Contents
Otosclerosis of the ear is a pathology in which there is an overgrowth of tissues connecting the inner and middle ear. As statistics show, women most often suffer from pathology. They account for up to 85% of all cases. Overall, otosclerosis is diagnosed in 1% of the population.
Pathology develops slowly. The average age of the patients is 20-35 years. The defeat is predominantly unilateral. The second ear is involved in the pathological process after several months or even years.
Otosclerosis – what is it?
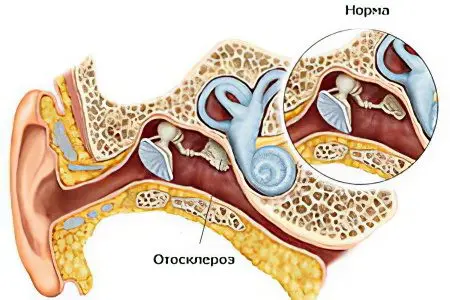
Otosclerosis – this is a lesion of the bone capsule of the labyrinth of the inner ear, during which the tissues undergo dystrophic changes. Over time, the stirrup loses its natural mobility, the patient develops hearing loss. According to ICD 10, otosclerosis is assigned the code H80.
In addition to damage to the tissues of the ear, internal organs and their systems can also be affected. The pathological process often involves the vegetative-vascular and neuroendocrine systems, as well as the musculoskeletal system. This leads to a variety of symptoms.
According to the International Union of Otolaryngologists, otosclerosis progresses in pregnant women. If the patient bears the first child, then the course of the disease worsens in 30% of future women in labor, during the second pregnancy this figure increases to 50%, and during the third pregnancy – up to 80%.
Predisposing factors
The risk of developing pathology increases as a result of exposure to the body of the following factors:
Hereditary predisposition.
Disorders in the endocrine system.
Failure in the metabolism of phosphorus and calcium.
Pregnancy and childbirth.
Deficiency in the body of magnesium and fluorine.
Transferred infectious diseases.
Severe intoxication of the body.
Diseases of the somatic sphere.
Received injuries of the inner ear.
Causes of otosclerosis
Causes that lead to the development of otosclerosis of the ear:
Hereditary predisposition. Violations in the growth and functioning of the tissues of the inner ear occur in close blood relatives in 40% of cases. Most of these patients suffer not only from damage to the middle and inner ear, but also from diseases of the joints, disorders in the thyroid gland, etc. Therefore, scientists suggest that the inferiority of the development of connective tissue is a consequence of genetic disorders that are inherited.
Transferred infectious diseases. They are especially dangerous for people who are prone to deafness at the genetic level. Most often, otosclerosis in such patients develops after measles.
Belonging to the female gender. It has been experimentally proved that excessive growth of bone tissue in the ear is observed in women during the period of hormonal instability. Pathology can manifest during puberty, after the first menstruation, during pregnancy, after childbirth, during menopause. About 80% of all patients are women. Tumors of the endocrine glands can provoke otosclerosis of the ear.
Ear injury. In terms of the development of otosclerosis, acoustic injuries are especially dangerous. Moreover, the duration of the sound effect on the structures of the ear does not matter.
Disturbance of blood circulation. If the internal structures of the ear do not receive normal nutrition, then this leads to the development of a pathological process.
Inflammation of the internal structures of the ear. Chronic sluggish processes are especially dangerous in terms of the development of the disease. The structures of the ear are constantly injured, which leads to the replacement of normal tissue with scar tissue.
Symptoms of otosclerosis

Otosclerosis can cause complete deafness, so it is important to know its symptoms and be able to distinguish them in time.
The main manifestations of pathology include:
Background tinnitus.
Dizziness that occurs with a sharp turn of the head.
Nausea and vomiting.
Ear pain. It is pressing, concentrated in the region of the mastoid process.
Ear congestion, hearing loss.
Heightened perception of high frequency sounds. On the contrary, a person hears sounds of low frequency worse.
Paracusis of Willis. A person with otosclerosis seems to improve his hearing when the environment is noisy.
Weber’s paracusis. Hearing loss occurs when chewing or while walking, in any situation where there is movement of soft tissues. This is due to irritation of the cochlea of the inner ear.
As the pathology progresses, a person ceases to perceive not only low, but also high sounds.
Manifestations of a neurasthenic symptom. The patient has headaches, he becomes apathetic, he is tormented by insomnia. During the day, a person looks tired, memory and attention are reduced.
Toynbee’s sign. It is manifested by an unclear perception of speech when several people are talking at once.
If a person does not receive the necessary treatment, then the disease progresses, its symptoms increase all the time. In some patients, one ear is involved in the pathological process, while in others, two organs of hearing are involved at once.
Classification
There are several classifications of otosclerosis.
Depending on the pathological changes in the inner and middle ear, there are:
Fenestrial (stapedial) otosclerosis. Pathological proliferation of tissues occurs in the region of the windows of the labyrinth. The ear ceases to perform its sound-conducting function normally. This form of the disease has the most favorable prognosis. If treatment is carried out on time (an operation is necessary), then the likelihood of a full restoration of hearing is high.
cochlear otosclerosis. The affected areas are concentrated in the area of the cochlear capsule. With this type of disease, the sound-conducting function of the inner ear worsens. Even surgery does not completely restore hearing.
Mixed form of pathology. The patient decreases not only the function of perception, but also the conduction of sound through the structures of the inner ear. Timely therapy allows you to restore hearing to complete hearing.
Depending on the rate of development of otosclerosis, its varieties are distinguished, such as:
Transient form of the disease. It is diagnosed in 11% of all patients.
slow form of the disease. It occurs most often and occurs in 68% of cases.
Spasmodic form of pathology. It is diagnosed in 21% of patients.
Otosclerosis goes through 2 stages:
Otospongiose. This is the active stage of the pathology.
Sclerotic. This stage is characterized by low activity of the pathological process.
The processes of softening and sclerosis of the bone tissue of the ear alternate all the time.
Diagnostics
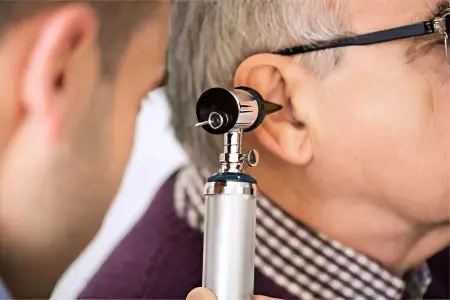
Diagnosis of otosclerosis is reduced to the following steps:
Taking an anamnesis, listening to the patient’s complaints. The person points to noise in the ears and in the head, to a feeling of pressure in the ear canal, etc.
Inspection of the tympanic membrane. During its implementation, the doctor does not visualize any pathological changes.
Using a tuning fork to determine hearing acuity.
Carrying out audiometry. This method allows you to measure the acuity of hearing, to determine the sensitivity of the hearing aid to sounds of different frequencies. During the procedure, the patient is put on headphones that give various signals. When a person hears a sound, he must press a button. This allows you to make a graph of hearing acuity (audiogram). In a patient with otosclerosis, there will be a violation of the air conduction of sound along the ossicular chain. At the same time, the function of sound perception by auditory receptors remains intact (bone conduction of sound).
Tympanometry. This study is aimed at determining the mobility of the tympanic membrane, assessing the conduction of sound by the auditory ossicles, and determining the level of pressure in the middle ear. Most often, no abnormalities are found in a patient with otosclerosis. Therefore, tympanometry is performed only if other diseases of the middle ear are suspected.
Ultrasound. This study makes it possible to distinguish otosclerosis from cochlear neuritis, since these pathologies give similar symptoms. However, with cochlear neuritis, the conductivity of ultrasonic waves through the tissues deteriorates greatly.
Vestibulometry, otolithometry, stabilography. These studies are aimed at assessing the patient’s vestibular function.
acoustic reflexes. They are evaluated by registering changes in the resistance of the elements of the outer and middle ear when exposed to high-frequency sounds. As a rule, acoustic reflexes are absent in patients with otosclerosis.
To clarify the diagnosis, the patient may need to consult an audiologist and a surgeon.
Treatment otosclerosis
Therapy for the patient is selected depending on the form of the disease and on the stage of its development. If the pathology was detected at a time when it had just begun to develop, then the prognosis is as favorable as possible and hearing loss develops very rarely. Moreover, only conservative methods of therapy can be dispensed with.
Medication Therapy
If the patient is diagnosed with an active or cochlear form of otosclerosis, then the disease can be dealt with by conservative methods.
The drugs are prescribed for 3 months. Then they take a break for the same period. As a rule, patients are required to complete at least 2 courses. Most often it is not possible to get by with drugs alone, since the drugs do not allow you to restore the function of hearing, but make it possible not to lose it, preventing the growth of otosclerosis foci. This is very important when the disease is in the active phase and it is not possible to perform an operation.
Surgery
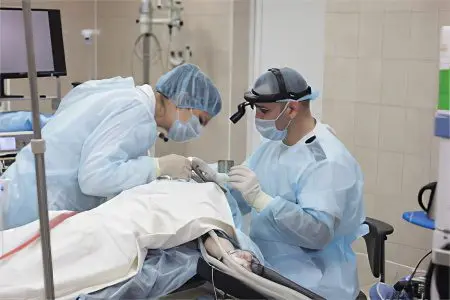
If the disease progresses, or the doctor believes that the drug correction will not bring an effect, then the patient is sent for surgery. It is not prescribed for patients with cochlear otosclerosis, since surgical intervention will not bring results. Such patients are shown medical correction and the use of a hearing aid.
Surgery for otosclerosis allows you to restore normal sound transmission in the middle ear.
Surgery can be of three types:
Stapedoplasty. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and involves the removal of the legs of the stirrup. They are replaced with a prosthesis that works like a piston. The prosthesis is made from the patient’s own tissue, or from titanium, Teflon, or ceramic. The operation allows you to achieve the desired results, since the mobility of the auditory ossicles is normalized. The effect is absent only in 1% of patients. First, the procedure is carried out on one ear. If everything goes well, then six months later, surgical intervention on the second ear is indicated.
Fenestration of the labyrinth. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, although local anesthesia is sometimes done. Control is carried out using a microscope. The doctor makes a new foramen ovale in the inner ear. It is located in the lateral semicircular canal. This procedure has been used less and less in recent years.
Mobilization stirrups. The operation allows you to restore the mobility of the stirrup in the patient. For this, bone adhesions are removed from the auditory ossicle, due to which it begins to work as before. However, after a few years, the hearing loss will return as the bone tissue grows back. This operation has been practiced less and less in recent years.
Physiotherapy
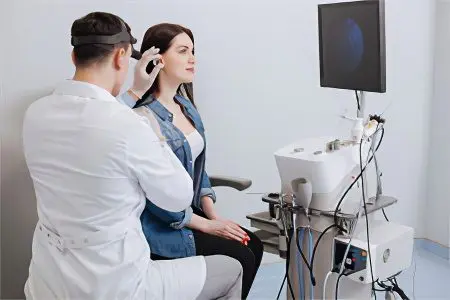
Physiotherapy can improve the effect of the treatment. Most often, experts recommend that patients with otosclerosis undergo electrophoresis on the mastoid region and darsonvalization.
Physiotherapeutic procedures increase blood flow in the affected area, due to which the nutrition of nerve fibers improves, the patient’s well-being stabilizes.
A patient with otosclerosis is prescribed:
Electrophoresis with Dibazol, nicotinic acid, Papaverine, Drotaverine.
Transorbital galvanization. This procedure improves tissue nutrition by increasing blood flow.
Darsonvalization. During the procedure, nerve fibers are irritated, which increases their excitability and improves microcirculation in tissues.
Diadynamotherapy. The procedure stimulates the conduction of impulses to the auditory nerve, normalizes the blood supply to the tissues.
Amplipulse therapy. The procedure has a neurostimulating effect.
Brain galvanization. This procedure has a calming effect, reduces his excessive excitability.









