Contents
Many people often experience pain in the elbow joint. In most cases, pain occurs against the background of various diseases, but sometimes it can appear for no apparent reason.
Most often, such a nuisance is faced by people who lead an active lifestyle, which involves playing sports, countryside holidays in the lap of nature and regular travel along difficult routes.
People working in difficult conditions are also at risk and often experience pain in the elbow joint.
The main causes of pain in the elbow joint
The elbow joint is covered with a synovial membrane and consists of three types of bones (ulna, radius and shoulder), the simple joints of which are interconnected by a common articular bag. It is fixed by ligaments, the functions of which are to organize the correct direction of the elbow. The range of possible movements of the elbow joint is increased due to the combination of bone joints (humoulnar, humeroradial and proximal radioulnar), which differ in functionality and structure.
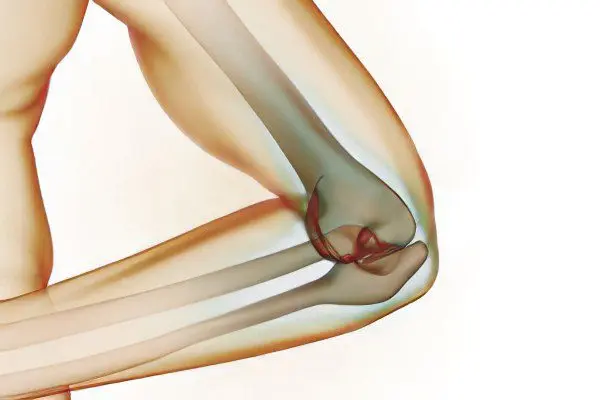
Near this joint are various anatomical connections:
muscle tissue;
nerve trunks;
tendons;
vessels, etc.
The cause of pain can be a banal fall, during which a person gets a bruise of the elbow joint. With such an injury, serious diseases (such as a fracture or fracture of a bone) are often detected, since this joint is very sensitive to any physical or mechanical impact.
The reasons for the development of pain in the elbow joint include the following:
inflammatory processes caused by serious diseases (arthritis, gout, osteochondrosis, etc.);
tendon rupture;
dislocation of the elbow joint;
lifting weights, against the background of which overload occurs, etc.
Diseases that cause pain in the elbow joint

Very often, pain in the elbow joint occurs against the background of the development of various diseases:
External and internal epicondylitis. With internal epicondylitis, the patient experiences pain even with a slight physical impact on the area of the elbow joint. With external epicondylitis, patients develop an inflammatory process in the tendons of the muscles, through which the bones are fixed. In this category of patients, pain occurs against the background of any physical load exerted on the elbow joint, especially during its flexion and extension.
Bursitis. With the development of this disease, patients experience inflammation of the articular bag, which is located at the junction of the three bones of the elbow joint. The appearance of bursitis is often preceded by various fall injuries, bruises, etc. At the stage of active development of bursitis, a rounded neoplasm is visually determined in the patient in the region of the olecranon, when exposed to which the person begins to experience pain.
Inflammatory diseases, tumors, osteoarthritis, chondrocalcidosis and tendonitis. These diseases are always accompanied by pain syndrome, which is removed by traditional medicines.
Synovial chondromatosis or osteochondritis dissecans. Against the background of the development of these diseases, movable bone-cartilaginous or bone bodies can be found inside the elbow joint. They are absolutely free to move around the joint cavity.
Neurotrophic arthropathy Charcot or hemophilia. These diseases are quite rare, but their main symptoms include severe pain.
diffuse fasciitis. During the progression of this disease in patients, in addition to the pain syndrome, there is a violation of the mobility of the elbow joint. The main symptoms of this disease include changes that occur with the skin in the region of the inner surface of the shoulders and forearms.
Infringement of the nerve bases (often observed with intervertebral hernia or with osteochondrosis). Almost all patients who have been diagnosed with nerve root entrapment have impaired mobility of the elbow joint. This condition can be caused by biceps atrophy and requires long-term treatment.
Elbow dislocations (rear, side and front). A dislocation can be the result of any trauma: a fall, a bruise, a blow. Sometimes in patients (with dislocations) fractures are detected, in the treatment of which plaster is applied for a certain time, and painkillers are prescribed. With severe injuries to the elbow joint, patients may experience tendon ruptures, due to which the biceps brachii cannot function normally.
Diagnostics

The appearance of pain in the elbow joint should alert the person. Pain can be a characteristic symptom of various diseases, which can be identified by a highly qualified specialist after serious diagnostic measures.
If the patient does not know who to turn to for help, he can go to a medical institution to his local doctor, who, after an examination, will redirect him to a narrow specialist:
rheumatologist (reveals various rheumatic lesions);
traumatologist (deals with injuries, fractures, sprains, dislocations, bruises);
neurologist (treats various nervous conditions, muscle lesions and other diseases of the nervous system).
The patient’s appointment begins with a personal examination (the doctor necessarily palpates the area of the elbow joint), after which the specialist begins to collect an anamnesis of the disease.
Before making a diagnosis, the patient is assigned an additional hardware examination:
ultrasound examination of the elbow joints;
X-ray
CT scan;
arthroscopy;
magnetic resonance imaging, etc.
Without fail, the patient is sent to the laboratory, where he will have to pass the following tests:
clinical blood test;
general urine analysis;
blood chemistry.
The results of the tests will reveal such dangerous diseases as gout, rheumatoid arthritis, etc. If the doctor has doubts about the diagnosis, he can prescribe a surgical procedure for his patient, during which a puncture will be taken. After assessing its contents, it will be possible to determine whether there are degenerative changes in the cartilage and select the most effective treatment method.
Treatment of pain in the elbow joint
Due to the fact that when contacting any of the specialists (traumatologist, rheumatologist or neurologist), patients experience severe pain, they are primarily prescribed:
painkillers;
corticosteroids;
After the patient has been relieved of the pain syndrome, the specialist begins to treat the disease, which was diagnosed during a comprehensive examination. In the treatment of diseases in which inflammation of the joints occurs, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs. Since all modern medicines have both positive and negative effects, the doctor prescribes them individually, taking into account all the characteristics of the patient’s body.
In the case when the patient has a number of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the attending physician replaces tablet preparations with injections. Most often, patients are given injections with hyaluronic acid, which is a substance produced by healthy joints.
A great effect in the treatment of diseases of the elbow joint is achieved after a course of physiotherapy procedures. Depending on the type of disease and its degree of development, patients may be prescribed:
magnetotherapy;
electrophoresis;
paraffin applications;
barotherapy;
mud wraps;
ozokerite, etc.
In most cases, patients are prescribed a course of physiotherapy procedures, which can consist of at least 10 sessions. Sometimes physiotherapists develop individual programs for patients, taking into account their general condition and tolerance of certain medications. A good effect can be achieved by using therapeutic heat and cold, as well as massage. The use of cold and hot compresses will restore the mobility of the elbow joint, as well as save the patient from pain.
Proper application of heat and cold will have a positive effect on the elbow joint and:
relieve puffiness;
reduce the inflammatory process;
relax muscles;
increase blood circulation, etc.
When undergoing medical therapy, each patient should regularly exercise the elbow joint. Correctly done exercises will gradually increase the strength of the joint and its flexibility.
Regular physical activity will be of great help to patients:
significantly reduce pain;
reduce fatigue;
improve the general condition of the body;
will keep the muscles in good shape, etc.









