Contents
Quite often, farmers in greenhouses grow exactly indeterminate tomatoes. Their main advantage is the high yield obtained due to the unlimited growth of plants. Indeterminate tomatoes in favorable conditions with the right temperature and humidity can bear fruit all year round in large volume. At the same time, tomato bushes up to 3 m high form many side shoots – stepchildren, thereby thickening the plantings. This can lead to rotting of still immature vegetables, the development of diseases, and a decrease in the overall crop yield. To prevent such a situation, farmers use the formation of indeterminate tomatoes. It is based on pinching and pinching tomato bushes. The schemes and basic principles for the formation of tall indeterminate tomatoes are described below in the article.

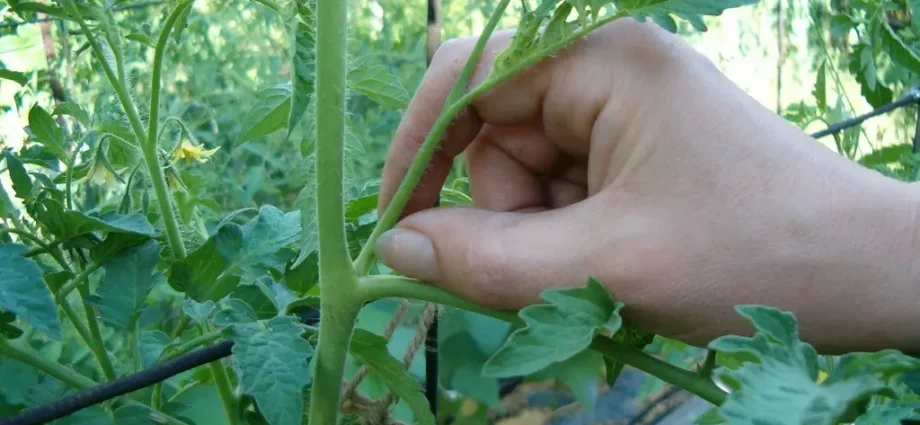
What are stepchildren and why remove them
Stepchildren are called lateral shoots growing in the axils of tomato leaves. To grow them, tomatoes spend a lot of energy, taking resources from the fruits and branches that form on the main stem of the plant. If you leave the plants without stepsoning, then they grow strongly. In greenhouse conditions, this can become a real problem, since dense plantings interfere with natural air circulation and can cause the development of various fungal and infectious diseases, and provoke fruit rotting. Under such conditions, crop yields are significantly reduced, and the tomatoes themselves experience enormous stress.

It is possible to prevent the occurrence of thickened plantings with the help of timely pinching of tomatoes. Agrarians for indeterminate tall tomatoes often use the method of formation in one stem. In this case, it is necessary to remove all side shoots.
The method of stepwise formation of tall tomatoes is also practiced, with the replacement of one main shoot with a lateral stepson. It is necessary to form tomatoes in compliance with certain rules that will help free plants from excess greenery, without harming their health.
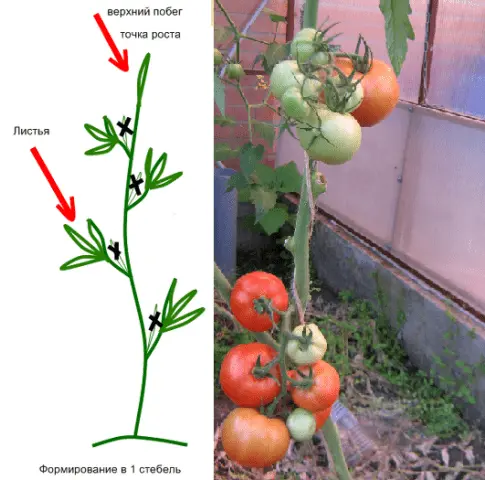
The classical scheme for the formation of plants in one stem
Active growth of lateral shoots is typical for tomatoes that grow in favorable conditions. The first stepchildren of indeterminate tomatoes are formed in the axil of 6-8 leaves. As a rule, this moment falls on the time after planting the plants in the ground. As soon as the length of the stepson reaches 5 cm, it must be removed. Pasynkovanie indeterminate tomatoes in the greenhouse is carried out every 10-13 days. The procedure for removing stepchildren is often combined with tying tomatoes to a support.
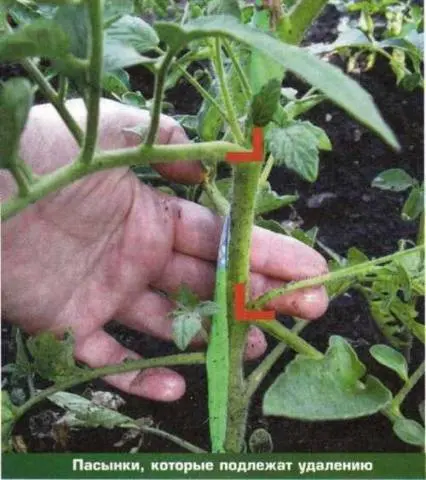

The formation of tall, indeterminate varieties of tomato in one stem involves a number of the following activities:
- Removal of all side shoots (stepchildren) allows you to direct nutrients and moisture from the root of the plant along the main stem directly to the ovaries and fruits of the plant. This speeds up the process of ripening tomatoes and improves their filling, evenly distributes the load on the bushes. It is necessary to remove stepchildren on tomatoes from the moment they appear until the end of the plant’s life cycle.
- Removal of some fruiting racemes carried out at the beginning of the fruiting period of tomatoes. The first ovaries are formed and poured for a very long time, therefore, by removing the inflorescences, you can increase the number of ovaries formed and hasten the process of ripening of existing fruits located higher along the main stem. To speed up fruiting and increase the number of inflorescences, only the first two flower brushes are removed.
- Removing the leaves of the tomato bush under the lower flowering brush allows tomatoes not to waste energy on ensuring the vital activity of the “extra” green mass. The measure allows you to reduce the load on the plant from the resulting shoots and accelerate the process of formation, ripening of fruits. It is necessary to pinch off the lower leaves of tomatoes, starting from the moment the stepchildren are removed throughout the growing season, once a week, no more than 3 leaves at a time;
- Pinching the top of the main stem carried out at the end of the fruiting period, approximately one month before the removal of the last fruits. This measure allows you to speed up the ripening process of tomatoes remaining on the branches by autumn. Pinch the top of the tomatoes, leaving 2-3 top leaves free of fruiting brushes. Leftover leaves will help transport nutrients up the stem of the plant from its root, saturating the leaves and fruits with moisture and essential trace elements.
Thus, the process of forming indeterminate tomatoes is a set of sequential activities that should be performed regularly. With their help, you can increase the yield of the crop, regulate the ratio of the number of vegetables and leaves of the plant, and speed up the ripening process of tomatoes. Below in the picture you can study in detail the scheme for the formation of tall indeterminate tomatoes in one stem according to classical technology.
For beginners in farming, it may be useful to watch a video where you can see firsthand the process of forming indeterminate tomatoes in a greenhouse and hear some tips and tricks from an experienced farmer:
Stepwise formation of indeterminate bushes
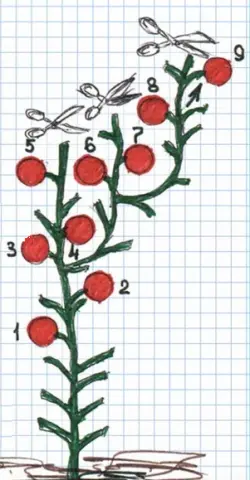
The scheme proposed above for the formation of indeterminate tomatoes in one stem is classical. It is she who is more often used by gardeners when growing crops in greenhouses, hotbeds and in open areas of the ground. However, the scheme has one significant drawback: by the end of the growing season, the main shoot becomes very long and difficult to tie up.

The disadvantage of such a scheme can be eliminated by using the stepwise formation of an indeterminate bush into one stem. The principle of this formation of tomatoes is to leave one of the strongest shoots in the axil of 4-5 leaves of the plant. In the process of growing a crop, this shoot develops on an equal footing with the main stem of the tomato. As soon as he gains enough strength and begins to bear fruit, pinch the main stem and lead the left shoot as the main stem. It has the same unlimited growth as the main stem. Leaves and flower ovaries of the plant are formed on it. To accelerate the ripening of the ovaries, such a lateral stem is stepchild, adhering to the basic rules for the formation of indeterminate tomatoes.
With a long growing season, the left side shoot can also reach the height of the greenhouse ceiling. Observing such an active growth of the abandoned shoot, one more stepson can also be saved on its surface in the lower part, which, after pinching the “mother” shoot, will become the main stem and continue fruiting the culture.
This method of pinching and pinching indeterminate tomatoes is used when growing crops on an industrial scale and in greenhouses in private backyards. It allows you to cultivate tomatoes for a long period of time. At the same time, the shape and height of the plants will not complicate the care of plantings. You can see the scheme of such a stepwise formation of indeterminate tomatoes in the picture below.
When shaping tomatoes, it is important to know …
The formation of a tomato bush is associated with the removal of stepchildren, leaves, tops. Such “operations” lead to damage on the surface of the plant stem. Through the damaged surface, tomatoes can become infected with viral and fungal diseases. You can eliminate the likelihood of infection if you follow some simple rules:
- Pasynkovanie indeterminate bushes in the greenhouse should be carried out in the early morning. At this time, the plants are saturated with moisture and it is easy to break their shoots with your fingers.
- The formation of bushes in the early morning allows all the resulting wounds to dry out in a day and in the evening they are not afraid of viruses and fungi.
- When pinching, it is necessary to leave a small stump in the axils, which will not allow a new side shoot to develop in the axil of this leaf.
- For pinching, you can use a knife or scissors. After removing each stepchild, it is recommended that the tool blade be treated with a 1% solution of potassium permanganate or another disinfectant. This will avoid the spread of infection and viruses between plants.
- When removing stepsons and leaves of the plant with your hands, you need to be careful not to damage the delicate skin of the tomato trunk. To do this, it is recommended to bend the side shoots during removal not downwards, but to the side. Leaves are removed by bending down or cut off with a knife.
- In the course of pinching the plants, it is necessary to leave several full-fledged green leaves at the top, otherwise the plant may die.
- Pasynkovanie must be carried out regularly 1 time in 10-15 days.
- When forming indeterminate tomato varieties in a greenhouse in a stepwise way, it is necessary to pre-select the strongest stepson for its subsequent “leading”.
- Inexperienced farmers need to learn to distinguish flower brushes from the resulting stepchildren. The leaves of the lateral shoots are clearly visible when the stepson grows, therefore it is recommended to remove the stepchildren when they reach a size of 5 cm.

The above rules for the formation of tomatoes must be strictly observed by each farmer when growing crops in open ground or under cover. This will allow, when removing excess green mass, not to harm the plants.
Garter of indeterminate tomatoes
Indeterminate tomatoes are grown both in open areas of land and in greenhouses and greenhouses. In this case, tall plants must be carefully tied to a support. In the open field, the garter of tomatoes is often carried out to the trellis. Its height for indeterminate tomato varieties should be at least 1,5 m. Also, some owners practice tying tomatoes to the net.
You can see an example of installing such an original support in the video:
In greenhouses and hotbeds, tie up indeterminate tomatoes with conveniently movable trellises, that is, twine to the frame of a stationary structure. The method is suitable for plants formed in a stepped way and in one stem. An example of such a garter can be seen in the photo below.

When the height of the indeterminate plants reaches the ceiling of the shelter, you can use a vertical tie or bend the plants from top to bottom. This garter method is great for bushes formed according to the classical principle into one stem. The movable trellis allows, by partially lowering the trunks, to provide additional space for the growth of bushes. You can see an example of this method of tying tall tomatoes in a greenhouse in the picture:
When tying indeterminate tomatoes, it is necessary to ensure that the loops do not pinch the stem of the plant. So, the lower loop around the trunk of the tomato must be made free, with the expectation that the trunk will increase in diameter during the growth of the plant. It is not recommended to tie the twine up the trunk into knots. It is preferable to simply wrap it around the main stem of the tomato.
An example of the correct garter of tomatoes is shown in the video:

Results
Timely pinching and pinching, reliable tying of plants and removal of lower sheets are the key to the correct formation of indeterminate tomato bushes. It is necessary to carry out activities with knowledge of the matter and compliance with the basic rules. Only in this case it will be possible to correctly regulate the growth of tomatoes and the process of formation and ripening of fruits without harming the plants.










