No living organism can ensure its vital activity (homeostasis) and regeneration of damaged cells without energy supply. Energy is released as a result of redox reactions, that is, reactions of addition or transfer of electrons. The vital activity of all living beings depends on the intensity and speed of these reactions.
What is OVP?

In the world that surrounds us, we do not see this, but there is a continuous exchange of electrons that occurs between substances in the air, on earth, in water and in our bodies. This phenomenon is known as ion exchange.
In an attempt to achieve a state of stability, substances that lack electrons are desperately looking for electrons wherever they can be: these substances are called oxidizing agents. In contrast, substances that have an excess of electrons are able to donate their extra electrons: these substances are called reducing agents or antioxidants.
Redox potential (or ORP) is a measurement that indicates the degree to which a substance is able to oxidize or reduce another substance. You can also find the definition: “ORP is a measure of the purity of water and its ability to destroy pollutants.” The value range is -2000 to +2000, and the units are “mV” (millivolts).
Positive ORP indicates that the substance is an oxidizing agent. The higher the value, the more it oxidizes. Thus, a substance with an ORP reading of +400 mV oxidizes 4 times more than a substance with an ORP reading of +100 mV.
Negative ORP indicates that the substance is a reducing agent. The lower the value, the more antioxidants. Thus, a substance with an ORP reading of -400 mV is 4 times more antioxidant than a substance with an ORP reading of -100 mV.
Almost all water available to us, including tap water and bottled water, are oxidizers because their ORP value is positive. For comparison, we can cite the ORP values of drinking water, it ranges from +200 to +300 mV, and sometimes even reaches +550 mV.
ORP of the human body, measured on a platinum electrode, during the experiment ranged from -100 mV (millivolts) to -200 mV. This is an indicator of the restored state of the liquid medium.
It is also worth noting that a large amount of pollutants in the water leads to less dissolved oxygen, since living organisms consume oxygen, their internal environment has a negative ORP value. The higher the ORP level, the greater the water’s ability to destroy foreign contaminants such as microbes or carbon contaminants.
Since all important systems consist of molecular structures with charges of different polarity, such complex processes depend on the activity of electrons as:
Energy storage;
Replication and inheritance of species traits;
Power consumption;
Selectivity and control over the biochemical processes occurring in the body;
The functioning of all enzymatic systems of the body.
Violation of the balance of the processes of oxidation and reduction, according to scientific research, leads to the emergence and further development of diseases. Water with a positive ORP enters the body and exposes its tissues to oxidative damage. This happens when water molecules steal electrons from cells that have a negative charge. The destruction of cell membranes, nucleic acids, cell organelles leads to the fact that organs and tissues lose their vital functions, and the human body ages and wears out.
This negative process can be slowed down and even stopped by drinking water (and cooking food with it) with a negative ORP. Such a liquid has protective and restorative properties, which is confirmed by scientific research by Russian and foreign scientists. If the fluid entering the body has a positive charge, it has to be converted through the electrical potential of cell membranes.
Even better, if the incoming fluid has an ORP lower than that of a person. Then the potential difference becomes a kind of reserve for nourishing the body and protecting it from an unfavorable external environment.
The destruction of the redox system of the body is facilitated by such negative factors as:
Poor quality drinking water;
Unbalanced diet:
Psycho-emotional overload, stress;
Alcoholism, addiction to smoking;
Exposure to toxins from the environment;
Frequent illnesses;
Drug abuse.
If oxidative reactions regularly prevail over reducing ones, sooner or later the body’s defenses reach the limit, it is no longer able to resist diseases. Antioxidants, their antioxidant effect, are called upon to slow down this process.
What is the pH of water?
pH is a measurement of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It has a value on a scale of 0 to 14, where 7 is neutral, less than 7 is more acidic, and more than 7 is more alkaline. The closer you move to 0, the more acidic the solution, and the closer you move to 14, the more alkaline the solution.
pH is often depicted in a graphical color scale, as shown below:
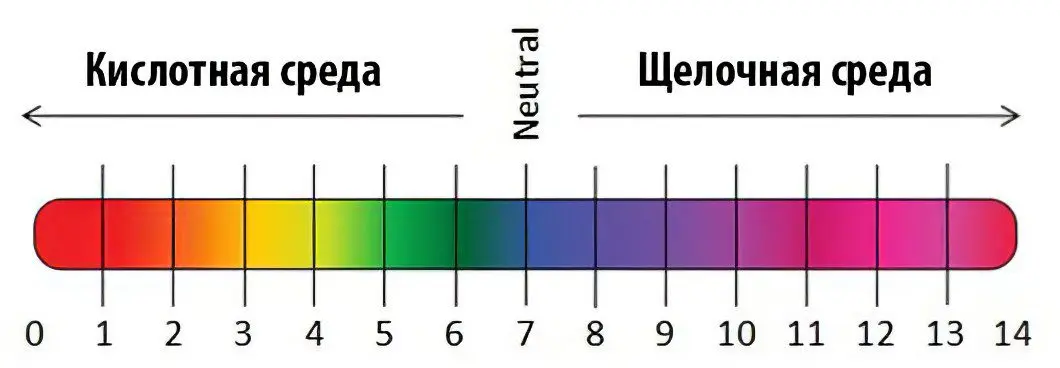
When it comes to water, its pH value is directly related to the ratio of positively charged hydrogen ions [H+] and negatively charged hydroxyl ions [OH—].
When water has the same concentration of H ions+ and OH—, it is considered neutral (pH = 7)
When water has a high concentration of H ions+, it is considered acidic (pH
When water has a high concentration of OH—, it is considered alkaline (pH > 7)
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale, which means that when pH increases or decreases by one unit, you change the concentration of H ions.+ 10 times. For example, a pH 8,0 solution is 10 times more alkaline than a pH 7,0 solution. A pH 9,0 solution is 100 times more alkaline than a pH 7,0 solution.
With increased acidity (relative to the norm), they speak of acidosis, and with increased alkalinity, they speak of alkalosis. Such conditions are dangerous for the body and indicate health problems.
[Video] Dr. Berg – a detailed scientific overview of what Ph. What affects the excess of acid and alkali in the body?









