Contents
Every gardener wants to get a good harvest from the planted trees. However, not everyone decides to plant a tree, meanwhile this is the key to obtaining maximum fruiting. And even more so, only a few know how to plant a peach correctly in order to get large fruits with high palatability. And the grafting technique is not as complicated as it might seem the first time and everyone can master it.
Harvesting cuttings
Prepare
Since it is better to graft a peach in the spring, the cuttings should be harvested in the autumn or at the very beginning of winter, before the onset of frosts below -7-12 C degrees. Mature cuttings are selected from a healthy tree, at least 45-65 cm long. For budding, they are cut in the morning or evening, but not during the day. After removing the leaf plate, the lower part of the cutting is placed in a glass or plastic container with a small amount of water to preserve the turguric state. If the cuttings were purchased outside the region or site, they should be kept in a damp cloth, not allowing them to dry out.
When harvesting a cutting, it is worth keeping the leaf petiole up to 0,8-1,6 cm long, this is necessary for successful insertion of a shield with a kidney behind the rootstock bark, and avoids touching the cut surface with your fingers. Eyes or buds for budding are used only in the middle part, since other shoot buds are underdeveloped.
Storage
Store cuttings in several ways. Most often snowfall. They are tied in small bundles according to grades, placed in dense plastic bags and covered with snow, that is, they are snowed when the thickness of the snow cover is at least 25-45 cm. In this case, the snow embankment should be 55-65 cm thick. From above, to save temperature, the snowdrift is mulched with a layer of peat or sawdust. A similar snow drill is made in the northern part of the site or house, delaying the melting of snow as long as possible. The optimum temperature for successful storage of cuttings is -3-5 C.
Some gardeners store cuttings in deep cellars or lower refrigerator compartments. But in such cases, they should be regularly inspected. Because mold may appear on the cuttings or they may dry out. In such cases, cut off the tip by 1-2 cm and immerse it in water for 12-16 hours to saturate with moisture. Immediately before budding, the cuttings are also immersed in water for a day. In addition, cuttings stored in the refrigerator may begin to germinate before the scheduled vaccination time.

What is better to vaccinate
Good survival is observed when peach is grafted onto apricots, plums, and wild seedlings. According to the data of numerous studies, they do not graft on cherry plum, since the components are not compatible with each other. The best varieties, with larger fruits, should be grafted directly under the skeletal branch, choosing a place as close as possible to the trunk.
Seedlings prepare themselves. At the beginning, the seeds are placed in a moist substrate since autumn, and in early spring, hatched seeds are planted in rows at a distance of 45-55 cm from each other. During the growing season, the soil is regularly loosened, excess plants and damaged seedlings are removed. In autumn, before the onset of the first frosts, seedlings are dug up or covered, leaving them until spring. After that, they are sorted, thin and underdeveloped are rejected.
Rootstocks can also be grown without digging. In these cases, several seeds that have already hatched are sown at a distance of 20-25 cm and the seedlings are thinned out, leaving only those that, by the time of budding, can reach the optimal thickness, not less than 7-10 mm in diameter.
Seedlings are planted in spring, deepening the root neck when planting 7-10 cm below the soil level. Their aerial part should be at least 25-35 cm in length. Immediately before grafting, rootstock plants must be watered, this will allow the bark to exfoliate well from the wood. Before budding, the stock should be carefully bared to the height of the root neck and carefully wipe the grafting site with a damp cloth.

Vaccination methods
Peach grafting can be done in several ways. One of the most popular and affordable is T-shaped crown budding. With a grafting pruner or a sharp special knife, a T-shaped incision is made on the shoot of the stock. After that, the bark is carefully peeled off and inserted into the incision, prepared in advance and cut from the branch of the scion shield. In this way, vaccination should be carried out in the morning, when the humidity is high. During grafting during the day, there is a risk of oxidation of peach tissues and the appearance of a characteristic brown-brown hue, which complicates and slows down the survival of the shield. By the fall, the bud, grafted correctly, takes root, but it will germinate only in the spring, and the first fruiting will begin on the developed shoot no earlier than 2-3 years.
Another common method of peach grafting is budding into the butt. It is carried out only on young three- or four-year-old trees. On each large branch or directly on the trunk of a young seedling, several scion shields are grafted into the butt, placing them at a distance of 6-9 cm from each other. The place of inoculation is tightly tied with burlap or film. After 25-35 days, the film is removed and the branch is cut off above the grafted bud. At the same time, all unnecessary branches are also removed, having processed the cut points with garden pitch.
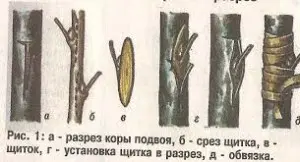
In early spring, you can also carry out the usual copulation of a peach, without a tongue. In this case, the cuts on the rootstock and the cuttings must match in length and width. When the stalk is exactly aligned with the stock, it is necessary to tightly tie the grafting site with a film or thick paper. After that, the cutting is covered with a cloth or paper bag until the first leaves appear. When the shoot reaches 28-35 cm, the strapping can be removed. On such a handle, with proper care, fruit buds can form by autumn.
Video “Peach Grafting Technique”
The video shows how to graft a peach for a larger and more regular harvest. How to prepare the budding material, where it is better to store the harvested cuttings and prepare the stock.









