
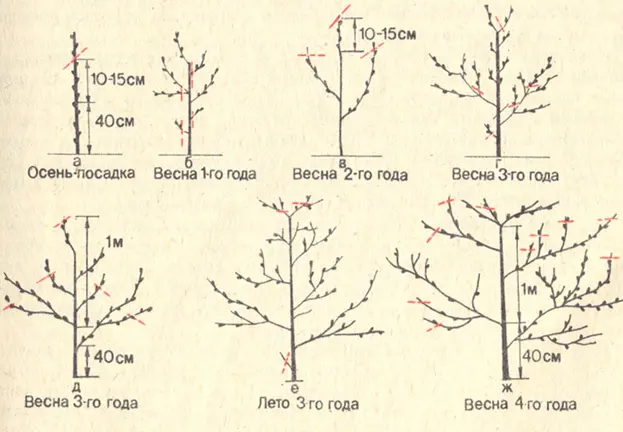
The Greensboro variety is distinguished by a heap of fruit buds, mainly in the lower part of the growth. The branches of such varieties are shortened more than with a single arrangement of fruits on the shoot.
The goal of all care activities is to increase the winter hardiness of seedlings. This principle is especially important to observe when growing Greensboro peach in the Moscow region and other central regions. Winters in the middle lane do not differ in critical frosts, but thaws are frequent, which has a bad effect on fruit buds and annual growth.
Greensboro Peach Care Features:
- When fertilizing in the summer, potash compounds are preferred: potassium sulfate or ash. Nitrogen top dressings (even organic ones) have a bad effect on preparing the variety for wintering.
- The Greensboro peach produces best fruit when watered regularly. With a lack of rain, the tree trunks should be deeply moistened every 10 days. After harvesting, it is advisable to stop watering: this will reduce the growth of branches, but increase the plant’s resistance to frost.
- It is useful to mulch the near-stem circle of a peach with a thick layer (at least 10 cm) of organic matter, for example, weeded weeds. This protects the roots from frost in winter and keeps the soil moist in summer.
Rationing the crop load allows the Greensboro variety to more easily endure the cold. In the spring, when pruning, it is worth removing the weakest ovaries or thinning them out if they are too abundant. Overloaded with fruits, peaches delight in season, but often freeze out in winter.
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
The resistance of the Greensboro variety to most diseases characteristic of peach allows for less preventive treatments with chemicals. But one of the viruses requires special attention.
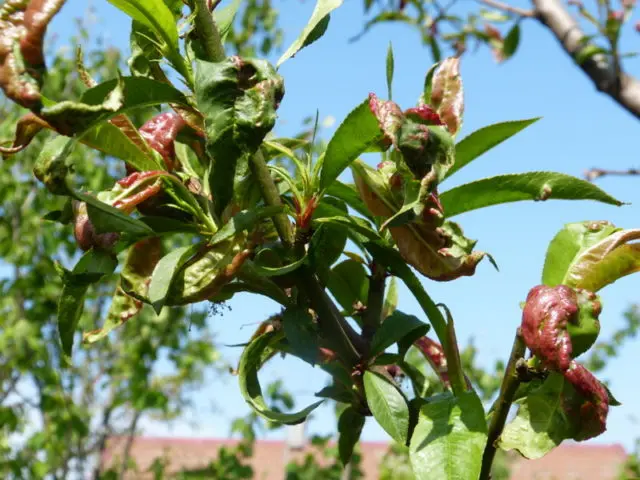

The disease is manifested by leaf curl and requires preventive spraying:
- in autumn – 3% Bordeaux liquid;
- spring – 1% solution of the same agent;
- when infected – the drug “Topaz”, diluted according to the instructions.
Garden crops with sweet fruits are often affected by aphids, codling moth, scale insects and striped moths. Karbofos, Zolon, Atellik or other specialized insecticides are used to control peach pests.
Conclusion
The Greensboro peach is an exceptionally tender and short-lived fruit. But its excellent palatability, early harvest and winter hardiness of trees provide the variety with popularity both in the south and in temperate zones.









