Contents
- Diseases that cause pain in the knee joint
- Gonarthrosis
- Meniscopathy
- Arthritis
- Periarthritis
- Tendonitis of the knee
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Bursitis
- Gout of the knee
- Paget’s disease
- Fibromyalgia
- Osteomyelitis
- Baker’s cyst
- Koenig’s disease
- Osgood-Schlatter disease
- Infectious diseases of the knee: Lyme disease, Reiter’s syndrome
Diseases that cause pain in the knee joint
Knee pain is an unpleasant sensation that many experience when walking, exercising, and even at rest.
The cause of discomfort can be injuries, as well as the following diseases:
Gonarthrosis;
Meniscopathy;
Arthritis;
Periarthritis;
Tendinitis of the knee joint;
Rheumatoid arthritis;
Bursitis;
Gout of the knee joint;
Paget’s disease;
Fibromyalgia;
Osteomyelitis;
Baker’s cyst;
Koenig’s disease;
Osgood-Schlatter disease;
Infectious diseases of the knee: Lyme disease, Reiter’s syndrome
Gonarthrosis
It is a destruction of the cartilaginous tissue of the knee joint, resulting in its deformation and dysfunction. Women are more likely to suffer from osteoarthritis than men. It is also called osteoarthritis of the knee.
According to the causes of occurrence, two types of the disease are distinguished. A factor contributing to the development of primary or idiopathic gonarthrosis is the patient’s advanced age. The exact external causes in medicine have not been established. This type of disease is bilateral, that is, it affects both legs. The second type of gonarthrosis occurs as a result of an injury to the knee joint or as a complication after infections. It can develop in a patient at any age and can be both unilateral and bilateral.
The main causes of gonarthrosis are fractures of the bones of the knee joint, arthritis, bone tumors, arthrosis and spondylitis.
The disease develops gradually and in the first stages it practically does not manifest itself. Among its main symptoms are acute pain in the knee joint after being at rest, changes in gait. Gradually, during movement, the discomfort disappears, but after a long rest it appears again. With gonarthrosis, osteophytes may appear. This is what is called bone growth. As a result of friction of cartilage tissue against these formations, the joint membrane becomes inflamed. The skin in this place is redder, a swelling appears, the patient has a fever.
Stages of gonarthrosis:
The deformity of the joint is almost imperceptible. Mild pain may occasionally occur;
At this stage, the deformation is clearly visible. The pain intensifies, the attacks become longer. Possible crunch in the knee joint;
The disease progresses rapidly. Now the pain is felt both during movement and at rest, the gait changes.
Gonarthrosis is diagnosed on the basis of x-ray and visual examination of the knee joint. It is recommended to perform foot massage to improve blood circulation. This will reduce the pain. For the same purpose, venotonics and vasoconstrictors are used. Analgesics help relieve pain. Chondroprotectors act on cartilage tissue. In the third stage of the development of the disease, surgical intervention may be required. Endoprosthetics allows you to replace the knee joint, fully restoring all its functions. With the help of arthroscopy, you can slow down the development of gonarthrosis.
Meniscopathy

The knee joint has two special cartilage pads that lighten the load on the joint during active movements. They are called menisci. The medial or inner meniscus is less frequently injured than the lateral, known as the outer. Such an injury can occur in a person, regardless of age and type of activity. Jumping, squatting, skiing contribute to the development of meniscopathy. At risk are those who suffer from gout or arthritis, diabetes, have weak ligaments or are overweight, which increases the load on the joints.
The main symptom of a meniscus injury is a clicking in the knee joint, followed by sharp pain. The younger the person, the more acutely he feels it. In the elderly, cartilage is not sufficiently saturated with moisture, so the sensations are weaker. When severe pain occurs, the patient stops moving. Gradually, the discomfort disappears, and then again the person can hardly walk. The next day, the knee swells, but this is a defensive reaction aimed at restoring a pinched meniscus after an injury. Otherwise, the disease becomes chronic. The duration of the attack of pain is several weeks. During this time, the swelling subsides. In the absence of the necessary treatment, meniscopathy is periodically manifested by bouts of severe pain and, as a result, can lead to arthrosis.
The most reliable diagnostic method in this case is magnetic resonance imaging. During it, the nature and degree of damage to the meniscus is determined. If it is completely torn off, surgery is needed. The surgeon removes the entire meniscus or part of it. Therapeutic methods are effective for pinching or tearing. In this case, it is possible to restore the functions of the knee joint in several sessions with a traumatologist or a chiropractor. Edema can be removed by corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. But first of all, the cause of the tumor should be eliminated.
Arthritis
Arthritis is considered the most common form of knee disease. It involves the defeat of the synovial membrane, capsules, cartilage. If this disease is not treated, the patient may lose his ability to work, lose the ability to walk and move actively.
Arthritis is of the following types:
rheumatoid – factors contributing to its development are unknown;
post-traumatic – is the result of sprains, bruises, ruptures, damage to the meniscus;
reactive – the cause of its appearance is food poisoning, tissue infection;
deforming – occurs when blood circulation is disturbed;
gouty – caused by malfunctions in the metabolism in the body, deposits of sodium urate.
In addition, arthritis is primary, when it occurs as a result of an injury and the development of an infection against its background, or secondary, when inflammation occurs in other tissues, and enters the knee joint with lymph or blood.
The development of the disease is promoted by excess weight, which increases the load on the joints, and old age, as cartilage and bone tissue wears out over time. Significant physical activity, frequent weight lifting, immunodeficiency also lead to arthritis.
Attacks of the disease are accompanied by discomfort in the knee joint, redness, swelling. They become longer and more painful as arthritis develops. When pus forms, the patient’s temperature rises.
Treatment involves measures aimed at eliminating swelling, discomfort, restoring the functions of the knee joint, and preventing new attacks. Relief from pain is carried out with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics. Effective warming and distracting ointments, as well as restorative drugs. During the period of remission, physiotherapy methods, massage and therapeutic exercises are prescribed.
If conservative treatment does not give the desired results, surgical intervention is performed.
Periarthritis
This disease affects the periarticular tissues: muscles, ligaments, tendons, joint capsule. Periarthritis is more susceptible to places that have a significant load during movement, including the knee joint.
The cause of its development is chronic diseases, frequent hypothermia, problems in the endocrine system, peripheral vessels. Post-traumatic periarthritis appears as a result of damage to the joints.
This disease is characterized by aching pain in the knee joint, the formation of edema. On examination, the doctor may reveal the presence of nodules and small seals. When pressing on them, the patient experiences palpable pain. When walking, there is discomfort in the knee joint.
During treatment, it is recommended to limit movement and to be more often at rest. Non-steroidal drugs, such as diclofenac, can relieve inflammation and reduce pain. With periarthritis, physiotherapy is performed. The most common effect is cold – local cryotherapy, infrared laser therapy, the imposition of paraffin-ozocerite applications is used. It is necessary to improve the condition of the periarticular tissues.
Older women often suffer from a special form of this disease – periarthritis of the crow’s foot bursa. It suggests inflammation of the knee tendons from the inside. Edema, deformation of the joint does not occur. Pain is felt only when moving on uneven surfaces, when wearing high-heeled shoes. If the disease is diagnosed on time, then in the early stages of development it can be cured quickly. To do this, it is necessary to carry out physiotherapy, to take the drugs prescribed by the doctor.
Tendonitis of the knee
It consists in inflammation of the tendon tissue in the area of its attachment to the bone or in the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe muscle-tendon transition. This condition is known as jumper’s knee. This is largely due to the fact that the cause of tendinitis is sports such as basketball, cycling, volleyball. Athletes, older people, teenagers and children are the most susceptible to the disease. It affects the ligament of the patella, which is responsible for the implementation of the flexion and extensor movement. Tendinitis can appear on only one leg or on both at once and is of two types: tendobursitis and tendovaginitis. In the first case, the tendon bag becomes inflamed, and in the second, the tendon sheath.
The causes of tendonitis are:
other diseases (gout, rheumatoid arthritis);
injuries, sprains, bruises;
uncomfortable shoes;
muscle imbalance;
weak immunity;
constant physical activity;
fungal infections, parasites.
With tendonitis, pain often appears when the weather changes. The knee joint swells, there is a limitation of its mobility, and creaking when moving. Attacks of pain provoke active movements. In the later stages of tendinitis, a rupture of the patellar ligament may occur.
During the X-ray, the disease is detected when the cause of its occurrence is the deposition of salts, bursitis or arthritis. Laboratory tests are helpful in diagnosing tendinitis when it occurs as a complication of an infection. Detailed information about the deformation of the tendons can be obtained by various types of tomography.
In the early stages of the disease, conservative methods of treatment can be dispensed with. Physical activity should be limited. In some cases, immobilization of the knee joint is required, so a cast or splint is used. The doctor prescribes medications (non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory) and physiotherapy. In critical situations, injections of corticosteroids and antibiotics are necessary. From physiotherapy, magnetic, iontophoresis and electrophoresis are more often used. Surgical removal of degenerative tissues in the last stages of tendinitis is performed. With the accumulation of pus in the area of the knee joint, an autopsy is performed and it is pumped out. Drug treatment can be combined with the use of traditional medicine to get the best result. Under the supervision of a trainer, it is also recommended to perform physical exercises. After recovery, you can go back to regular sports. Yoga has a positive effect on the condition of the knee joint with tendinitis.
Rheumatoid arthritis
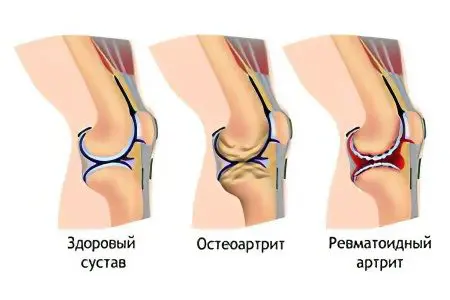
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease that manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the connective tissue. The exact reasons for its appearance are unknown. There is a genetic predisposition to rheumatoid arthritis. At the time of weakening of the immune system, the disease begins to develop actively. It affects both men and women at any age. It affects the connective tissue in the joints, which account for a significant load, including the knee. Lack of timely diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in most cases leads to disability and even death. Death occurs from infectious complications and renal failure.
There are factors that contribute to the development of rheumatoid arthritis. This is a constant emotional stress, frequent hypothermia of the body.
In accordance with the symptoms, the following stages of development of rheumatoid arthritis are distinguished:
There is swelling and swelling of the knee joint. The patient is in pain. Possible increase in body temperature;
Inflamed cells are actively dividing. This causes a compaction of the synovial membrane;
At the last stage, bone and cartilage tissue is affected. The knee joint is deformed and does not perform its functions. Attacks of pain become stronger and longer.
Rheumatoid arthritis develops slowly. At first, it may appear only in the form of stiffness in the knee joint after being at rest for a long time, for example, in the morning when waking up. Pain occurs at night and with a sharp change in weather.
The disease is diagnosed on the basis of a biochemical blood test, X-ray and externally expressed symptoms: redness of the skin, swelling, joint deformity, pain in it. If the arthritis is caused by an infection, then antibiotics are prescribed. Corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help relieve joint pain and inflammation. It is also necessary to engage in therapeutic exercises and massage regularly.
Bursitis
Inflammation that occurs inside the synovial sac is called bursitis in medicine. Its cause is the accumulation of exudate, that is, a liquid containing dangerous microorganisms. Bursitis occurs as a result of an injury to the knee joint, significant physical exertion on it, or as a complication of an infectious disease. Arthritis or gout also contribute to its development.
Bursitis can be identified by stiffness of movements, pain in the knee joint. Inflammation is especially noticeable after pressing movements on the skin. The patient experiences weakness, malaise, and may lose his appetite. If the cause of bursitis is an infectious disease, the body temperature rises. Its important difference from arthritis is the preservation of the ability to perform flexion-extensor movements.
During the diagnosis, the doctor examines the symptoms of the disease, examines the knee joint. To accurately determine the nature of the accumulated fluid, a puncture is performed. In the first stages of the development of bursitis, it can be dealt with with the help of compresses, body wraps. The patient must comply with bed rest. In chronic bursitis, a puncture is made to remove the fluid accumulated inside the bag, and then the cavity is washed.
Gout of the knee

This chronic disease is associated with deposits of sodium monourate, which provokes bouts of acute pain in the knee joint. Gout is more common in men than in women. The causes of its development are considered to be a violation of urinary metabolism, as a result of which the level of uric acid in the blood rises. This leads to the consumption of excessive amounts of foods containing purines. These include meat and fish. Contributes to the development of the disease and alcohol abuse.
Gout manifests itself in the form of sharp pains in the knee joint and redness of the skin in this area. In soft tissues, dense nodules are formed – tophi. They are accumulations of uric acid. Sometimes the tophi are torn, and it comes out. Attacks of gout pain can last for several days or even a week.
Gout can be diagnosed by a high level of uric acid in the blood. For this, a biochemical analysis is performed. X-rays are also taken as part of the diagnosis. To cope with an attack of gout, you should follow a diet, move less. The patient must be provided with emotional and physical rest. The diet is combined with drug therapy.
Paget’s disease
Violation of the processes of formation of bone tissue leads to deformation of the skeleton, fragility of bones. In medicine, this phenomenon is called Paget’s disease. It affects the tubular bones of the legs and can cause pain in the knee joint. Men have Paget’s disease more frequently than women. It usually occurs in older people.
Determining the presence of this disease is difficult, as it may not be accompanied by any symptoms. In some cases, patients may feel pain at night, and warmth is felt at the site of the affected bone. Diagnosis of Paget’s disease is carried out using a biochemical blood test, which shows an increased content of phosphatase, biopsy and X-ray.
Pain can be relieved with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Basically, the treatment is aimed at preventing the complications of Paget’s disease: increasing the strength of the bones, reducing their fragility. This is possible due to the intake of bisphosphonates and drugs that serve as a source of calcium. You should regularly take tests and see a doctor. In advanced cases, rehabilitation is carried out in the clinic. With Paget’s disease, it is worth following a diet, exercising under the supervision of a specialist, and avoiding falls and injuries. Due to the fragility of the bones, fractures are more likely.
Fibromyalgia
This disease occurs in at least 5% of the population. Fibromyalgia is expressed in the form of symmetrical musculoskeletal pain, often appearing in the knee joint. The causes of its occurrence are poorly understood, but it is known that discomfort is not caused by inflammatory processes.
The main complaints in patients, in addition to musculoskeletal pain, are poor sleep, fatigue, loss of strength, intestinal disorders, cramps and spasms, numbness and morning stiffness. Commonality of symptoms often leads to misdiagnosis. Fibromyalgia can be confused with depression.
The cause of the disease is stress, emotional stress, accelerated serotonin metabolism, physical trauma. Diagnosis of fibromyalgia is carried out by various methods and is selected by the doctor individually. Often, the presence of a disease is determined even by excluding the presence of other ailments.
Treatment is carried out by drug and non-drug methods. In most cases, the patient is prescribed antidepressants, painkillers. It is recommended to avoid stressful situations, go in for sports, follow a diet, and have massage sessions.
Osteomyelitis
The diagnosis of “osteomyelitis” is made if the patient develops a purulent-necrotic process of the bone and soft tissues around it. They are caused by special bacteria that produce pus. Infectious agents penetrate in various ways: endogenously – through the blood, spreading from the focus of inflammation, exogenously – as a result of the treatment of fractures, filling teeth. Osteomyelitis can be caused by trauma or Staphylococcus aureus.
There are 2 main types of the disease: hematogenous and traumatic. In the first case, osteomyelitis does not manifest externally for a long time. However, the patient may experience malaise, weakness. Then there is a sharp increase in body temperature and acute pain appears. The inflammatory process proceeds very quickly. Sepsis is possible, leading to the death of the patient. Traumatic osteomyelitis develops when treatment is started too late. Attacks of pain in this case alternate with a state of rest.
Treatment of osteomyelitis is carried out medically with the help of antibiotics and surgically. During the operation, pus, dead tissue cells are removed.
Baker’s cyst
In medicine, a Baker’s cyst refers to a knee or popliteal hernia. Its size can vary, but rarely exceeds a few centimeters. Most often occurs in people over 30 years of age and in children aged 3-7 years. Baker’s cyst is formed due to damage to the knee. Diseases such as arthritis and osteoarthritis also contribute to its appearance.
Due to their small size, a Baker’s cyst can sometimes go unnoticed even by a doctor. It does not cause anxiety in the patient, there are no changes in his state of health. There may be pain in the knee area, swelling, discomfort during flexion-extensor movements. In some cases, the cyst resolves on its own over time.
In the presence of severe pain, aspiration is performed. It is also necessary if the cyst is large. Non-steroidal drugs help to relieve pain well, but they can only be taken under the supervision of a doctor. To relieve inflammation allows the imposition of compresses, performing physical exercises aimed at strengthening the knee.
Koenig’s disease
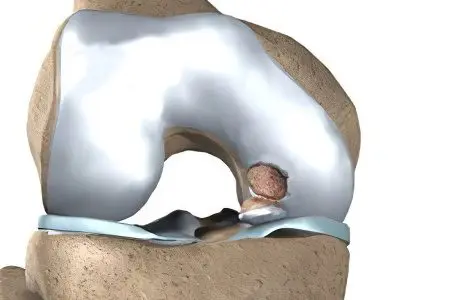
This disease is often called dissecting osteochondrosis. A piece of cartilage can separate along the bone and move freely in the knee joint. This makes movement difficult and causes pain. This phenomenon is called Koenig’s disease. Most often it occurs in the knee joint. Allocate an adult form of the disease, which is more difficult to treat, and a child. In the course of development, Koenig’s disease goes through 4 stages.
Its symptoms include dull pain, synovial fluid accumulates in the joint. Unpleasant sensations are felt most strongly during movement. The separation of the cartilage exposes the bone, which is accompanied by inflammation, which is manifested by edema. The most informative is the radiation method of diagnosis in Koenig’s disease.
At the initial stages, it can be dealt with with the help of conservative methods of treatment. For older patients, as well as in advanced stages, surgery is usually required. The patient needs physical and emotional rest.
Osgood-Schlatter disease
This disease manifests itself in the form of the formation of a painful lump in the region of the patella. Children and teenagers suffer from them. A high risk of developing Osgood-Schlatter disease in those who play sports, such as basketball, figure skating, ballet. Most often, problems with the patella occur in boys. Doctors attribute this to the fact that they are subject to more serious physical stress than girls.
The main symptoms of the disease are swelling in the knee area, swelling, sharp pains when moving: running, jumping. The bumpiness is noticeable to the touch. Osgood-Schlatter disease usually affects only the knee of one leg.
It goes away on its own with age. But in some cases, physical therapy or medication is required, which involves taking painkillers. You can do cold compresses on your own. It is necessary to use the patella when performing physical exercises. Therapeutic gymnastics helps to strengthen the tendons, but it should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Infectious diseases of the knee: Lyme disease, Reiter’s syndrome
Lyme disease develops after the bite of an infected tick. It becomes chronic and recurrent as pathogens multiply in the body. Diagnosis of the disease can be based on a biochemical blood test.
In Lyme disease, the patient experiences pain in the muscles and tendons. Most often, it affects the knee joints. Possible arrhythmia, headaches, depression, weakness. When diagnosed, Lyme disease is easily confused with another disease, so at the first suspicion, you should consult a doctor to confirm the infection and prescribe antibiotics.
Reiter’s syndrome is called inflammation of the genitourinary tract, eyes and joints, including the knees. When urinating, patients feel itching, pain and burning. Severe pain is felt in the knee joints, and the lesion is usually asymmetrical. The skin in the knee area acquires a reddish tint, edema is formed. The disease can be both acute and chronic. It is caused by a urinary or intestinal infection. After diagnosis, treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is carried out.









