Contents
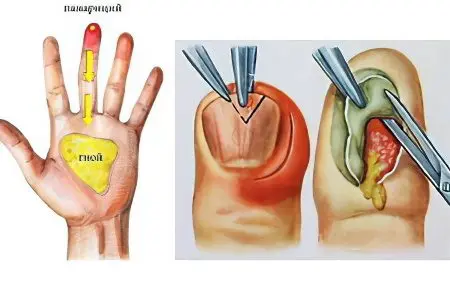
According to statistics, panaritium is the reason why 20-30% of patients (of the total mass of patients) go to the doctor. This disease is accompanied by acute inflammation of the fingers or toes, from the side of the palms or from the soles. Also, the periungual spaces are involved in the pathological process.
Panaritium often leads to the development of a purulent process. If treatment is not started on time, phlegmon may develop. Although the superficial form of the disease is most often diagnosed.
What is panaritium?
Panaritium is a purulent inflammation of the fingers or toes. A variety of injuries, even minor damage to the skin, are capable of provoking its development. Through the damage, the infection penetrates inside and causes acute inflammation.
Reasons for the appearance of panaritium

The main cause of panaritium is an infection that penetrates the soft tissues of the patient. The entrance gate for it can be microscopic skin injuries, cuts, punctures, burns, abrasions, splinters. Sometimes even a strong scratch or insect bite causes inflammation.
Microbial flora leads to suppuration, namely:
Staphylococci.
Streptococci.
Gonococci
Enterococcus.
Sometimes there is a mixed infection. In addition, the herpetic and fungal nature of panaritium cannot be ruled out.
Risk factors for the development of panaritium:
Poor wound care.
Use of manicure accessories that have not been sterilized.
Incorrect cutting of the nail plates.
Wearing shoes that do not fit well and are poorly ventilated.
Skin macerations.
Diabetes.
Vitamin deficiency.
immunodeficiency states.
Violations of blood microcirculation in the fingers or toes. The reason may be constant vibrations, hypothermia of the extremities, the effect on the body of toxic substances, such as quicklime, mineral oils or metals.
Some chronic diseases: allergic dermatitis, psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus and other skin pathologies.
Classification
Panaritium can be purulent or serous. Depending on which tissues were involved in the pathological process and where exactly the inflammation is concentrated, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
Superficial panaritium:
Every form. Compared to other types of the disease, it has the mildest course. The purulent process is concentrated in the epidermis.
Paronychia or periungual panaritium. Inflammation is concentrated next to the nail fold. The main cause of inflammation is a manicure, which was carried out in violation of the technique.
Deep panaritium:
Subcutaneous felon. Pus accumulates in the subcutaneous tissue from the palmar side of the fingers.
Bone panaritium. Bone structures are involved in the pathological process.
Subungual panaritium. Pus will accumulate under the nail.
Articular felon. The inflammation spreads to the joints of the fingers.
Tendon panaritium. The tendons of the extremities are affected.
Pandactylitis. The disease develops when the purulent process spreads to all tissues of the limb. This is the most severe form of the disease and can cause loss of fingers or even a hand.
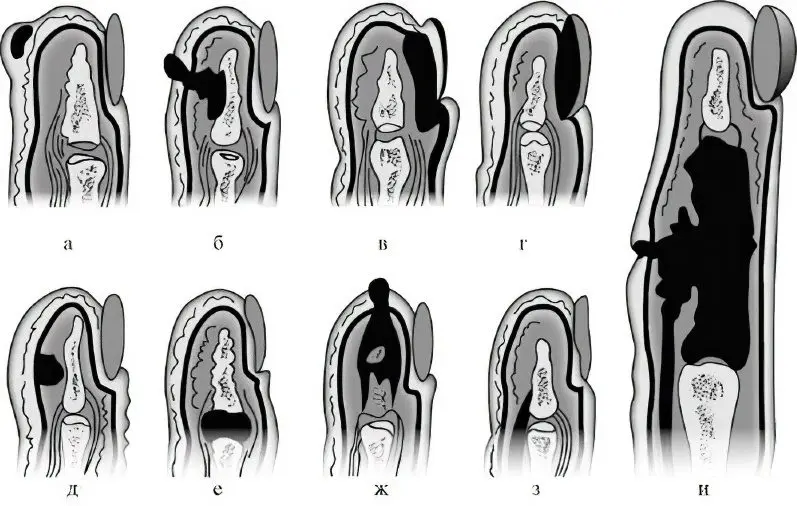
Stages of defeat
There are 3 stages in the development of the disease:
First stage. The infection penetrates into the soft tissues of the finger. During this period, symptoms of the disease may be absent.
The second stage is infiltration. A person develops swelling, pains appear, the skin in the affected area turns red, becomes hot to the touch.
The third stage is an abscess. Pus melts the tissues of the infiltrate, leading to the formation of a specific cavity – an abscess.
You can cope with panaritium without the help of a surgeon if the disease is at stage 1 or 2 of development. When an abscess is formed, an operation is indicated.
Symptoms of Panarity
Symptoms of panaritium are divided into general and local. Their intensity depends on the depth of tissue damage, on the type of pathogen and on the state of the human immune system.
Common symptoms of panaritium:
Intoxication of the body: headache, palpitations, weakness, decreased performance.
Increased body temperature.
Fever.
Local symptoms of panaritium:
Pain.
tissue hyperemia.
Edema in the affected area.
Local rise in temperature.
Pus may show through the stretched skin. When the dermis breaks, it comes out.
Symptoms of panaritium may differ depending on the type of disease:
Cutaneous panaritium leads to the formation of a purulent bladder on the finger. The skin turns red, there is a pulsation.
Periungual panaritium is accompanied by swelling of the tissues. They become hot to the touch. As inflammation progresses, a purulent focus is formed in the periungual fold. A person begins to be disturbed by severe pain.
The subcutaneous form of the disease is more common than others. The skin in the affected area turns red, becomes hot to the touch. The pain is throbbing, aggravated by touch.
Subungual panaritium is accompanied by an accumulation of pus under the nail. It can be seen through the plate. The finger is swollen and difficult to move. Perhaps a significant deterioration in general well-being, an increase in body temperature to high levels.
Bone panaritium. The patient’s body temperature rises, severe pain appears. All symptoms of intoxication of the body are present.
Articular felon. Pathology is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of the bone form of the disease, but is complemented by difficulties in bending the joints.
Tendon panaritium. The person complains of severe pain. They get worse when you try to move your fingers. The hand swells, the symptoms of intoxication of the body are pronounced.
Pandactylitis. The patient has severe intoxication, purulent axillary lymphadenitis develops. This condition is dangerous for the development of sepsis.
Diagnostics
Doctors do not experience difficulties with the diagnosis. In order to determine panaritium, an external examination of the patient is sufficient. To determine the infectious flora that provoked inflammation, fluid is taken from the pustule.
If the doctor cannot visualize pustules with pus, then he uses a bellied probe. With its help, the place of maximum pain and the depth of inflammation are determined.
If there is a suspicion that the patient develops panaritium of the joints or tendons, then he is sent for an x-ray. To clarify the severity of the disease, a general blood test with the determination of the leukocyte count and ESR may be required.
Treatment of panaritium
Therapy depends on the stage of development of the disease, as well as on its variety. It is possible to cope with the pathology by conservative methods in the early stages.
Conservative treatment
In the early stages, the doctor will prescribe a number of medicines that relieve inflammation and suppuration. At home, it is permissible to make therapeutic baths. Potassium permanganate, saline solution are diluted in them. You can use herbal decoctions.
Sometimes even deep felon can be cured with conservative methods. To do this, you need to contact the doctor in time.
Surgery
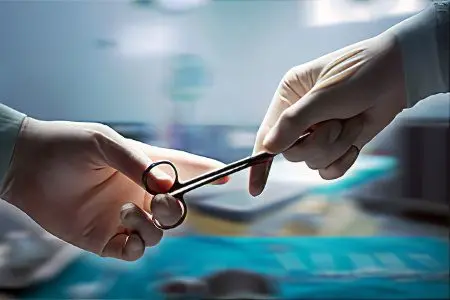
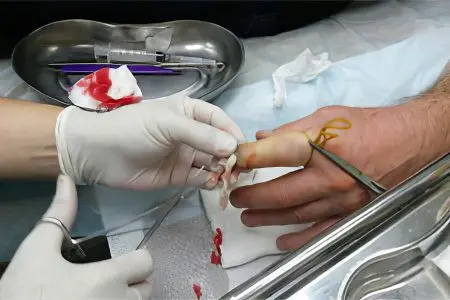
Surgery is the most effective method of treating panaritium. The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia. If the inflammation has spread to the joints or bones, then general anesthesia is required.
Further stages of treatment:
The doctor performs an incision and removes the pus, along with dead tissue.
The affected cavity is sanitized with the use of antiseptics.
A drain is inserted into the wound to drain the pus.
A bandage is applied over the wound.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed painkillers, antibiotics. The wound is regularly bandaged and treated with Furacilin or Betadine. For the speedy recovery of tissues, physiotherapy is indicated.
Complications
Complications of panaritium include:
Blood poisoning. At the same time, purulent foci are formed in other internal organs, DIC develops. Sepsis often ends in the death of the patient.
Purulent tendovaginitis with damage to the synovial bags of the hands and forearm. This complication is most often caused by panaritium, concentrated on the I or V finger of the hand.
Cyst phlegmon.
Osteomyelitis of the metacarpal and carpal bones.
Vessel thrombosis with tissue necrosis, periphlebitis and thrombophlebitis of the extremities.
Purulent lymphadenitis. Sometimes it is lymphadenitis and general intoxication of the body that become the first symptoms of panaritium.
Finger contractures. This complication develops against the background of the articular or tendon form of the disease.
Prophylaxis panaritsia
To prevent the development of panaritium, the following preventive measures must be observed:
Keep your hands clean. However, it is not worth washing too often, as overdried skin is easily injured, microcracks appear on it. They can become entry gates for infection.
Use gloves while working with the ground, during cleaning. If they are not, then the hands must be treated with a protective cream. After completion of labor activity, they are washed and smeared with a greasy cream.
Observe safety rules when working with cutting tools. Especially when there is a high risk of infection entering the wound, for example, while peeling potatoes, or when cutting fish.
Using your own manicure supplies. During the processing of nails, you should try not to injure the skin and soft tissues. The cuticle should not be trimmed, it is enough to push it back.
Video: Elena Malysheva in the program Live Healthy “Suppuration on the finger”









