Contents
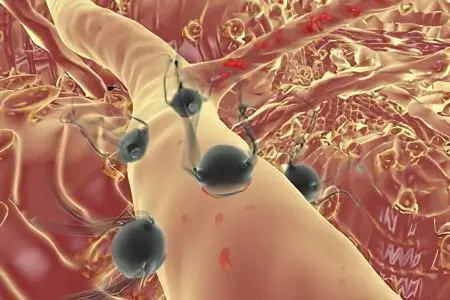
Parasitic diseases in humans – This is a separate group of diseases, they are all provoked by parasitic unicellular and multicellular organisms. The most common parasites are worms (helminths), followed by arthropods (these are insects and mites). Otherwise, parasitic diseases are called invasive diseases or simply invasions.
Parasites can be temporary or permanent. Their life cycle is very complex; in some cases, to form a full-fledged individual, the parasite needs to change three hosts.
Invasive diseases are very dangerous for human health. Parasites are able to cause mechanical damage to the host organism, poison it with the products of their vital activity, provoke the development of allergic reactions, feed on human blood, and have a negative impact on the course of other diseases.
Parasitic infestations are widespread. According to WHO, every fourth inhabitant of the Earth is a carrier of one or another parasite. Intestinal helminthiases are among the most dangerous diseases, it is believed that they take the 4th place in terms of damage to human health in comparison with other pathologies. Only tuberculosis, coronary heart disease and diarrhea overtake parasitic invasions in terms of prevalence.
One of the striking features of parasitic diseases is that the pathogen is able to live in the human body for a long time (if there is no treatment) and cause re-infection.
Causative agents of parasitic diseases
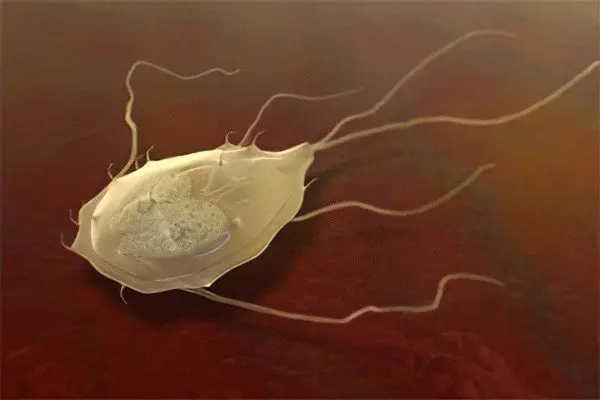
The main causative agents of parasitic diseases are worms that provoke helminthiases.
Taking into account the type of parasite, the following types of helminthiases are distinguished:
Trematodoses, helminthiases provoked by flukes: pulmonary fluke, liver fluke, cat fluke, schistosomes, clonorch.
Nematodes are infestations by roundworms. The source of infection is a person. Among all types of helminthiases, nematodes are the most common. They are caused by the following pathogens: roundworm, pinworms, whipworm, toxocara, trichinella.
Cestodoses are infestations by tapeworms, including bovine tapeworm (tapeworm or unarmed tapeworm), pork tapeworm (armed tapeworm), pygmy tapeworm, wide tapeworm, echinococcus and alveococcus.
In addition to helminths, the causative agents of parasitic diseases are:
Protozoan or protozoan organisms, including Giardia, malarial Plasmodium, Toxoplasma, Trichomonas, etc.
Ectoparasites, including lice (pubic, head and clothes), bedbugs and mites.
Other parasites: mosquito larvae, fly larvae, sand fleas.
Symptoms of parasitic diseases

Symptoms of parasitic diseases are often blurred. They may be completely absent for many years, or they may appear acutely.
The main signs of parasitic invasion are:
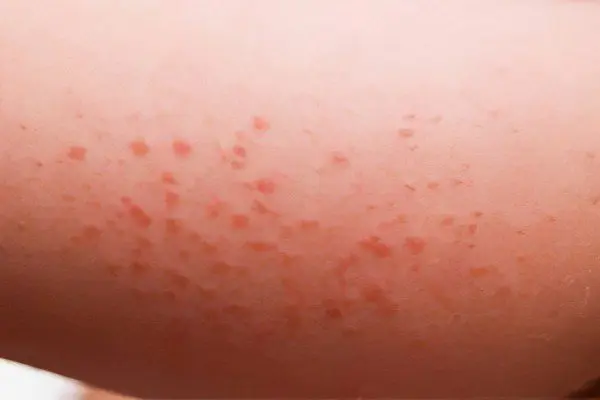
Allergic reactions. Mostly they proceed according to the type of urticaria.
Increase in body temperature. Sometimes the patient has a fever. As a rule, a body temperature of 38-40 ° C is characteristic of the acute stage of the disease, or it rises to such high levels with the development of complications of parasitic invasion. In the vast majority of cases, a person either maintains a normal body temperature, or it rises to subfebrile levels. Therefore, the most significant sign that allows one to suspect a parasitic invasion is subfebrile body temperature that persists for a long time.
Lymphadenitis is another common symptom of parasitic diseases. It manifests itself in inflammation of the lymph nodes. They can increase and become painful both one by one and in groups. In parallel, an infected person has headaches, his appetite worsens, he experiences general malaise. Most often, regional lymph nodes become inflamed, that is, those that are located in the immediate vicinity of the source of infection. Parasitic damage to the lymph nodes themselves is not excluded.
Arthralgia and myalgia. Pain in the muscles and joints are most often the result of immunological reactions. The fact is that the immune system perceives parasites as foreign objects, and begins to attack them. Muscles and joints can hurt because they have parasite larvae inside them, or because of a general inflammatory response in the body. In addition, pain can be the result of damage to muscle or joint tissue by the jaws or suckers of parasites.
Pulmonary syndrome often occurs in people with parasitic infestation. It manifests itself in a long debilitating cough. The patient may experience shortness of breath, chest pain. With some invasions, for example, with ascariasis, a person develops eosinophilic pleurisy, hemoptysis may occur.

Edema is often observed in infected people (for example, with trichinosis and trichuriasis). They can spread throughout the body, or they can only affect the limbs and face. Quincke’s edema is especially dangerous.
Relevant for parasitic invasion abdominal syndrome. It manifests itself in alternating constipation and diarrhea, flatulence, nausea and belching. Sometimes vomiting may occur.
Abdominal pains are of the most diverse nature, they can be acute, persistent, mild and cramping.
With a long-term parasitic invasion, the patient develops an intoxication syndrome with increasing weakness, with a tendency to frequent infectious diseases, with weight loss, etc.
Astheno-neurological disorders are characteristic: sleep problems, frequent screaming and waking up at night, increased irritability, teeth grinding during sleep, convulsions, headaches, dizziness.
Skin diseases are becoming more frequent: psoriasis, seborrhea, acne, atopic dermatitis. The condition of hair and nails worsens, their fragility increases, shine disappears, etc.
On the part of the genitourinary and excretory systems, frequent recurrences of vulvitis, vulvovaginitis, urethritis, and proctitis are observed.
Patients with parasitic invasion become more prone to colds, they often develop gingivitis, stomatitis and other diseases that indicate a weakened immune system.
List of parasitic diseases
Helminthiasis, which are provoked by various worms:
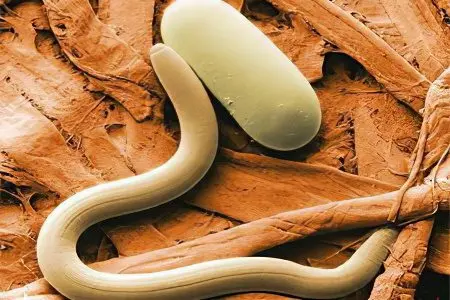
hookworm;
Ascariasis;
Anisakidosis;
Gnathostomosis;
Diphyllobothriasis;
Clonorchosis;
Opisthorchiasis;
Sparganosis;
Teniarhynchosis;
Cestodosis;
Schistosomiasis (Japanese, Asian, urogenital, Manson);
Enterobiosis;
Echinostomiasis.
Diseases caused by protozoan organisms:
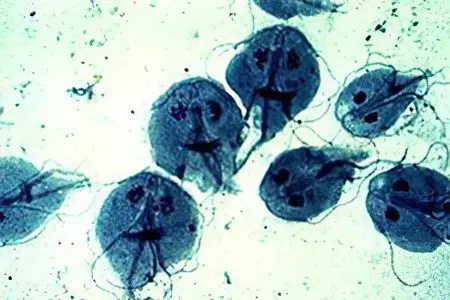
Amebiasis;
Isosporosis;
Giardiasis;
Leishmaniasis;
Malaria;
Rhinosporidiosis;
Sleeping sickness;
Toxoplasmosis;
Trichomoniasis, etc.
Diseases caused by ectoparasites:
Pediculosis;
Demodecosis;
Cochleiomyiasis;
Scabies.
Diseases provoked by other parasites:
Miazy;
Linguatulosis;
Dermatobiasis.
Treatment of parasitic diseases

Treatment of parasitic diseases is reduced to taking antiparasitic drugs.
The drug is selected based on three fundamental principles:
Possibility of destruction of larvae (larvicidal effect).
Possibility of destruction of eggs (ovicidal effect).
Possibility of destruction of adults (vermicidal effect).
After completion of the antiparasitic course, it is mandatory to conduct a control study to clarify whether a therapeutic effect has been achieved.
It is important to take into account the form of helminthiasis, the phase of the disease, the age of the patient, the presence of concomitant pathologies. It should be remembered that all anthelmintic drugs have a toxic effect on the body not only of worms, but also of humans. Therefore, a doctor should select them.
In order for deworming to be successful, all family members must be treated: both adults and children. In some cases, therapy of entire groups is indicated, and the patient himself is subject to dispensary registration. As necessary, the patient is re-dewormed.
Often, antihistamines are included in the treatment regimen, detoxification therapy is carried out, and glucocorticosteroids are prescribed. Severe forms of parasitic diseases require surgical intervention.
Prevention of parasitic diseases

Prevention of parasitic diseases is reduced to the following recommendations:
First of all, you must follow the rules of personal hygiene. This applies to washing hands before eating, after every trip to the toilet, after visiting public places and after contact with animals.
All food products must be properly processed. Fruits and vegetables, herbs and berries should be washed with running water and, if necessary, soaked in disinfectant solutions (for example, in a soda solution).
Meat and fish must be thermally processed.
Water should be boiled.
If there are pets in the house, then they need to conduct preventive antiparasitic courses. The toilet and eating area of the pet must be kept clean. Hands should be washed after each contact with an animal.
The room should be regularly wet cleaned.
When working with the ground, hands must be in gloves.
When traveling to tropical and subtropical countries, you should take care in advance to undergo helminthiasis prophylaxis with tablets if there are risks of invasion (a doctor should prescribe drugs).
These are the main measures for the prevention of parasitic diseases, which will allow you to protect yourself and loved ones from possible invasion as much as possible.










بھت اچھا