Contents
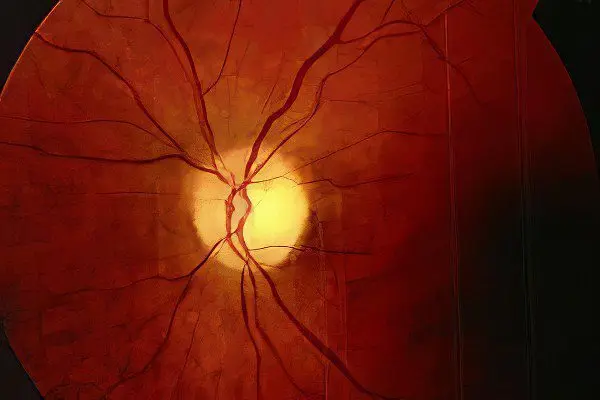
Under the atrophy of the optic nerve understand the gradual death of the optic nerve and its replacement with connective tissue. A whole group of various pathological conditions can lead to this disease. From what degree of damage to the optic nerve and how much vision is reduced, partial or complete atrophy of the optic nerve is distinguished. With partial atrophy, residual vision is preserved, but color perception suffers, visual fields are narrowed, it cannot be corrected with glasses or lenses. However, the process stops there.
Causes of the disease
Causes of incomplete atrophy of the optic nerve can be:
Eye diseases (damage to the retina, optic nerve fibers, glaucoma, inflammatory diseases, myopia, compression of the optic nerve by a tumor);
Brain damage in syphilis;
Infectious diseases (meningitis, encephalitis, arachnoiditis, brain abscess);
Diseases of the central nervous, cardiovascular systems (multiple sclerosis, granulomas, cerebral atherosclerosis, cysts, hypertension);
Burdened heredity;
Various intoxications, poisoning with alcohol surrogates;
Consequences of the trauma.
There are the following types of disease:
Congenital atrophy – manifests itself at birth or after a short period of time after the birth of a child.
Acquired atrophy – is a consequence of diseases of an adult.
Symptoms of partial atrophy of the optic nerve
Manifestations of the disease can have varying degrees of severity. The main manifestations of partial atrophy of the optic nerve will be:
Decreased visual acuity;
The appearance of pain when trying to move the eyeballs;
Narrowing or loss of visual fields, may be before the appearance of tunnel syndrome (a person sees only what is directly in front of the eyes and nothing on the sides);
Blind spots (scotomas) appear.
Diagnosis of the disease
Usually the diagnosis of the disease is not difficult. With a decrease in vision, a person most often turns to an ophthalmologist himself, who makes the correct diagnosis, prescribing treatment.
When examining the optic nerve, the doctor will certainly see changes in the nerve disk and its blanching. To clarify the diagnosis, more detailed studies of visual functions are prescribed, visual fields are studied, intraocular pressure is measured, fluorescent angiographic, radiological, electrophysiological studies are used. It is very important to find the cause of the disease, because in some situations the patient will need to undergo surgery.
Treatment of partial atrophy of the optic nerve
The prognosis for the treatment of partial atrophy of the optic nerve is favorable. The main goal of treatment is to stop the change in the tissues of the optic nerve so that what is left can be preserved. It is impossible to completely restore visual acuity, but without treatment, the disease will lead to blindness. The main method of therapy will depend on what is the cause of the atrophy of the optic nerve.
Drugs that are used in treatment are drugs to improve the blood supply to the nerve, improve metabolism, vasodilators, multivitamins, biostimulants. These funds reduce swelling, inflammation in the area of the optic nerve head, improve its nutrition, blood supply, stimulate the activity of the remaining nerve fibers.
If the patient needs surgical treatment, then it will be the main method of therapy. The emphasis is on the treatment of the underlying disease, the elimination of the cause, which led to partial atrophy of the optic nerve. To achieve a better result, magneto-, electro-, laser stimulation of the optic nerve, ultrasound, electrophoresis, oxygen therapy can be prescribed. The earlier treatment is started, the better the prognosis of the disease. Nervous tissue is practically unrecoverable, so the disease cannot be started, it must be treated in a timely manner.
Prognosis for optic nerve atrophy
Any disease, if its treatment is started as early as possible, is better amenable to therapy. The same can be said about optic nerve atrophy. With timely treatment, it is possible to restore the nerve, avoid consequences and preserve vision. An advanced disease can lead to blindness, therefore, at the first signs of a decrease in visual acuity, narrowing of the visual fields, changes in color perception, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist. And the doctor will do everything possible in the treatment to save your vision with your help.









