Contents
- Types of parasites that infect humans
- How does infection occur and why?
- Common signs of the presence of parasites in the body
- What are the symptoms of pinworms in children
- Signs of ascariasis in a child
- Signs of other parasitic infestations
- How to remove parasites from a child?
- Prevention of infestation by parasites
- 3 myths about parasites
According to medical statistics, 2 million inhabitants of Russia have a history of parasitic infestation. Statistics on the sale of funds for its treatment suggests that in fact at least 22 million people in Russia suffer from parasites. Approximately 80% of this number are children of preschool and primary school age. Medicine knows 342 species of parasites, of which about 70 are found on the territory of our country. The danger of this disease is that it is not always possible to make an accurate diagnosis for a child based on the symptoms.
Types of parasites that infect humans

The causative agents of invasion, for which a person is an intermediate or main host:
Nematodes or roundworms – pinworms (causative agents of enterobiasis), roundworms (causative agents of ascariasis), trichinella (causative agents of trichinosis), whipworm (causative agent of trichuriasis), they are more often than other species diagnosed in children.
Cestodes or tapeworms – bovine tapeworm (the causative agent of teniarachnosis), pork tapeworm (the causative agent of teniasis), pygmy or rat tapeworm (the causative agent of hymenolepiasis), wide tapeworm (the causative agent of diphyllobothriasis), echinococcus.
Trematodes, or fluke worms – cat or Siberian fluke (causative agent of opisthorchiasis), schistosome, liver fluke (causative agent of fascioliasis).
The localization of all these parasites in children is not only the intestines, but also the liver, lungs, muscles, heart, brain, gallbladder. In the body, they migrate through the blood vessels with the blood flow.
How does infection occur and why?

Most often in Russia and Ukraine, cases of infection with nematodes (pinworms, roundworms), less often with whipworm are recorded. Diseases caused by tapeworms and flukes are not typical for this region. From 2 to 5% of registered cases of invasion by these parasites are the consequences of travel to exotic countries, contact with infected animals, the use of undercooked and undercooked meat and fish, as well as gross violation of sanitary rules. A large proportion of diseases in this group account for the invasion of a wide tapeworm due to the use of uncooked river fish.
Pinworms and roundworms enter the body from dirty hands that are not washed well enough after communicating with animals, going to the toilet, before eating, and also after soil particles from poorly washed vegetables, fruits, and herbs enter the digestive system. Contact with a person infected with nematodes is dangerous, using the same household items with him. The eggs of these parasites can enter the body of healthy people from banknotes and coins, from door handles and public transport seats.
Even after careful treatment of enterobiasis, the risk of self-infection is not excluded. Reinvasion occurs after the cured carrier of pinworms again transfers their eggs into his mouth after contact with household items, where they fell from his own hands after combing the anus.
Younger preschoolers, due to the characteristics of their age, up to 5-6 years old cannot independently observe the rules of personal hygiene, but they are extremely active. Kindergartens, playrooms in shopping centers, outdoor playgrounds are places where negatives are concentrated. An additional factor in the easy infection of children with parasites is the increased susceptibility of the child’s body due to the imperfection of the protective barriers of the digestive system.
The widespread occurrence of this disease in the children’s environment is explained by untimely and imperfect diagnosis of parasitic infestations. Dimly expressed symptoms of infection, their similarity with other diseases, prevent parents in time to establish the real cause of the child’s poor health.
With enterobiasis, the female pinworm does not descend into the rectum every day in order to lay eggs. Therefore, scraping for enterobiasis in some cases can be false-negative even in the presence of pinworms in the intestine. In order to detect a disease with a minor invasion, an analysis is required three times: first with a frequency of one day, and the third time after 2 weeks.
Increased risk factors for ascariasis and enterobiasis in children:
Rare change of underwear (that is, it is not changed daily, it is better to do this 2 times a day, it is very important to change panties in the morning);
Unsanitary living conditions, flies and cockroaches in the dwelling where the child is located;
Contact of the child with domestic animals – possible carriers of eggs and larvae on wool;
Absence of the habit of regularly washing hands after a walk, before eating, after going to the toilet;
Negative addictions of the child to biting nails, sucking a pencil, toys, household items;
The child has long and dirty nails;
Insufficient hygienic processing of vegetables, fruits, herbs, and the use of such products for food.
Common signs of the presence of parasites in the body

Some types of parasites in children may not manifest themselves for many years, noticeable symptoms are detected only with a decrease in immunity. Researchers involved in their study, back in the last century, put forward the theory that these pathogens are the cause of many pathologies, including cancer.
It is difficult to find a child free from the carriage of viruses, larvae and eggs of parasites, pathogens. They disrupt the vital activity of the child with their toxins, physical damage to tissues and organs, and cause serious diseases.
General symptoms of intoxication that appeared in adults and children due to parasitic invasion:
headache, dizziness;
Nausea, increased salivation;
Alternating constipation and diarrhea;
Various manifestations of allergies;
Excessive appetite, not accompanied by weight gain, or, conversely, its absence;
Pain in the abdomen or in the right hypochondrium of varying intensity;
Inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx (sinusitis, adenoids, sinusitis, polyps in the nose), diseases of the genital organs;
Fragility of nails and hair, as a result of beriberi and iron deficiency anemia;
Nervous system disorders (irritability, insomnia or drowsiness, cognitive impairment, memory impairment) due to increased concentrations of toxins;
Symptoms of anemia (decreased hemoglobin, increased eosinophil count) recorded in the results of blood tests;
Manifestations of allergies and intoxication, aggravated after vaccinations.
What are the symptoms of pinworms in children

Pinworms are the causative agents of enterobiasis, having a small size (no more than 1 cm). A carrier of enterobiasis can transfer pinworm eggs to clothes, doorknobs, household items, and toys. The viability of pinworms is quite large. For them, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, boiling is deadly. Disinfectants are not always able to completely disinfect items infected with pinworms. The route of human infection with enterobiasis is fecal-oral. From the oral cavity, pinworm eggs enter the digestive tract, reach sexual maturity in 2 weeks. After that, the female begins to lay her own eggs.
A characteristic symptom of enterobiasis is itching around the anus. It appears at night when the child is warm under the covers, and his muscles relax. Thanks to this, the female freely penetrates into the anus of the baby, lays up to 5 thousand eggs in the skin folds. The child unconsciously combs the irritated skin, while the eggs get under the nails, on clothes, underwear and bed linen, and the skin of the hands.
Additional symptoms of enterobiasis in children:
Itching in the anus leads to violations of children’s sleep (anxiety, insomnia, intermittent disturbing sleep);
Weight loss, differences in the child’s body weight from age standards;
Increased fatigue, irritability, anxiety, capriciousness, learning disorders, lack of attention;
Enuresis, more common in girls, is due to pinworm irritation of the urethra;
Vulvovaginitis and other inflammatory diseases of the vagina, provoked by the penetration of pinworms, possible infection and inflammation of the fallopian tubes;
Acute appendicitis, the cause of which is the concentration of pinworms in the caecum;
Presumably – gnashing of teeth in young children at night;
Dyspeptic manifestations – alternating constipation and diarrhea, enterocolitis with a protracted course, nausea, pain in the navel;
A significant drop in immunity in children due to impaired absorption of nutrients and vitamins, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, often recurring infectious and viral diseases with a protracted course;
Symptoms of intoxication – weakness, frequent dizziness and headaches, nausea, weight loss.
Signs of ascariasis in a child
According to the statistics of laboratory tests for the presence of parasitic infections, it can be concluded that about 80% of preschool children have been treated or are currently being treated for parasitic infestation. Infection of this kind is a very serious problem, since the growing organism is deprived of most of the nutrients it needs, the internal organs of the child are affected, and it is subjected to intoxication.
With such a dangerous invasion as ascariasis, its pathogens affect almost all organs: the brain, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, liver and gallbladder, heart, pancreas. Ascariasis is transmitted by the fecal-oral route, when eggs from the soil enter the mouth and then into the digestive system. Provoking factors are contact with soil and sand, poor hygiene, eating greens, vegetables and fruits with food particles, flies as egg carriers.
Ascaris eggs that enter the oral cavity and further into the small intestine develop in it and become larvae. Ascaris larvae migrate with the blood flow to the liver, lungs, and heart. Ascariasis is manifested in children with subfebrile temperature (up to 38 ° C), weakness, cough with blood, general malaise, symptoms of obstructive bronchitis, asthma, pleurisy, pneumonia. X-ray examination diagnoses moving pulmonary infiltrates.
At the initial stage of the disease, children are diagnosed with an increase in lymph nodes, an increase in the liver and spleen. A characteristic symptom of ascariasis is allergic urticaria on the skin of the hands and feet, dermatitis.
In the intestinal phase of ascariasis, which begins 3 months after the introduction of the infection, roundworms move into the intestines. This happens when children swallow phlegm from the lungs containing a huge number of larvae. Symptoms of parasites entering the intestines in children are violations of the functions of the digestive system (cramping abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, alternating constipation and diarrhea, irritation of the skin of the anus). Reduced immunity as a result of a long-term illness cannot resist infections – purulent processes of the skin and mucous membranes, relapses of stomatitis.
The toxic effect of ascaris waste products negatively affects the nervous system. Children develop disorders of the psyche and nervous system: sleep disturbances, seizures like epileptic seizures. There may be symptoms such as a drop in blood pressure, photophobia, enlarged pupils. Complications of ascariasis are characterized by a severe course. These are peritonitis, acute appendicitis, obstructive jaundice and intestinal obstruction, arising from the fact that roundworms close the lumen of the intestine and bile ducts.
Signs of other parasitic infestations

Opisthorchiasis (causative agent – cat, or Siberian fluke) – violations of the digestive system, hepatitis, liver enlargement, pain in the abdomen and in the right hypochondrium, skin rashes, manifestations of allergies, myocardial dystrophy, swollen lymph nodes, catarrhal syndrome, joint pain, subfebrile temperature, blood count disorders (elevated ESR, the number of eosinophils , low hemoglobin).
Trichuriasis (causative agent – whipworm) – the symptoms in children are minimal, dyspepsia, diarrhea mixed with blood, alternating with constipation, bloating, vomiting may occur, with a massive long-term invasion, a lag in mental and physical development is diagnosed in children.
Diphyllobothriasis (causative agent – a wide tapeworm Diofillobotrium latum), provoked by the use of fish that has not undergone full heat treatment – manifested by intestinal disorders, allergy manifestations, anemia with vitamin B deficiency12.
Hymenolepiasis (causative agent – rat, or pygmy tapeworm) – has no specific symptoms, can be manifested by gastrointestinal disorders (pain, heartburn, alternating diarrhea and constipation, nausea, decreased appetite), allergic and vasomotor rhinitis, increased fatigue.
Toksokaroz (causative agent – Toxocara, transmitted to children from infected cats and dogs) – pronounced manifestations of allergies (cough, suffocation, swelling of the face, fever, skin rash), eye damage (keratitis, ophthalmitis, choriretinitis), enlarged liver, lymph nodes, x-rays – infiltrates in the lungs.
How to remove parasites from a child?

To eliminate parasites in children, the pharmaceutical industry produces a large number of highly effective antiparasitic drugs. Almost all of them have a toxic effect on the child’s body, so they are taken only on the recommendation of an infectious disease specialist, a parasitologist. Treatment is carried out according to the results of the diagnosis, which determines the type of infection. Although there are complex remedies, specific drugs may be required to expel a particular species.
To stop the toxic effect of the waste products of parasites in children, manifested in the form of allergic reactions, the doctor prescribes antihistamines. In pediatrics, for this purpose, effective and safe drugs are used in the form of drops or suspensions (Zodak, Cetrin, Zirtek, Loratidin).
Effective remedies for the treatment of nematode infestation in children:
Medicine name | Features, analogues and price |
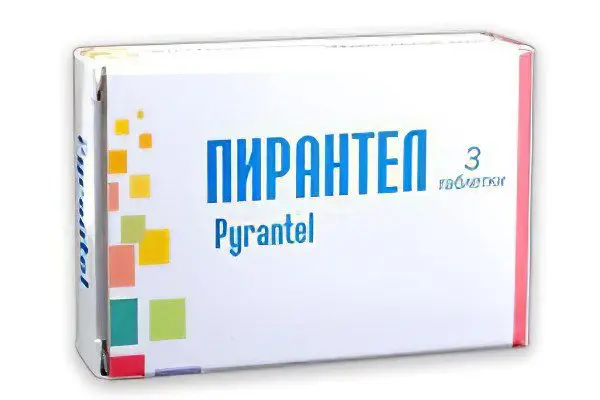
Pirantel | Pirvinium, Helmintox (90-130 rubles), Nemocide, Pirantel-Combanthrin – drugs of this group are less toxic to the child’s body |
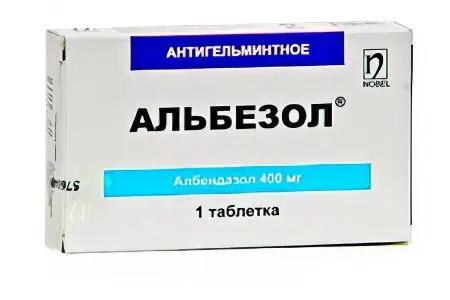
Albendazole | Albendazole – Vormil, Nemozol (130-150 rubles), Gelmodol-VM |
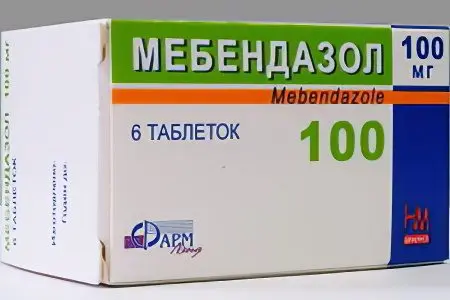
Mebendazole | Mebendazole – Vermox (90-100 rubles), Vermakar, Mebeks, Thermox, Vero-Mebendazole, Wormin (20-30 rubles) – drugs that effectively act both on adults and on their eggs and larvae are used for treatment severe invasion; |
Piperazine | Has a minimum of contraindications; |
Levamisole | Decaris (80-100 rubles). |
In most cases, with enterobiasis, a second course of therapy is performed to prevent self-infection. The frequency of treatment courses is 2 weeks.
Folk recipes for removing parasites in children (the use of garlic and pumpkin seeds) can serve as an auxiliary or prophylactic agent. The main treatment of invasion is carried out with medicines.
Prevention of infestation by parasites

Long heat treatment of meat and fish dishes.
Thorough washing of greens, berries, fruits, vegetables.
Fight against insects – carriers of eggs and larvae (flies, cockroaches, mosquitoes).
Preventive treatment for parasites, regularly performed in pets.
Washing hands with soap and water after contact with animals, soil, sand, after using the toilet, before eating.
Processing nipples, toys, before giving them to the baby, as well as after falling to the floor, to the ground.
Fighting bad habits: sucking pencils, pens, fingers, nail biting.
Careful nail care, timely shortening, keeping them clean.
In case of enterobiasis – the use of tight panties to prevent the spread of pinworms in bed at night.
Ironing children’s underwear with a hot iron after washing.
With enterobiasis, frequent change of underwear (2 times a day), hygienic washing with soap of the anus and the area around it.
3 myths about parasites
Myth one: Absolutely all pets are carriers of the infection. Pet owners do not agree with this statement. They believe that it is their pet who is completely healthy, and he does not need treatment.
Reality: Any animal, even outwardly healthy in appearance, can become a carrier of the disease (cats, dogs, decorative rodents).
Second myth: Prophylactic treatment of parasitic infections in pets is carried out only before vaccination.
Reality: To be completely sure that the pet is perfectly healthy, you need to carry out such prevention at least 4 times a year, that is, quarterly.
The third myth: To provide cats and dogs with nutrients and cheer up your pet, you need to feed raw meat from time to time.
Reality: Nutrients in modern pet food are balanced and provide all the needs of pets. Raw meat and fish are a risk factor for parasites.