Contents
Oral leukoplakia – this is a pathological area of compaction on the mucous membrane, which is characterized by excessive keratinization. The disease has a chronic course and can malignize, that is, degenerate into a malignant neoplasm.
What is leukoplakia?
Leukoplakia – This is a disease that affects the mucous membranes, causes keratinization of the integumentary epithelium of varying severity. Leukoplakia affects mainly the mucous membranes of the cheeks, especially the corners of the mouth, the lower lip, it also happens on the back or lateral surface of the tongue, the alveolar process and in the region of the floor of the mouth. The surface of the integumentary epithelium is covered with unevenly keratinized scales.
The risk group is mainly people aged 30 years. This disease begins to develop in the area of mucous surfaces, such as the tongue, corner and bottom of the mouth, lower lip, cheeks; in the vagina, on the clitoris and vulva, in the cervix, it occurs, but less often, in the region of the preputial sac and glans penis or in the region of the anus. If leukoplakia begins on the cheeks and tongue, then keratinization occurs along the line of connection of the teeth. Leukoplakia is a consequence of smoking and alcoholism. It provokes a lack of vitamins, and this is accompanied by a sluggish chronic inflammation. It has an immune effect on chronic irritation of the mucous surface. Leukoplakia is divided into different forms.
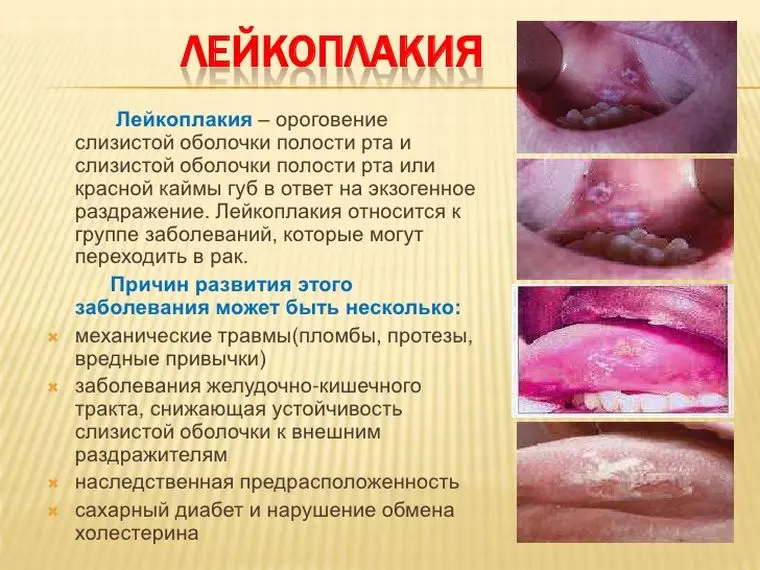
Symptoms of oral leukoplakia
Plaques are formed most often in the corners of the mouth, on the tongue, on the inner surface of the cheeks, on the gums and on the lips. As the pathology progresses, leukoplakia can spread to the organs of the digestive system, to the nasal cavity, to the respiratory organs.
Leukoplakia is not an independent pathology, it indicates that something is wrong in the body. If the doctor has found characteristic rashes on the mucous membrane, it is necessary to begin treatment.
Symptoms of leukoplakia of the oral cavity can be distinguished as follows:
Bleeding of the affected area.
Pain in the area of inflammation.
The appearance of a compaction area.
Rapid increase in leukoplakia in size
The appearance of growths in the form of papillae on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
Peeling of the affected area.
If such symptoms appear, you need to be wary, as they may be signs of the degeneration of leukoplakia.
Causes of oral leukoplakia
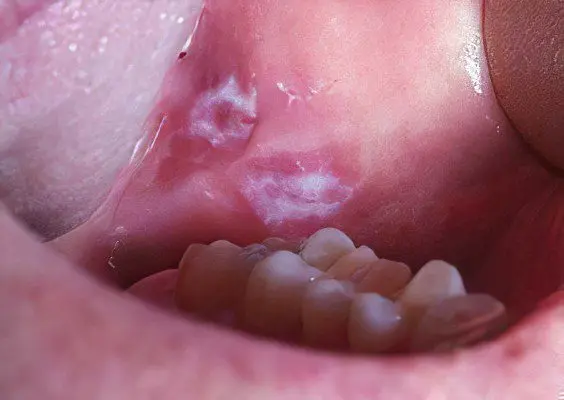
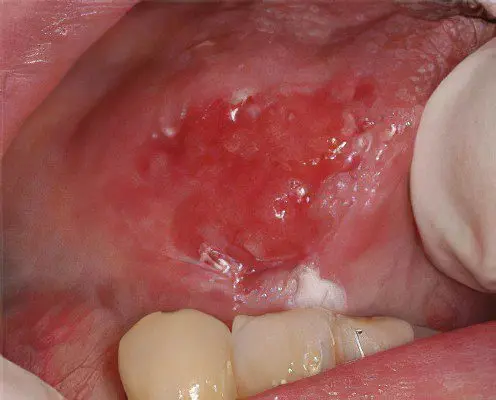
To date, scientists cannot name the exact causes of oral leukoplakia. However, they identified some factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease. The main one is chronic injury to the oral mucosa.
Other reasons include:
Smoking. Harmful is not only the inhalation of smoke from ordinary cigarettes, but also smoking a hookah, chewing tobacco. The toxic substances contained in them lead to the fact that the epithelium does not have time to recover, thereby creating prerequisites for pathological changes in its cells.
Eating very hot or very cold food (drinks). In this regard, spicy, salty and sour dishes are dangerous.
Alcohol abuse.
Oral injuries. A common cause of mechanical damage to the mucous membranes are crowns, fragments of teeth, orthodontic structures, and prostheses.
Influencing the current on the body, in the presence of metal crowns in the mouth.
Work in a harmful enterprise. Contacts with varnishes, resins, aniline dyes and other chemicals negatively affect health.
Hereditary predisposition to leukoplakia.
HIV infection or AIDS stage.
Impact on the body of ultraviolet radiation.
Taking medications.
Deficiency in the body of vitamin A.
Deficiency in the body of iron, potassium and magnesium.
Anemia.
Chronic diseases of the digestive system.
Diabetes.
Diseases of the endocrine system, accompanied by hormonal imbalance.
Types and forms of oral leukoplakia
There are several types of oral leukoplakia:
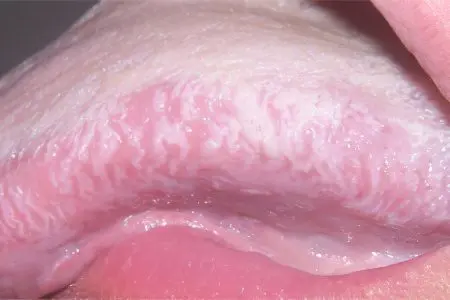
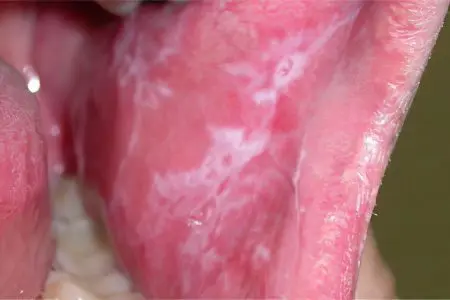
Flat leukoplakia manifests itself in the form of a sharply limited continuous clouding of the shell, sometimes it resembles a film that cannot be torn off. The color of the lesion ranges from pale gray to white, depending on the intensity of keratinization. The surface is rough and dry. The borders of the focus are usually jagged. There are usually no seals at the base of the keratinized areas. In the corners of the mouth along the edges of leukoplakia, slight hyperemia may occur. In the form of folds, leukoplakia is located on the cheeks, and in the form of a wrinkled grayish-white film on the bottom of the oral cavity.
The flat form of the disease basically does not cause any particular complaints in patients, only sometimes there is a feeling of constriction.
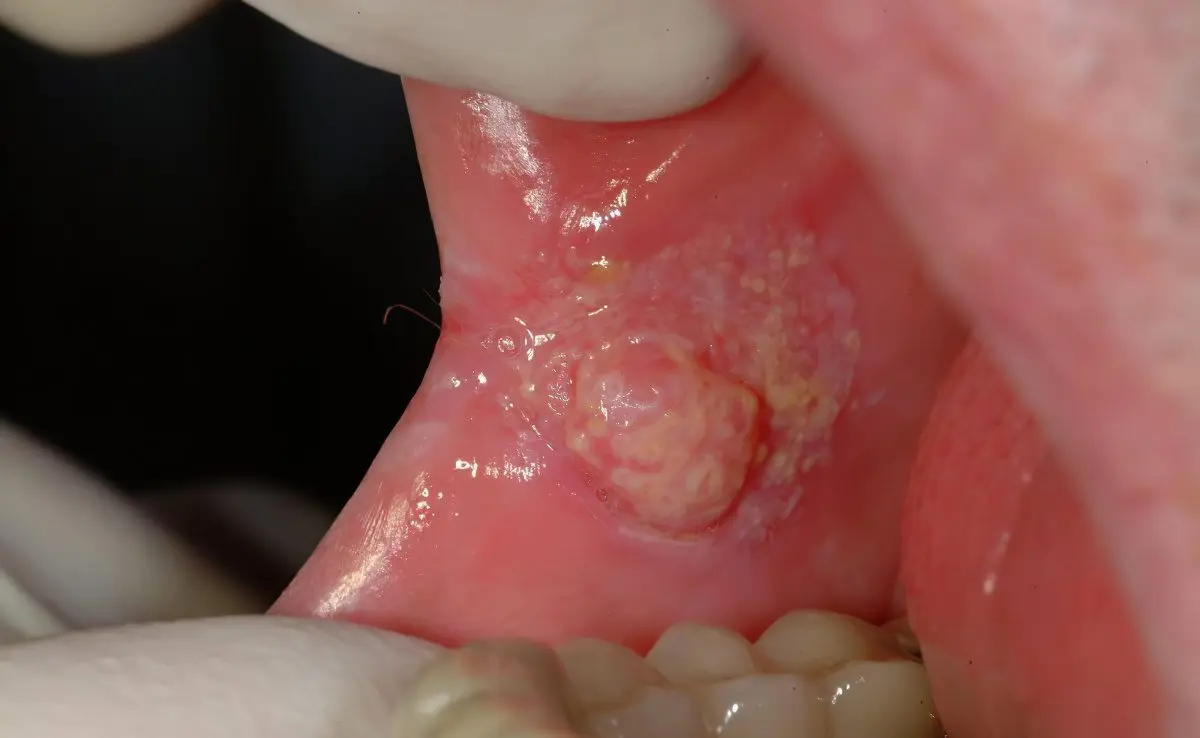
Verrucous leukoplakia manifests itself in the form of a raised milky-white smooth plaque. It may also appear as dense, bumpy, greyish-white, 2–3 mm protruding warty growths, very often in the background of a flat form of leukoplakia.
Erosive leukoplakia (Ilink) causes cracks and erosion, contributes to the development of other forms of the disease. It is formed in the foci of flat or verrucous leukoplakia of various shapes and sizes. This form of the disease causes pain. If left untreated, the defects progress rapidly.
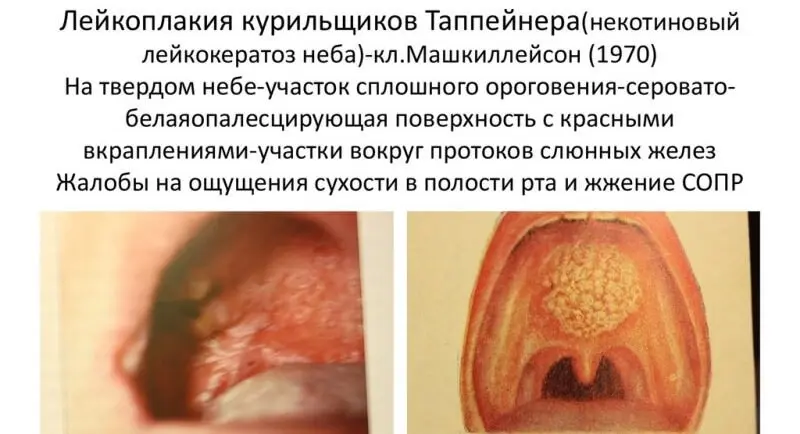
Leukoplakia of smokers (tappeiner) manifests itself in the form of continuous keratinization of the hard and adjacent areas of the soft palate, usually grayish-white. Against the background of all this, red dots are visible, which are the gaping mouths of the excretory ducts of the salivary glands. With the most pronounced form, nodules form in the keratinization zone, which makes the disease similar to Darya’s disease on the oral mucosa. However, smokers’ leukoplakia has a red dot at the top of the nodule, and as soon as the person stops smoking, the disease goes away.
Upholstered leukoplakia. This form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of a tumor. There is no inflammation, but the tissues are edematous and have a gray-white color. The boundaries are fuzzy, the cells of the affected tissues are flaky. If you try to remove the peeling, then under the exfoliated particles you can see an eroded area covered with cracks. The cheeks, lips and tongue are affected. Children and young people often suffer from it.
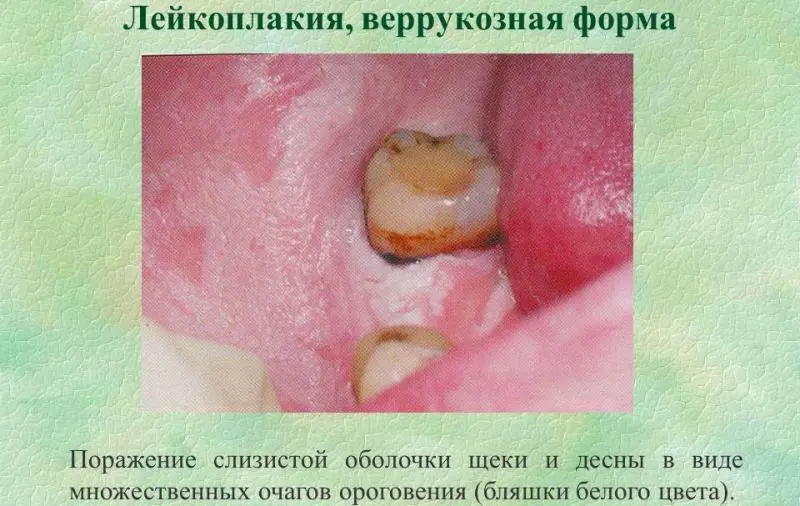
Diagnosis of oral leukoplakia
To begin with, the doctor examines the oral cavity and palpates the affected areas. It is important to study the patient’s history, as well as to clarify the state of his health and the presence of chronic diseases.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to perform a biopsy of the altered tissues and conduct their cytological analysis. If necessary, the doctor prescribes additional studies to the patient.
It is important to carry out differential diagnosis with pathologies such as:
Chronic oral candidiasis. Affected tissues during a fungal infection will be well separated, and regenerated cells are found under them.
Lichen planus. It focuses not only in the mouth, but also on the skin.
Systemic lupus erythematosus. fabrics atrophy, the foci of inflammation have a rich red color.
Bowen’s disease. Plots mucous red, pasty. It is not difficult to remove plaque, and rough spots of red color are visible under it. The skin is affected, and not just the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Erythroplakia. Damaged tissues turn red and itch. Spots in diameter reach 20 mm, have clear boundaries, are located on the tongue at the throat. Sometimes they form on the labia, next to the vagina. This disease, as well as leukoplakia, can be malignant.
Leukopenia. With this pathology, ulcerative defects are formed in the oral cavity. They can appear not only in the mouth, but also on the intestinal walls. The patient’s body temperature rises, weakness increases, he is haunted by a headache. The tonsils swell and hurt, the spleen increases in size.
Pachydermia. With this disease, plaques form on the mucous membranes of the larynx, which in appearance resemble warts. They also form on the vocal cords. The color of the plaques is yellow or whitish-gray. The mucous membrane becomes loose, has a blue color.
Pachydermia of the head. The scalp suffers from this disease. It is covered with folds, the skin is thickened. Due to the disease, the surface of the head begins to resemble the brain.
SOPR. This pathology affects the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. The cause of its development may be lichen planus, viral infections, stomatitis. If the pathology is not treated, then it threatens to turn into a cancerous tumor.
Treatment of oral leukoplakia
In order for the treatment to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to eliminate all risk factors that could provoke the development of oral leukoplakia.
The main directions of therapeutic effects:
Making lifestyle adjustments. You need to give up cigarettes, eat right, enrich the menu with foods rich in vitamin B, vitamin C. You can take tocopherol and retinol.
The doctor must qualitatively sanitize the oral cavity, cure teeth and gums, replace prostheses and crowns that can injure soft tissues.
If leukoplakia has affected the lips, then you will need to use photoprotective agents.
Regenerative drugs such as Sodium nucleinate or Metacin are used to treat erosive-ulcerative leukoplakia.
If the affected tissues are not restored, then the patient is shown surgery.
Supplement the main treatment with physiotherapeutic methods.
At an early stage of leukoplakia, conservative treatment is sufficient. Patients are prescribed drugs to increase immunity, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamin and mineral complexes.
If a patient is diagnosed with a verrucous form of leukoplakia, then he is given blockades with a solution of Delagil or Khonsurid.
Remove areas of leukoplakia in the oral cavity by cryodestruction. However, after the procedure, there is a risk of scar tissue formation. Also, affected areas can be eliminated with a laser or electro-excision method.
Leukoplakia is a disease that can affect not only the oral cavity, but also other organs. Pathology can develop in the bladder and on the genitals, leading to a thickening of their tissues. For a long time, the disease remains undiagnosed. It is often discovered by accident.
Leukoplakia can affect the organs of the digestive system, larynx, intestines, esophagus, stomach. Sometimes the airways are affected. To date, the causes of leukoplakia have not been established. The first scientific reports on this problem appeared only 10-15 years ago.









