Contents
The warty euonymus is widespread in Our Country. It is considered the most winter-hardy of the species and is planted even in regions where other members of the genus suffer from frost. The photo and description of the warty euonymus in autumn explain the reasons for its popularity as an ornamental plant. Ease of care and undemanding to growing conditions have made the culture indispensable in park plantings.

Description of the warty euonymus
Euonymus warty, in Latin – Euonymus verrucosus, a species belonging to the genus Euonymus, is widespread in temperate climates. Under natural conditions, it grows in rare deciduous and coniferous forests, oak forests, in clearings throughout the European part of Our Country. The species is distributed from Narva in the north to the Krasnodar Territory in the south.
The warty euonymus is a deciduous tree up to 6 m high, but more often it is an upright shrub about 2 m (rarely – 3,5 m). Under natural conditions, the plant lives up to 80 years, as an ornamental culture – no more than 50.
The warty euonymus develops slowly, it even retains cotyledons for up to three years in sunny areas, under undergrowth – about 7-8. The species gives the main increase in the first 15 years, when it stretches up to one and a half meters. Then the increase in size is extremely slow, and after 30 it stops.
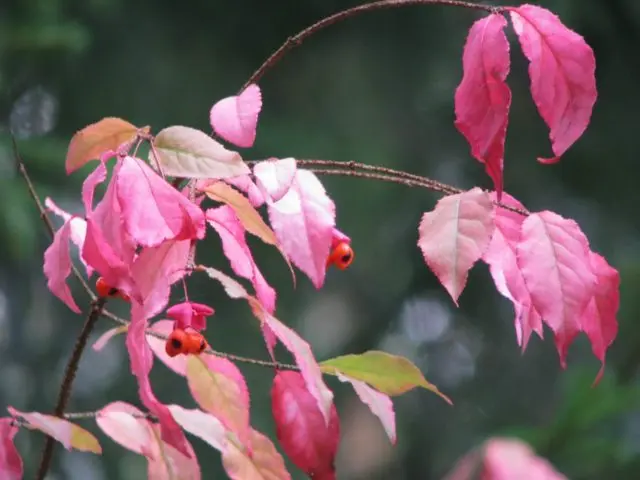
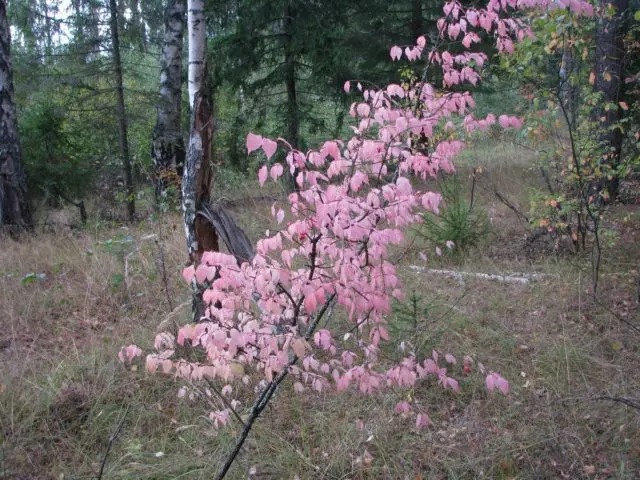
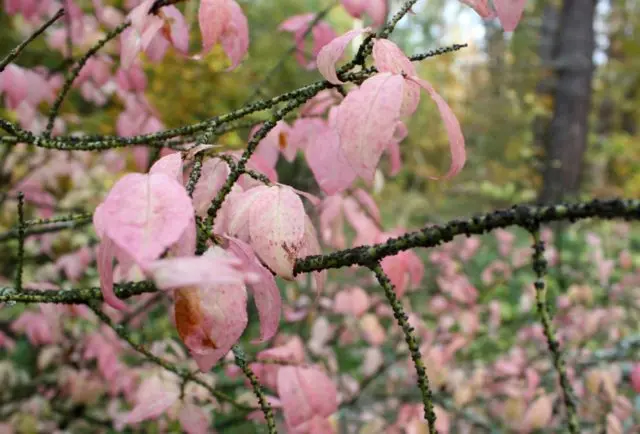
The leaves are opposite, elliptical or oblong-ovate, light green, 2 to 6 cm long, with a pointed apex. The edge of the plate is finely serrate, the surface is smooth, sometimes pubescent along the veins. With sufficient lighting in the fall, the crown of the warty euonymus changes color to one of the shades of pink.

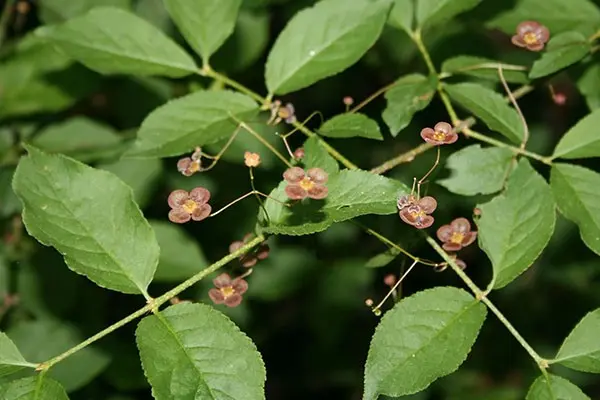
Small brownish-green flowers with four petals are collected 3-7 pieces in panicles that emerge from the leaf axils. The buds open in May, at the same time as the lily of the valley. Flowering lasts a little less than a month, usually 27 days. The warty euonymus is pollinated mostly by flower flies, they are attracted by the unpleasant smell of the plant, which for some reason is called mouse.

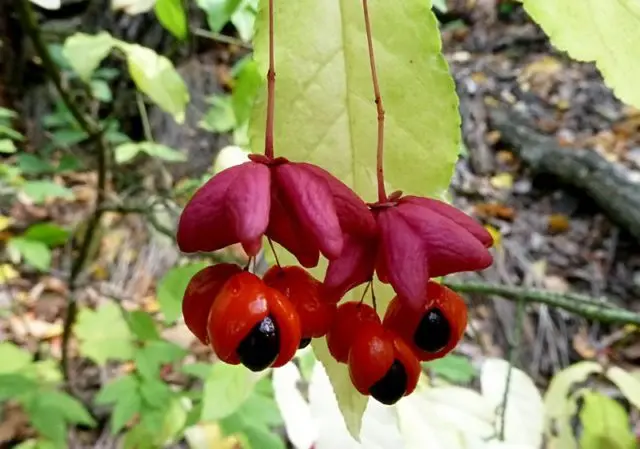
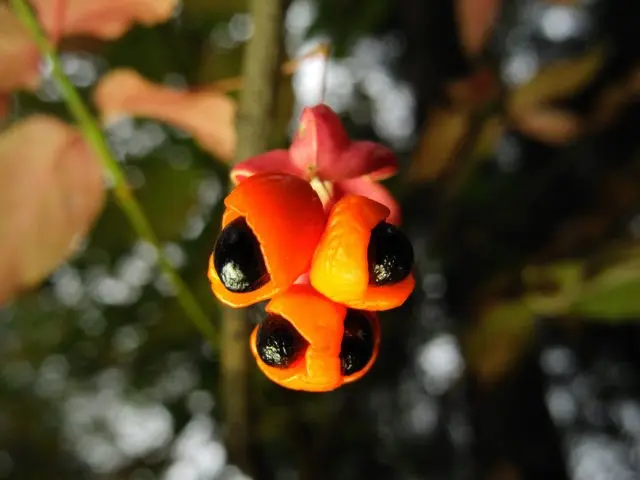
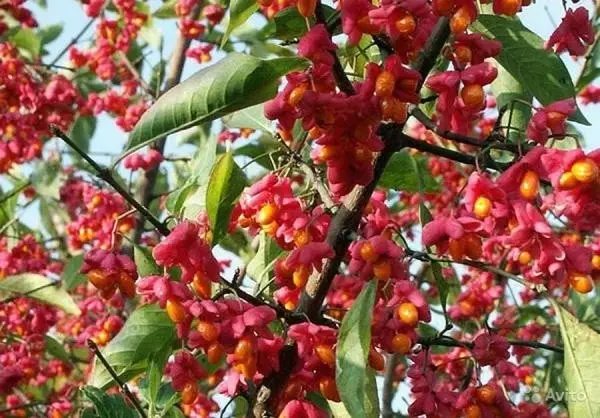
The fruits are pink boxes with a diameter of 8-12 mm in the form of an oblate ball. Black seeds up to 3 mm long, reaching maturity in late August or September, fall off after 7-10 days. The seeds are red, the berries are half surrounded. Fruiting begins at the age of six. The ovary gives only 1-3% of the flowers.

The warty euonymus got its name due to shoots covered with growths similar to lentils. This is a loose tissue that allows branches to breathe, the bark of which has corked due to the high content of gutta-percha. We can say that this species lives precisely thanks to the “warts”. Young shoots are very thin, green or olive. Over time, they darken, crack and become almost black.
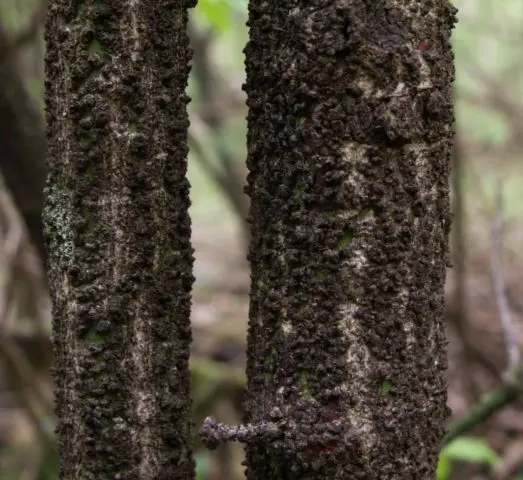

The roots of the warty euonymus are superficial, fibrous, well developed.
Use of warty euonymus
The wood of the warty euonymus is yellow, hard, formerly used for the manufacture of spindles and shuttles. Today, combs, musical instruments, hairpins, knitting needles are made from it. The fatty oil extracted from the seeds is used in soap making. A brown and yellow natural dye is prepared from the fruit wings.
The use of warty euonymus in medicine
Leaves, bark, branches, seeds, horses and fruits have medicinal properties. They are dried in warm rooms protected from the sun with good ventilation. Leaves are harvested during the flowering period, seeds – at a time when they are already ripe, but have not yet had time to fall to the ground.

The healing properties of the warty euonymus are due to the chemical composition, among other ingredients stand out:
- glycosides that regulate cardiac activity;
- carbohydrates;
- pectin;
- organic acids;
- vitamin C;
- alkaloids;
- tannins;
- steroids;
- flavonoids;
- anthraglycosides, which have a laxative effect.

Preparations, in the manufacture of which the warty euonymus is used, lotions, decoctions, infusions on alcohol help in the treatment of:
- headaches;
- edema;
- liver;
- nervous disorders;
- hypertension;
- impotence;
- to normalize the heart rhythm;
- bowel disorders.
What is dangerous euonymus
The most poisonous are the berries of the warty euonymus. They have, though not too pleasant, but a sweetish taste, besides they look elegant, therefore they attract children. An adult is unlikely to eat so many fruits to be seriously poisoned, but for a fragile growing organism, poison can be really dangerous.

Even an overdose of euonymus warty preparations can cause:
- heart rhythm disorder;
- nausea and vomiting;
- intestinal inflammation and diarrhea;
- convulsions, chills.
First aid for poisoning – gastric lavage, enema, intake of sorbents. The patient should remain at rest, his cardiac activity should be monitored.
The use of rubber from the warty euonymus
The roots, bark and leaves of Euonymus contain gutta-percha, the chemical composition of which is the same as rubber. Most of the valuable technical substance can be obtained from the Warty and European species. In the first half of the last century, bush plantations were even established to extract gutta-percha in the northern latitudes.

But with the development of the chemical industry and the advent of cheap artificial polymers, the need for them has disappeared. Deciduous euonymus grows slowly, and most gutta-percha is contained in the roots, so today it is unprofitable to extract it from plants.
Use as an ornamental plant
Warty euonymus – ornamental trees and shrubs, which are widely used in the creation of hedges, decorating fences and outbuildings. They are planted on the steep slopes of ravines and along the steep banks of water bodies to prevent soil erosion. In the landscaping of parks and forest parks, the warty euonymus often acts as an undergrowth.
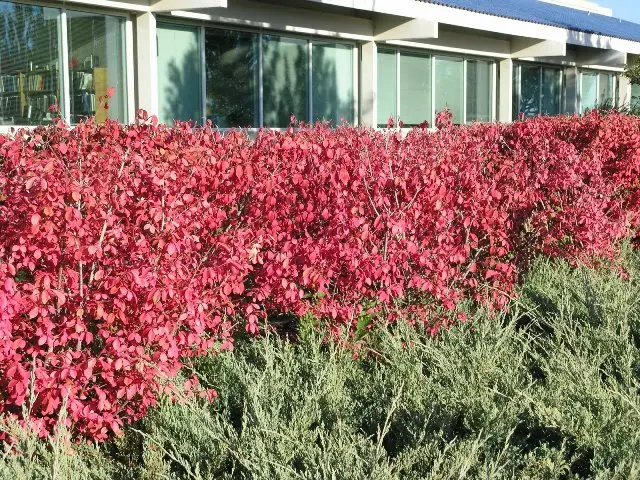

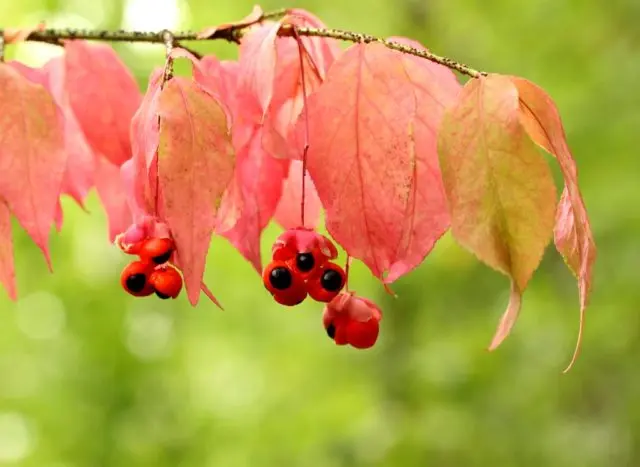
The plant is not of great decorative value in spring and summer. Although the bushes look attractive, they cannot compete with other crops, including evergreen species. But in autumn everything changes. As you can see in the photo, the warty euonymus is dressed in pink foliage, the same color fruits with red seedlings hang on long pedicels. The plant looks fantastic.
You can plant warty euonymus as part of large and small landscape groups or as a tapeworm (single focal plant). Recently, automnalia – gardens of autumn flowers – have come into fashion. There, deciduous spindle trees, including warty, are more than appropriate.
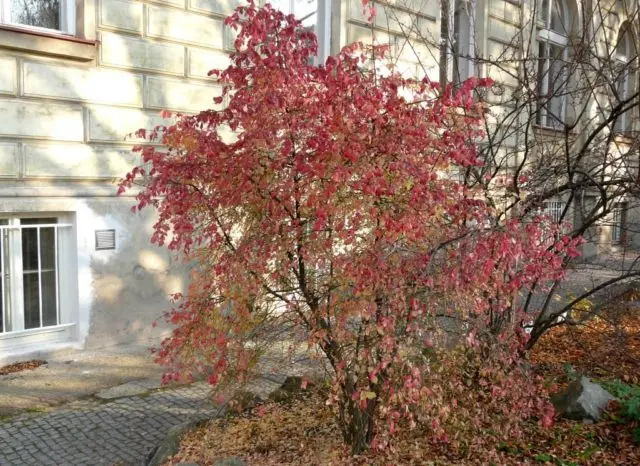

Planting and caring for warty euonymus
Euonymus is an easy-to-care culture. But different species may have different requirements for growing conditions. The warty euonymus, in comparison with others, is more demanding on soil fertility. Under natural conditions, it most often grows as an undergrowth of deciduous forests, on loose, humus-rich soils, neutral or slightly alkaline.
Rules of landing
The warty euonymus is planted in the south in early autumn, in other regions – in the spring, when the snow melts and the soil warms up a little. The place should be chosen dry, the culture does not tolerate soiling of the roots. Sand, peat or compost should be added to dense soil, acidic soil is improved with chalk or lime. The warty euonymus grows best on higher ground under the protection of larger trees.
On well-permeable, moderately fertile soils, it is enough to dig a planting hole, 2 times the volume of the root system, cover it with earth, compact, and water it abundantly. If groundwater comes close, or the landing site is prone to wetting, a drainage layer of 15-20 cm should be arranged from broken red brick, expanded clay, gravel.

In extremely poor soils, sandstones add a handful of complex fertilizers. Fat chernozems are brought in accordance with the requirements of warty euonymus with the help of sand. The plant takes root well, but does not like transplants, especially in adulthood. It is necessary to immediately take into account the size of the deciduous spindle tree in 10-15 years.
When creating a hedge, a shallow ditch is made instead of holes. After planting and watering, the trunk circle is mulched with low-lying peat, well-rotted sawdust or tyrsa can be used.
Watering and top dressing
The warty euonymus tolerates overdrying of the soil well. It should be specially watered only in the driest summer in the absence of rain. This species has a slightly higher nutritional requirement than the others. It responds well to spring fertilizer with a mineral complex with a high nitrogen content and autumn phosphorus-potassium.

Shade tolerance of the warty euonymus
In relation to light, the warty euonymus can be called a culture that does not like extremes. If you plant it in a deaf shade, it will not die, just the shoots will stretch out and become thinner, in the fall the leaves will not turn pink, but simply turn brown. Flowering will also be scarce, and since only 1-3% of berries are tied, they will not be able to serve as a decoration for the bush.
In strong sun, the distance in the internodes will decrease, the warty euonymus will become compact, but the foliage will burn, which will also not add decorative effect. The best place for the plant should resemble the conditions in the wild – light partial shade or good lighting part of the day, preferably in the morning.

Trimming
All euonymus well endure pruning. Although deciduous species gain height slowly, side shoots grow well. The warty euonymus does not need special molding. Only frozen, dry, diseased, broken branches and those that are too long or simply spoil the view or block the view of other crops are cut out from him.
If in the landscape group the plants are located close to each other, it is necessary to remove some of the shoots that are not visible from the point of view and come into contact with other trees or shrubs. This will not harm the euonymus, and the composition will become much more attractive, and the neighbors will exchange less diseases and pests.
Since the culture has attractive not only leaves, but also fruits, it is better to do the forming pruning in the fall, after the seeds have fallen.
Preparation for winter
It is believed that warty is the most winter-hardy of spindle trees. Under natural conditions, it grows even in the Leningrad region. It is usually not covered for the winter. An increase in resistance to frost is facilitated by autumn moisture charging and top dressing at the end of the season with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
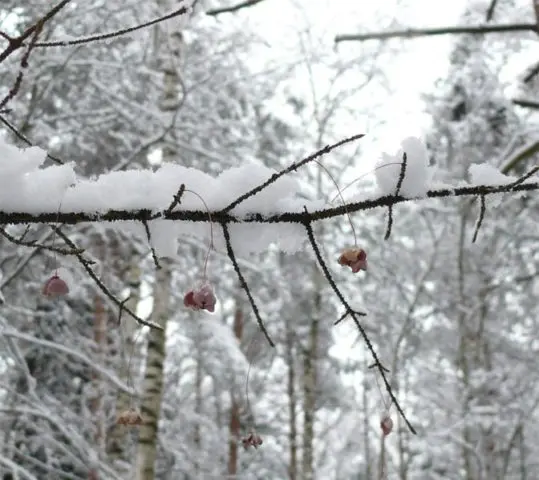

You can protect a crop planted in an open area by covering the bush with a cape made of white agrofiber or lutrastil.
Fruits of the euonymus warty
Berries are the most poisonous part of the warty euonymus, their taste is at least sweetish, but not very pleasant. An adult will not be able to eat enough to get seriously poisoned, and, most likely, get off with vomiting and diarrhea. But the taste of children can be bizarre, some babies gobble up safe, but disgusting, bitter black privet berries on both cheeks. It is the younger generation that needs to be closely monitored, being next to a bush hung with bright red and pink earrings.
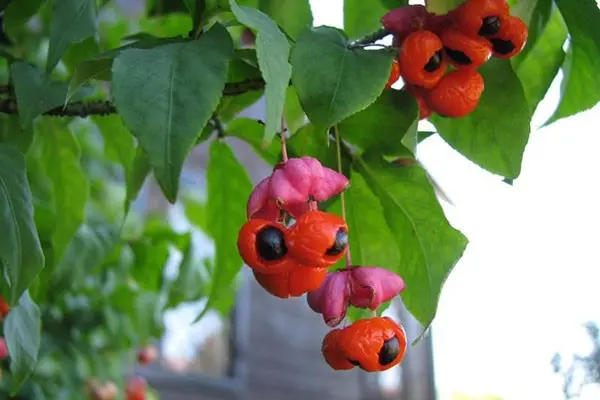

But in the nutrition of birds, the fruits of the euonymus occupy an important place. The berries that ripen in August-September are especially fond of linnet. Passing through the digestive tract of the bird, the seeds increase their germination.
Reproduction
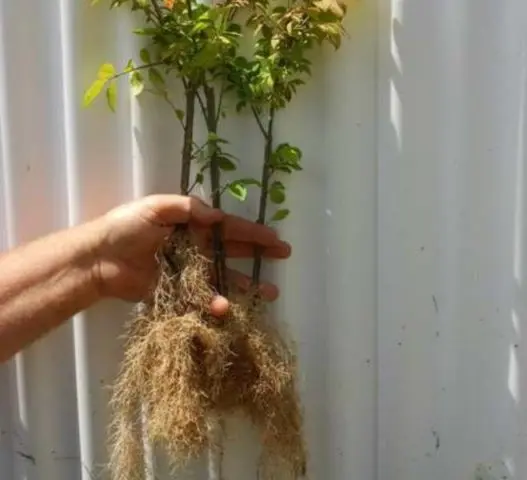
The warty euonymus is best propagated by root offspring, which you just need to plant in spring or autumn.
Layers root well too. In early spring, a branch located near the surface of the ground or inclined to the ground is fixed in a shallow groove and sprinkled with soil. All summer they water a little, and in the fall or at the beginning of the next season they plant them in a permanent place.

Green cuttings cut in June-July are rooted in a peat-sand mixture or perlite. They do not allow the substrate to dry out, and in the fall they are planted in a school or in a permanent place.
The warty euonymus can be propagated by seeds. But they do this only when you need to get a lot of plants. Even nurseries that sell the crop in dozens rather than hundreds of specimens prefer vegetative rather than seed propagation.
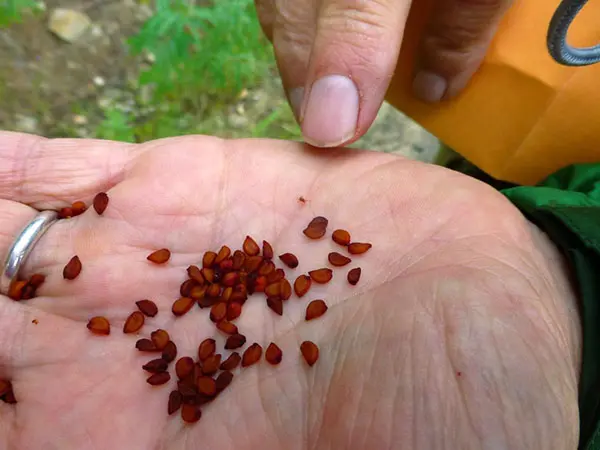

The fastest ornamental plant can be obtained from the offspring. In the next place – layering, they are delayed in development for about a year. Not all cuttings take root, but they give a completely satisfactory result and may even bloom in 2-3 years. Euonymus obtained from seeds is planted in open ground after 2-3 years, and all this time it needs to be kept somewhere and carefully looked after. It will bloom no earlier than in 6 years.
Diseases and pests
Unlike its relatives, the warty euonymus is resistant to the euonymus moth. The following pests pose the greatest danger to the species:
- aphids that destroy flowers, young leaves and shoots;
- spider mite, tightening the reverse side of the leaf with thin threads and sucking the juice out of it;
- weevil eating leaves in spring;
- caterpillars, which the euonymus seems to “pull” onto itself from other crops, including fruit crops;
- euonymus moth eating berries.
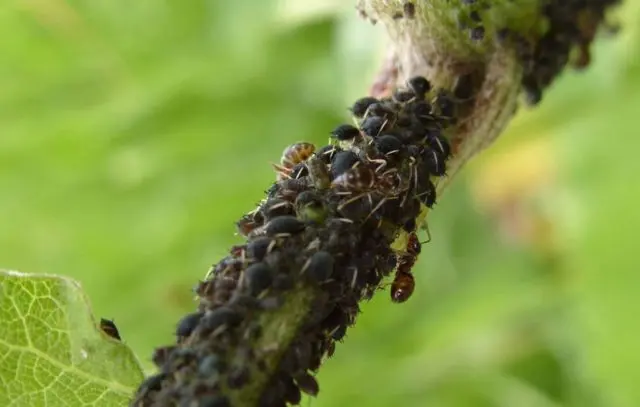

Control pests with appropriate insecticides.
You should pay attention to such diseases of the euonymus:
- viral mosaic, starting with the appearance of yellow spots on the leaves, which deform over time;
- powdery mildew – a fungal disease that manifests itself in the form of a white coating on the vegetative organs;
- spotting – spots first appear on the leaves, then pads or dots with fungal spores;
- necrosis, in which the bark changes color, then cracks, exfoliates, dies.
To date, they have not learned how to treat viruses, and in case of fungal diseases, the bush is treated with fungicides, in advanced cases – three times, with an interval of 2-3 weeks.

Conclusion
Photos and descriptions of the warty euonymus give an idea of the shrub in different periods of the growing season. Its main purpose is to serve as an ornamental plant in private and public gardens, to attract birds to the site. The warty euonymus looks especially beautiful in autumn. Hobbyists will appreciate the bizarre appearance of the plant after leaf fall and before blooming points, when bulging lenticels on the almost black cracked bark are especially noticeable.









